|
Germia Park
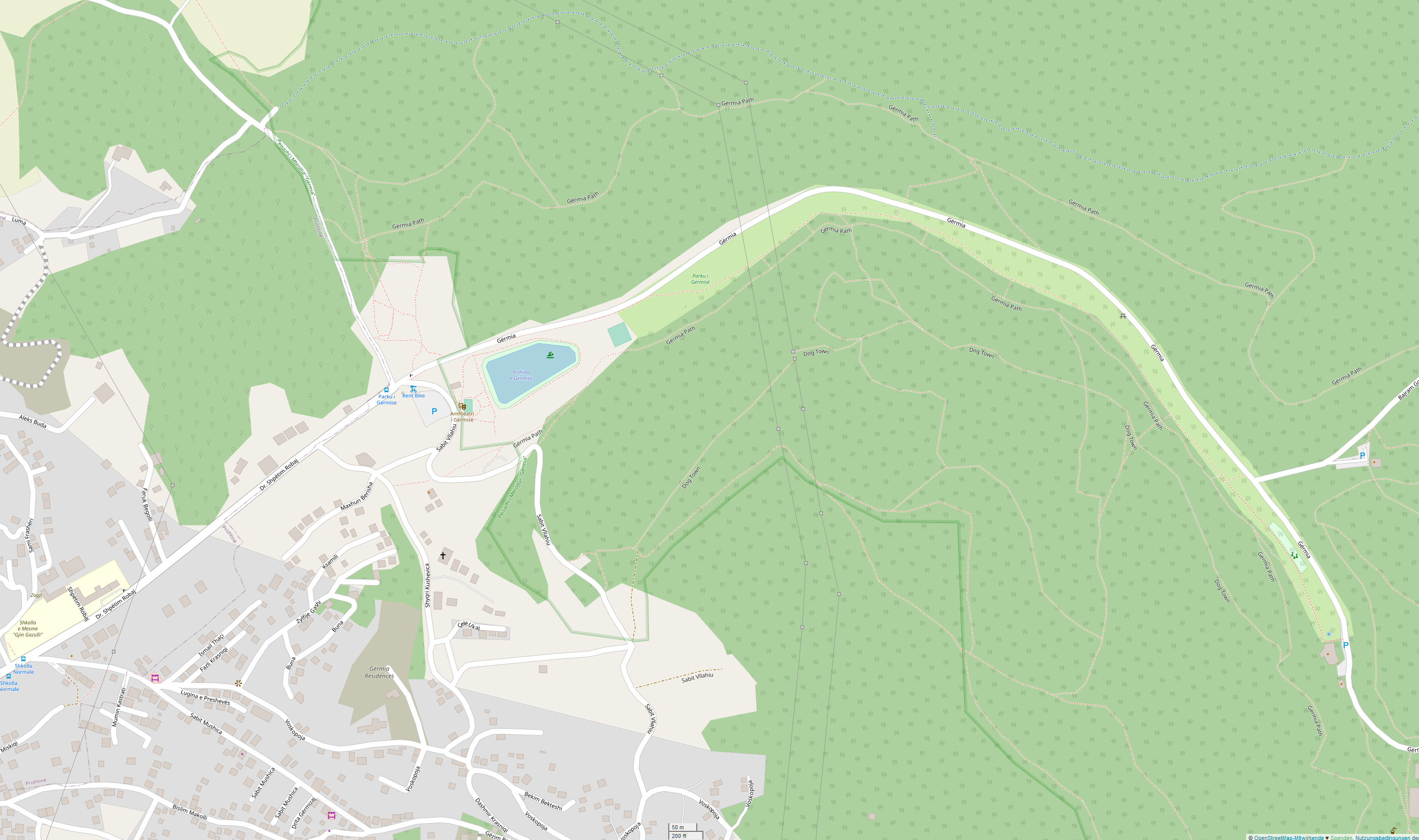
Germia ( sq, Parku i Gërmisë, sr-cyr, Грмија) is a regional park located in the northeast of Prishtina, Kosovo, and covers an area of 62 square kilometres. This mountain massif is a part of the Rhodope Mountains, which lie from the Black Mountain of Skopje to Kopaonik mountains. Its highest point, Butos Peak, is 1050 meters above sea level and its lowest 663 meters above sea level. Due to its geographical position and climate conditions, Germia massif has a rich fauna with 63 species of animals and a variety of about 600 species of flora. In 1987, the "Germia" complex was taken under protection by Pristina's Municipal Assembly in the category of the Regional Nature Park and is now managed by the publicly owned enterprise "Hortikultura". However, according to International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Germia should be designated as a protected landscape. History According to the classification of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prishtina
Pristina, ; sr, / (, ) is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. The city's municipal boundaries in Pristina District form the largest urban center in Kosovo. After Tirana, Pristina has the second largest population of ethnic Albanians and speakers of the Albanian language. Inhabited by humans since prehistoric times, the area of Pristina was home to several Illyrian peoples. King Bardyllis of the Dardanians brought various tribes together in the 4th century BC and established the Dardanian Kingdom.''The Cambridge Ancient History: The fourth century B.C.'' Volume 6 of The Cambridge Ancient History Iorwerth Eiddon Stephen Edwards, , , Authors: D. M. Lewis, John Boardman, Editors: D. M. Lewis, John Boardman, Second Edition, Cambridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Trojana
''Quercus trojana'', the Macedonian oak is an oak in the turkey oak section ( ''Quercus'' sect. ''Cerris''). It is native to southeast Europe and southwest Asia, from southern Italy east across the southern Balkans (Croatia, Albania, Serbia, North Macedonia and Greece) to western Turkey, growing at low to moderate altitudes (up to in the south of the range in southwestern Turkey), in dry areas. Description ''Quercus trojana'' is a small to medium-sized tree reaching tall, late deciduous to semi-evergreen, with gray-green leaves long and 1.5–4 cm broad with a coarsely serrated margin with sharply pointed teeth. The acorns are 2–4 cm long when mature (about 18 months after pollination) and largely enclosed in the scaly acorn cup. Fossil record Fossils of ''Quercus trojana'' have been described from the fossil flora of Kızılcahamam district in Turkey, which is of early Pliocene age. References External links ''Quercus trojana''- information, genetic conservat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of prey, birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. These birds are dark brown, with lighter golden-brown plumage on their napes. Immature eagles of this species typically have white on the tail and often have white markings on the wings. Golden eagles use their agility and speed combined with powerful feet and large, sharp talons to hunt a variety of prey, mainly hares, rabbits, and marmots and other ground squirrels. Golden eagles maintain home ranges or territories that may be as large as . They build large bird nest, nests in cliffs and other high places to which they may return for several breeding years. Most breeding activities take place in the spring; they are monogamous and may remain together for several years or possibly for life. Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann's Tortoise
