|
Germanic Heroic Legend
Germanic heroic legend (german: germanische Heldensage) is the heroic literary tradition of the Germanic-speaking peoples, most of which originates or is set in the Migration Period (4th-6th centuries AD). Stories from this time period, to which others were added later, were transmitted orally, traveled widely among the Germanic speaking peoples, and were known in many variants. These legends typically reworked historical events or personages in the manner of oral poetry, forming a heroic age. Heroes in these legends often display a heroic ethos emphasizing honor, glory, and loyalty above other concerns. Like Germanic mythology, heroic legend is a genre of Germanic folklore. Heroic legends are attested in Anglo-Saxon England, medieval Scandinavia, and medieval Germany. Many take the form of Germanic heroic poetry (german: germanische Heldendichtung): shorter pieces are known as heroic lays, whereas longer pieces are called Germanic heroic epic (). The early Middle Ages preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
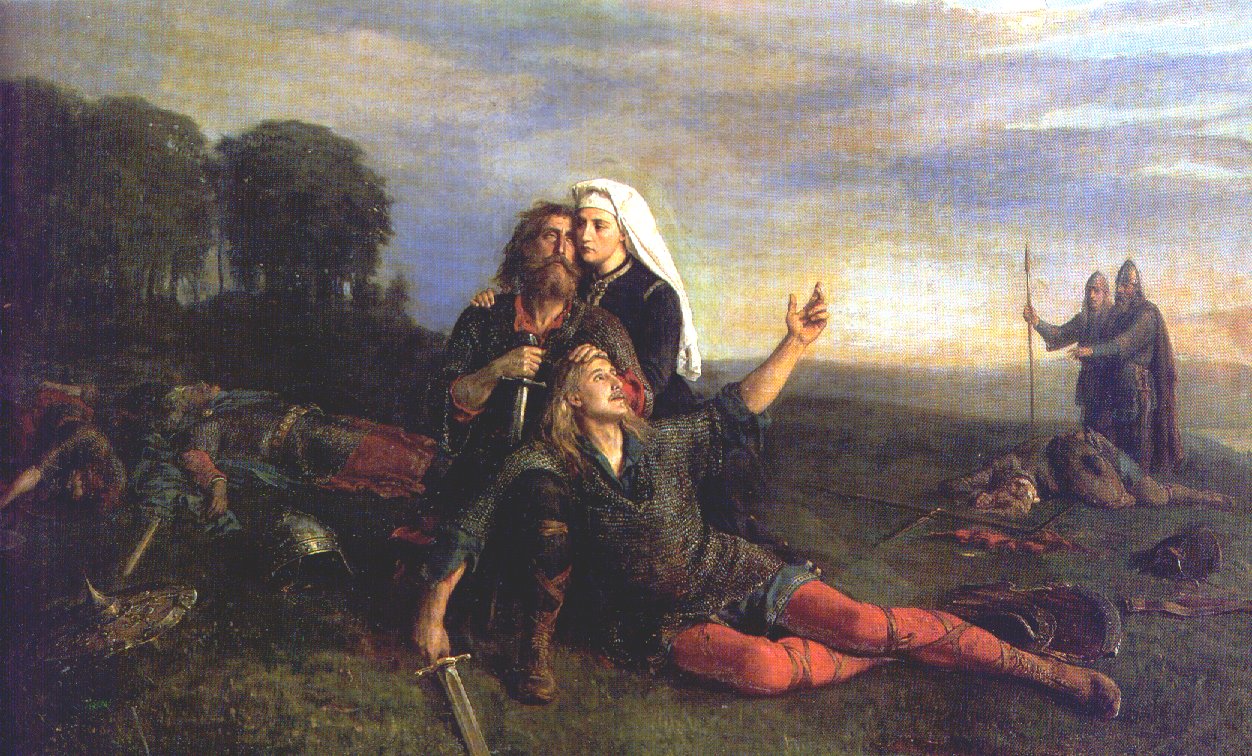
Sigurd
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovingian dynasty, with Sigebert I being the most popular contender. Older scholarship sometimes connected him with Arminius, victor of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. He may also have a purely mythological origin. Sigurd's story is first attested on a series of carvings, including runestones from Sweden and stone crosses from the British Isles, dating from the eleventh century. In both the Norse and continental Germanic tradition, Sigurd is portrayed as dying as the result of a quarrel between his wife ( Gudrun/Kriemhild) and another woman, Brunhild, whom he has tricked into marrying the Burgundian king Gunnar/Gunther. His slaying of a dragon and possession of the hoard of the Nibelungen is also common to both traditions. In other respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliterative Verse
In prosody, alliterative verse is a form of verse that uses alliteration as the principal ornamental device to help indicate the underlying metrical structure, as opposed to other devices such as rhyme. The most commonly studied traditions of alliterative verse are those found in the oldest literature of the Germanic languages, where scholars use the term 'alliterative poetry' rather broadly to indicate a tradition which not only shares alliteration as its primary ornament but also