|
Georgina Frost
Georgina "Georgie" Frost (29 December 1879 – 6 December 1939) was an Irish court official who was the first woman to hold public office in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Early life Georgina Frost was born in Sixmilebridge, County Clare, on 29 December 1879, the daughter of Margaret Kett (1847-1888) and Thomas Frost (1842–1938). Thomas Frost was the petty sessions clerk for Sixmilebridge and Newmarket-on-Fergus. Frost's maternal grandfather, Michael Kett, had held that role in Sixmilebridge in the early 1840s.Abstract Return from Clerks of Petty Sessions in Ireland of Amount of Fees received, 1842-44, at http://eppi.dippam.ac.uk/pdf1/9261.pdf Career and court appeals In the six years immediately before Thomas Frost's retirement in 1915, Frost had assisted her father in his duties, often performing them herself. She became a well known figure in the area, travelling around by bicycle. Upon his retirement, she was appointed to succeed him by the local magis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
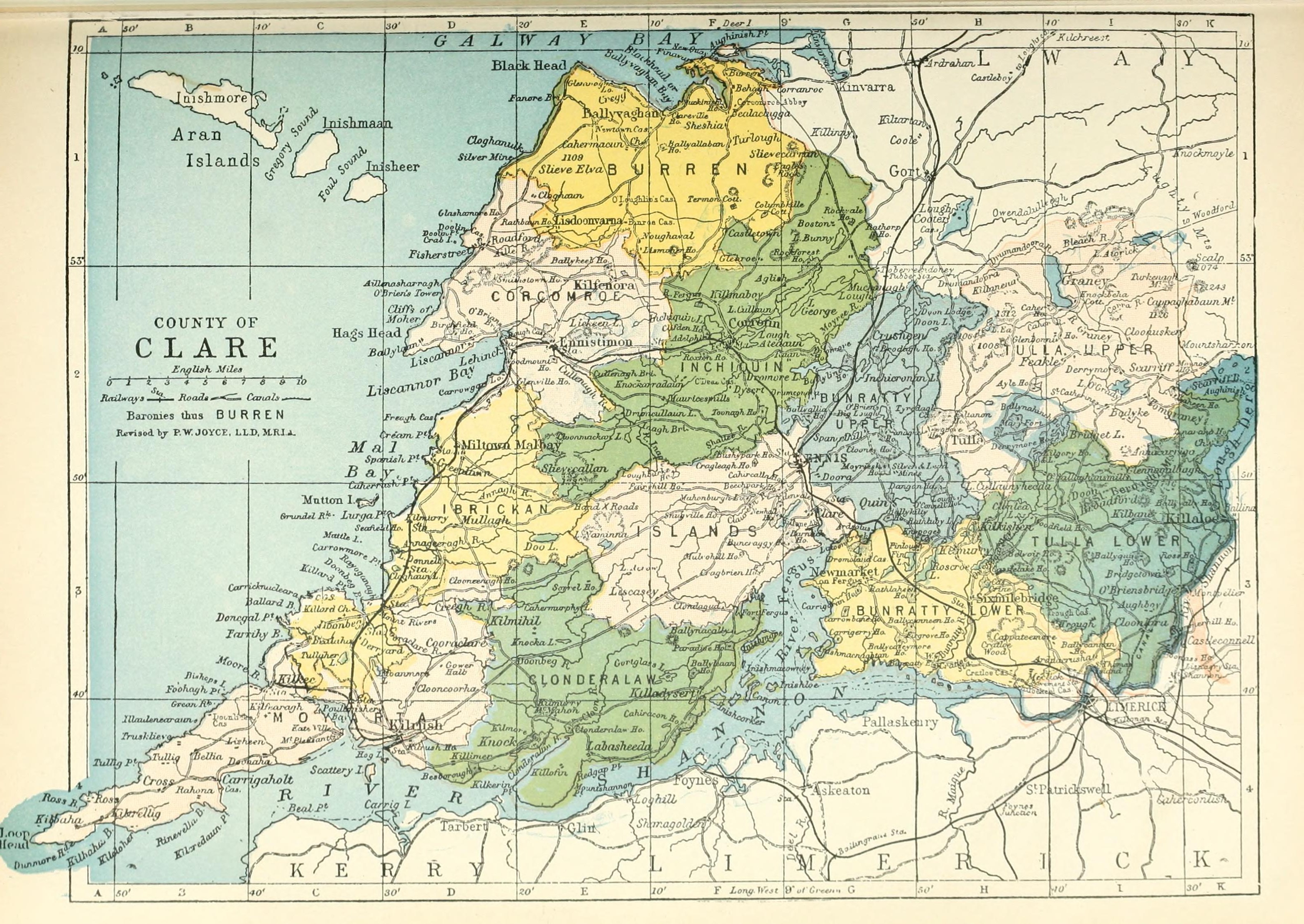
Sixmilebridge
Sixmilebridge (), is a large village in County Clare, Ireland. Located midway between Ennis and Limerick city, the village is a short distance away from the main N18 road. Sixmilebridge partly serves as a dormitory village for workers in the Limerick city, Ennis and Shannon region, with a number of modern housing developments having been built to accommodate demand. History Evidence of prehistorical settlement in the area dates to the Bronze Age, and a number of ringforts, mounds, enclosures and wedge tombs are located in the parish. In antiquity, the name of the village was Cappagh (that name still present in local townlands), chiefly on the west side of the river, and Ballyarilla on the east. The name Cappagh is an anglicized form of an Irish word meaning a cultivated field, while Ballyarilla is named after the castle that once stood before Mount Ievers Court was built. An ancient name of the river appears to be Raite, today anglicised into Ratty; as the river flows past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an Chláir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,817 at the 2016 census. The county town and largest settlement is Ennis. Geography and subdivisions Clare is north-west of the River Shannon covering a total area of . Clare is the seventh largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties in area and the 19th largest in terms of population. It is bordered by two counties in Munster and one county in Connacht: County Limerick to the south, County Tipperary to the east and County Galway to the north. Clare's nickname is ''the Banner County''. Baronies, parishes and townlands The county is divided into the baronies of Bunratty Lower, Bunratty Upper, Burren, Clonderalaw, Corcomroe, Ibrickan, Inchiquin, Islands, Moyarta, Tulla Lower and Tulla Upper. These in turn are divided into civil parishes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newmarket-on-Fergus
Newmarket-on-Fergus, historically known as Corracatlin (), is a town in County Clare, Ireland. It is 13 kilometres from Ennis, 8 kilometres from Shannon Airport, and 24 kilometres from Limerick. History The English rendering of the name 'Newmarket-on-Fergus' probably owes its origin to the fact that an older 'Market' at nearby Bunratty (on the Ogarney River) predated the 'newer' market located at the village and hence Newmarket-on-Fergus; there is also a popular myth attributing the name-change to Lord Inchiqin who supposedly renamed the village after the famous racecourse, and following a victory at the horse-racing centre in England having wagered Dromoland Estate on the race. In the grounds of his neo-Gothic mansion, Dromoland Castle, is the most extensive hill-fort in Ireland, Mooghaun Hill-Fort, with several acres of ground encompassed within its treble walls. It is supposed to have been the site of a prehistoric walled village and a meeting- place in about 500 BC. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Lieutenant
A lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility over the local militia was removed. However, it was not until 1921 that they formally lost the right to call upon able-bodied men to fight when needed. Lord-lieutenant is now an honorary titular position usually awarded to a retired notable person in the county. Origins England and Wales Lieutenants were first appointed to a number of English counties by King Henry VIII in the 1540s, when the military functions of the sheriffs were handed over to them. Each lieutenant raised and was responsible for the efficiency of the local militia units of his county, and afterwards of the yeomanry and volunteers. He was commander of these forces, whose officers he appointed. These commissions were originally of temporary duration, and only when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tim Healy (politician)
Timothy Michael Healy, KC (17 May 1855 – 26 March 1931) was an Irish nationalist politician, journalist, author, barrister and a controversial Irish Member of Parliament (MP) in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. His political career began in the 1880s under Charles Stewart Parnell's leadership of the Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) and continued into the 1920s, when he was the first governor-general of the Irish Free State. Family background He was born in Bantry, County Cork, the second son of Maurice Healy, clerk of the Bantry Poor Law Union, and Eliza (née Sullivan) Healy. His elder brother, Thomas Healy (1854–1924), was a solicitor and Member of Parliament (MP) for North Wexford and his younger brother, Maurice Healy (1859–1923), with whom he held a lifelong close relationship, was a solicitor and MP for Cork City. His father was descended from a family line which in holding to their Catholic faith, lost their lands, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunbar Barton
Sir Dunbar Plunket Barton, 1st Baronet Privy Council of Ireland, PC (29 October 1853 – 11 September 1937) was an Anglo-Irish British politician, author and judge. Barton was born in Merrion Square, Dublin, the eldest son of the magistrate Thomas Henry Barton, a younger son of Dunbar Barton of Rochestown, County Tipperary, who was High Sheriff of Tipperary in 1810. His mother was Hon. Charlotte Plunket, daughter of John Plunket, 3rd Baron Plunket and Charlotte Bushe. Barton was descended from Lord Chief Justice Charles Kendal Bushe; and from the co-founder of the celebrated wine merchants Barton and Guestier. He attended Harrow School, Harrow and Corpus Christi College, Oxford. Nephew of the Anglican Archbishop of Dublin (Church of Ireland), Archbishop of Dublin, Barton was a sincere Protestant, but exceptionally tolerant in all matters of religion: Maurice Healy recalled him quoting a saying of his father that whether one is a Protestant or a Catholic is largely a chance of bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignatius O'Brien, 1st Baron Shandon
Ignatius John O'Brien, 1st Baron Shandon, (31 July 1857 – 10 September 1930), known as Sir Ignatius O'Brien, Bt, between 1916 and 1918, was an Irish lawyer and politician. He served as Lord Chancellor of Ireland between 1913 and 1918. Early life O'Brien was born in Cork, the youngest son of Mark Joseph O'Brien and Jane, daughter of William Dunne. He was educated at the Vincentian School there and, at the age of 16, entered the Catholic University of Ireland in Dublin but left after two years due to family circumstances. O'Brien thought the university system was too biased towards the classics and took a lifelong interest in science and technical education. He worked as a junior reporter for the ''Saunders Newsletter'', a Dublin Conservative daily newspaper and then for ''Freeman's Journal'' while studying part-time for the Bar. Called to the Irish Bar, King's Inn, in 1881, O'Brien was slow to build a practice and continued to support himself through freelance journalism, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Molony