Hermann's tortoise (''Testudo hermanni'') is a species of tortoise. Two subspecies are known: the western Hermann's tortoise (''T. h. hermanni'' ) and the eastern Hermann's tortoise (''T. h. boettgeri'' ). Sometimes mentioned as a subspecies, ''T. h. peleponnesica'' is not yet confirmed to be genetically different from ''T. h. boettgeri''. Etymology The specific epithet, ''hermanni'', honors French naturalist Johann Hermann.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Testudo hermanni'', p. 121; ''T. h. boettgeri'', p. 29). The subspecific name, ''boettgeri'', honors German herpetologist Oskar Boettger. Geographic range ''Testudo hermanni'' can be found throughout southern Europe. The western population (''T. h. hermanni'') is found in eastern Spain, southern France, the Balearic islands, Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, southern and central Italy (Tuscany). The easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacertidae
The Lacertidae are the family (biology), family of the wall lizards, true lizards, or sometimes simply lacertas, which are native to Afro-Eurasia. It is a diverse family with at least 300 species in 39 genera. They represent the dominant group of reptiles found in Europe. The group includes the genus ''Lacerta (genus), Lacerta'', which contains some of the most commonly seen lizard (thus "true" lizard) species in Europe. Habitat The European and Mediterranean species of lacertids live mainly in forest and scrubland, scrub habitats. ''Eremias'' and ''Ophisops'' species replace these in the grassland and desert habitats of Asia. African species usually live in rocky, arid areas. ''Holaspis'' species are among the few arboreal lacertids, and its two species, ''Holaspis guentheri'' and ''Holaspis laevis'', are gliders (although apparently poor ones), using their broad tail and flattened body as an aerofoil. Description Lacertids are small or medium-sized lizards. Most species are le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Tree Frog
The European tree frog (''Hyla arborea'') is a small tree frog. As traditionally defined, it was found throughout much of Europe, Asia and northern Africa,Frost, Darrel R. ''Amphibian Species of the World''. Allen Press, Inc., 1985, p. 126. but based on molecular genetic and other data several populations formerly included in it are now recognized as separate species (for example, '' H. intermedia'' of Italy and nearby, '' H. molleri'' of the Iberian Peninsula, '' H. meridionalis'' of parts of southwestern Europe and northern Africa, and '' H. orientalis'' of parts of Eastern Europe, Turkey and the Black Sea and Caspian Sea regions), limiting the true European tree frog to Europe from France to Poland and Greece.Duellman, William E. (2003). ''Grzimek's Animal Encyclopedia''. 2nd Ed., Vol. 2. Gale, p. 235.Stöck M., Dufresnes C., Litvinchuk S.N., Lymberakis P., Biollay S., Berroneau M., Borzée A., Ghali K., Ogielska M., and Perrin N. (2012). Cryptic diversity among Western Palearct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fagus Sylvatica
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech is a deciduous tree belonging to the beech family Fagaceae. Description ''Fagus sylvatica'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more typically tall and up to trunk diameter. A 10-year-old sapling will stand about tall. It has a typical lifespan of 150–200 years, though sometimes up to 300 years. In cultivated forest stands trees are normally harvested at 80–120 years of age. 30 years are needed to attain full maturity (as compared to 40 for American beech). Like most trees, its form depends on the location: in forest areas, ''F. sylvatica'' grows to over , with branches being high up on the trunk. In open locations, it will become much shorter (typically ) and more massive. The leaves are alternate, simple, and entire or with a slightly crenate margin, long and 3–7 cm broad, with 6–7 veins on each side of the leaf (as opposed to 7–10 veins in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Petraea