certain metrical characteristics. The Old English epic ''Beowulf'', as well as most other Old English poetry, the Old High German ''Muspilli'', the Old Saxon ''Heliand'', the Old Norse ''Poetic Edda'', and many Middle English poems such as ''Piers Plowman'', ''Sir Gawain and the Green Knight'', and the '' Alliterative Morte Arthur'' all use alliterative verse. While alliteration can be found in many poetic traditions, it is 'relatively infrequent' as a structured characteristic of poetic form.Frog, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunther
Gundaharius or Gundahar (died 437), better known by his legendary names Gunther ( gmh, Gunther) or Gunnar ( non, Gunnarr), was a historical king of Burgundy in the early 5th century. Gundahar is attested as ruling his people shortly after they crossed the Rhine into Roman Gaul. He was involved in the campaigns of the failed Roman usurper Jovinus before the latter's defeat, after which he was settled on the left bank of the Rhine as a Roman ally. In 436, Gundahar launched an attack from his kingdom on the Roman province of Belgica Prima. He was defeated by the Roman general Flavius Aetius, who destroyed Gundahar's kingdom with the help of Hunnish mercenaries the following year, resulting in Gundahar's death. The historical Gundahar's death became the basis for a tradition in Germanic heroic legend in which the legendary Gunther met his death at the court of Attila the Hun (Etzel/Atli). The character also became attached to other legends: most notably he is associated with Siegf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
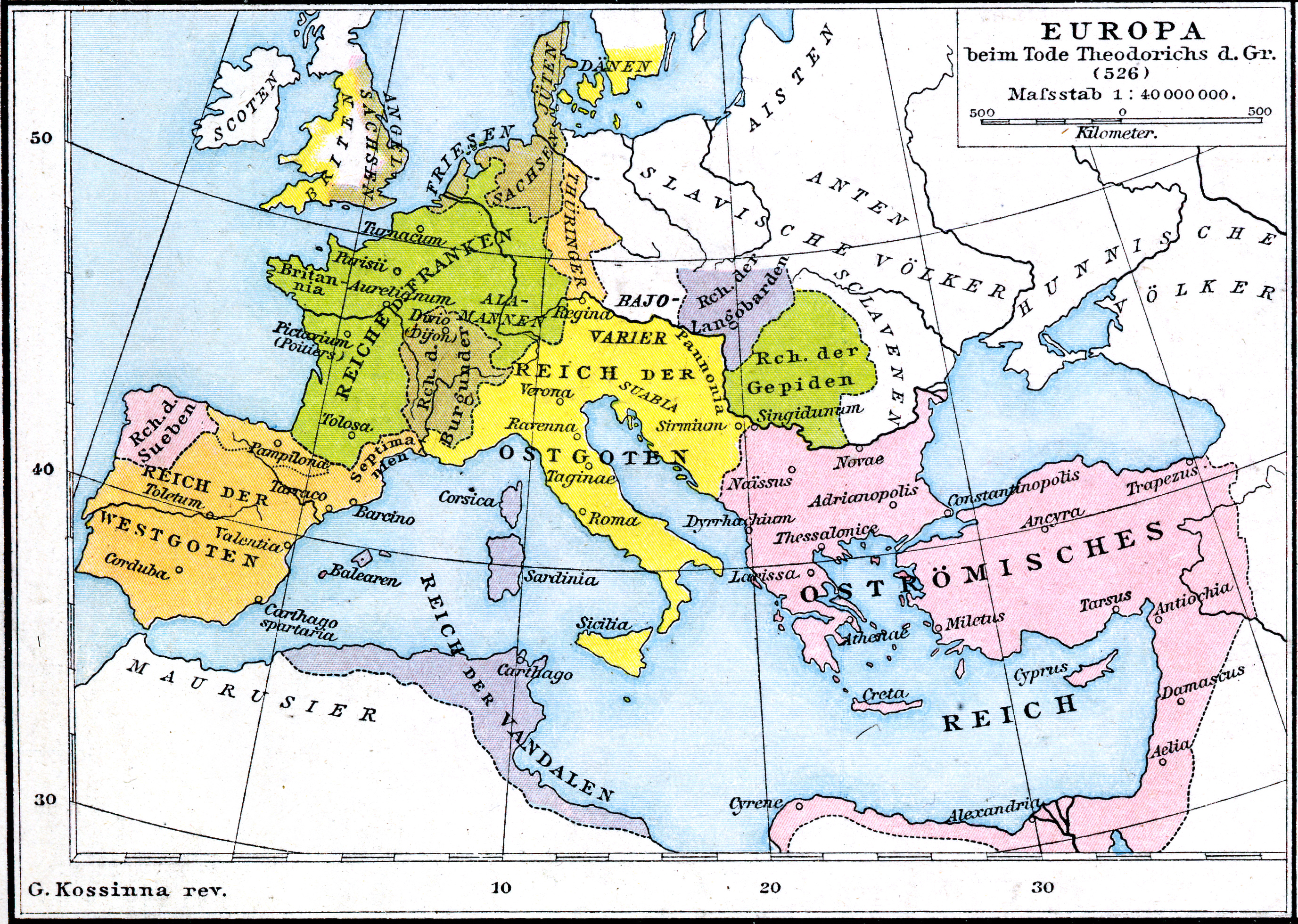
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
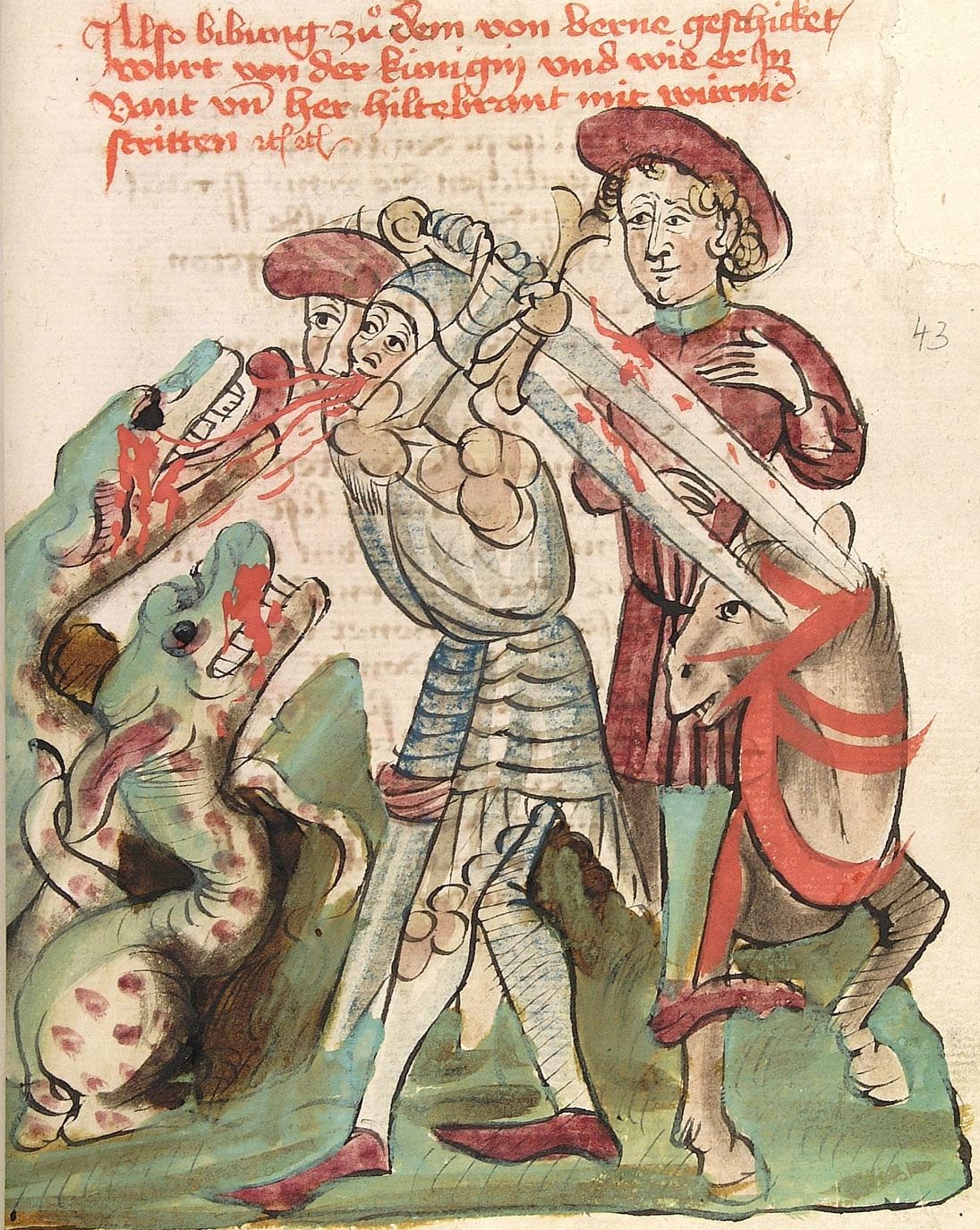
Dietrich Von Bern
Dietrich von Bern is the name of a character in Germanic heroic legend who originated as a legendary version of the Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great. The name "Dietrich", meaning "Ruler of the People", is a form of the Germanic name "Theodoric". In the legends, Dietrich is a king ruling from Verona (Bern) who was forced into exile with the Huns under Etzel by his evil uncle Ermenrich. The differences between the known life of Theodoric and the picture of Dietrich in the surviving legends are usually attributed to a long-standing oral tradition that continued into the sixteenth century. Most notably, Theodoric was an invader rather than the rightful king of Italy and was born shortly after the death of Attila and a hundred years after the death of the historical Gothic king Ermanaric. Differences between Dietrich and Theodoric were already noted in the Early Middle Ages and led to a long-standing criticism of the oral tradition as false. Legends about Theodoric may have exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundians
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and were later moved into the empire, in the western Alps and eastern Gaul. They were possibly mentioned much earlier in the time of the Roman Empire as living in part of the region of Germania that is now part of Poland. The Burgundians are first mentioned together with the Alamanni as early as the 11th panegyric to emperor Maximian given in Trier in 291, and referring to events that must have happened between 248 and 291, and they apparently remained neighbours for centuries. By 411 a Burgundian group had established themselves on the Rhine, between Franks and Alamanni, holding the cities of Worms, Speyer, and Strasbourg. In 436, Aëtius defeated the Burgundians on the Rhine with the help of Hunnish forces, and then in 443, he re-settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nibelungenlied
The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poetry, epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of Germanic heroic legend that has some of its origin in historic events and individuals of the 5th and 6th centuries and that spread throughout almost all of Germanic languages, Germanic-speaking Europe. Scandinavian parallels to the German poem are found especially in the heroic lays of the ''Poetic Edda'' and in the ''Völsunga saga''. The poem is split into two parts. In the first part, the prince Sigurd, Siegfried comes to Worms, Germany, Worms to acquire the hand of the Burgundians, Burgundian princess Kriemhild from her brother King Gunther. Gunther agrees to let Siegfried marry Kriemhild if Siegfried helps Gunther acquire the warrior-queen Brünhild as his wife. Siegfried does this and marries Kriemhild; however, Brünhild and Krie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Völsunga Saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century poetic rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the story of Sigurd and Brynhild and the destruction of the Burgundians). It is one of the most famous legendary sagas and an example of a "heroic saga" that deals with Germanic heroic legend. The saga covers topics including