''Quercus petraea'', commonly known as the sessile oak, Cornish oak, Irish Oak or durmast oak, is a species of oak tree native to most of Europe and into Anatolia and Iran. The sessile oak is the national tree of Ireland, and an unofficial emblem in Wales and Cornwall. Description The sessile oak is a large deciduous tree up to tall, in the white oak section of the genus (''Quercus'' sect. ''Quercus'') and similar to the pedunculate oak (''Q. robur''), with which it overlaps extensively in range. The leaves are long and broad, evenly lobed with five to six lobes on each side and a petiole. The male flowers are grouped into catkins, produced in the spring. The fruit is an acorn long and broad, which matures in about six months. Comparison with pedunculate oak Significant botanical differences from pedunculate oak (''Q. robur'') include the stalked leaves, and the stalkless (sessile) acorns from which one of its common names is derived. It occurs in upl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30–40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Origin of names The common English name ''hornbeam'' derives from the hardness of the woods (likened to horn) and the Old English ''beam'' "tree" (cognate with Dutch ‘’Boom’’ and German ''Baum''). The American hornbeam is also occasionally known as blue-beech, ironwood, or musclewood, the first from the resemblance of the bark to that of the American beech ''Fagus grandifolia'', the other two from the hardness of the wood and the muscled appearance of the trunk and limbs. The botanical name for the genus, ''Carpinus'', is the original Latin name for the European species, although some etymologists derive it from the Celtic for a yoke. Taxonomy Formerly some taxonomists segregated them with the genera ''Corylus'' ( hazels) and ''Ostrya'' (hop-hornbeams) in a separate family, Coryl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Cerris
''Quercus cerris'', the Turkey oak or Austrian oak, is an oak native to south-eastern Europe and Asia Minor. It is the type species of ''Quercus'' sect. ''Cerris'', a section of the genus characterised by shoot buds surrounded by soft bristles, bristle-tipped leaf lobes, and acorns that usually mature in 18 months. Description ''Quercus cerris'' is a large deciduous tree growing to tall with a trunk up to in diameter. The bark is dark gray and deeply furrowed. On mature trees, the bark fissures are often streaked orange near the base of the trunk. The glossy leaves are long and 3–5 cm wide, with 6–12 triangular lobes on each side; the regularity of the lobing varies greatly, with some trees having very regular lobes, others much less regular. The flowers are wind-pollinated catkins, maturing about 18 months after pollination; the fruit is a large acorn, long and 2 cm broad, bicoloured with an orange basal half grading to a green-brown tip; the acorn cup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantharellus Cibarius
''Cantharellus cibarius'' (Latin: ''cantharellus'', "chanterelle"; ''cibarius'', "culinary") is a species of golden chanterelle mushroom in the genus ''Cantharellus''. It is also known as girolle (or ''girole''). It grows in Europe from Scandinavia to the Mediterranean Basin, mainly in deciduous and coniferous forests. Due to its characteristic color and shape, it is easy to distinguish from mushrooms with potential toxicity that discourage human consumption. A commonly eaten and favored mushroom, the chanterelle is typically harvested from late summer to late fall in its European distribution. Chanterelles are used in many culinary dishes, and can be preserved by either drying or freezing. An oven should not be used when drying it because can result in the mushroom becoming bitter. Taxonomy At one time, all yellow or golden chanterelles in North America had been classified as ''Cantharellus cibarius''. Using DNA analysis, they have since been shown to be a group of related s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