the quarrel between Sigi and Skaði, a huge family tree of great kings and powerful conquerors, the quest led by Sigmund and Sinfjǫtli to save princess Signý from the evil king Siggeir, and, most famously, Sigurd killing the serpent/dragon Fáfnir and obtaining the cursed ring Andvaranaut that Fáfnir guarded. Context and overview The saga is largely based on the epic poetry of the historic ''Elder Edda''. The earliest known pictorial representation of this tradition is the Ramsund carving in Sweden, which was created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legendary Sagas
A legendary saga or ''fornaldarsaga'' (literally, "story/history of the ancient era") is a Norse saga that, unlike the Icelanders' sagas, takes place before the settlement of Iceland.The article ''Fornaldarsagor'' in ''Nationalencyklopedin'' (1991) There are some exceptions, such as '' Yngvars saga víðförla'', which takes place in the 11th century. The sagas were probably all written in Iceland, from about the middle of the 13th century to about 1400, although it is possible that some may be of a later date,Einar Ól. Sveinsson, "Fornaldarsögur", in ''Kulturhistorisk leksikon for nordisk middelalder fra vikingtid til reformasjonstid, bd. 4'' (Copenhagen, 1959) such as ''Hrólfs saga kraka''. Description of the sagas In terms of form, ''fornaldarsögur'' are similar to various other saga-genres, but tend towards fairly linear, episodic narratives. Like sagas in other genres, many quote verse, but in the ''fornaldarsögur'' that verse is almost invariably in the metre of Eddaic v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square (video game company), Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to the PlayStation 2. The series is notable for its emphasis on open world exploration, Nonlinear gameplay, non-linear branching plots, and occasionally unconventional gameplay. This distinguishes the games from most of Square's other franchises. Development The ''SaGa'' series was created by game designer Akitoshi Kawazu, whose contributions prior to the franchise's introduction include ''Final Fantasy (video game), Final Fantasy'' and ''Final Fantasy II''. At a time when Nintendo's Game Boy The is an 8-bit fourth generation handheld game console developed and manufactured by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan on April 21, 1989, in North America later the same year, and in Europe in late 1990. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