Sir Thomas Francis Molony, 1st Baronet, PC(Ire), KC (1865–1949) was the last Lord Chief Justice of Ireland. He was also the only Judge to hold the position of Lord Chief Justice of Southern Ireland although he did not hold that position under that title. Early career and politics Molony qualified as a barrister in 1887 and became a Queen's Counsel in 1899. He served as Solicitor-General for Ireland (24 June 1912 to 10 April 1913) when he was appointed Attorney General for Ireland (10 April 1913 to 20 June 1913). Later in 1913, Molony was made a judge of the High Court for Ireland and from 1915 sat as a judge of the Court of Appeal for Ireland. He was also appointed to several governmental inquiries, notably one on certain shootings including that of Francis Sheehy-Skeffington in the wake of the 1916 Irish Easter Rising. In terms of his own politics, Molony has been described as ''“a Home Ruler of the old stamp"''. He was opposed to the partition of Ireland. When the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Ronan
Stephen Ronan, PC (13 April 1848 – 3 October 1925) was an Irish lawyer and judge. He was Irish Lord Justice of Appeal A Lord Justice of Appeal or Lady Justice of Appeal is a judge of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales, the court that hears appeals from the High Court of Justice, the Crown Court and other courts and tribunals. A Lord (or Lady) Justice ... from 1915 to 1924. References https://www.dib.ie/biography/ronan-stephen-a7787 {{DEFAULTSORT:Ronan, Stephen 1848 births 1925 deaths Members of the King's Inns Irish Queen's Counsel Lords Justice of Appeal for Ireland Lawyers from Cork (city) Alumni of Queens College Cork Members of the Inner Temple English King's Counsel 19th-century Irish lawyers 20th-century Irish judges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Shaw, 1st Baron Craigmyle
Thomas Shaw, 1st Baron Craigmyle (23 May 1850 – 28 June 1937), known as The Lord Shaw from 1909 to 1929, was a Scottish radical Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party politician and judge. The son of Alexander Shaw of Dunfermline, Fife, Craigmyle was educated at the Dunfermline High School and at Edinburgh University. He was appointed an Faculty of Advocates, advocate in 1875 and became a Queen's Counsel in 1894. He gained an LLD from St Andrews University in October 1902 and from the University of Aberdeen in 1906 and was also Hamilton Fellow in Mental Philosophy at Edinburgh University. Craigmyle sat as Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for Hawick Burghs (UK Parliament constituency), Hawick Burghs from 1892 to 1909 and served as Solicitor General for Scotland from 1894 to 1895 and as Lord Advocate from December 1905 to 1909. He resigned from parliament and ministerial office and was created a life peer as Baron Shaw, of Dunfermline in the County of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Disqualification (Removal) Act 1919
The Sex Disqualification (Removal) Act 1919 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom. It became law when it received Royal Assent on 23 December 1919.''Oliver & Boyd's new Edinburgh almanac and national repository for the year 1921''. p. 213 The act enabled women to join the professions and professional bodies, to sit on juries and be awarded degrees. It was a government compromise, a replacement for a more radical private members' bill, the Women's Emancipation Bill. Provisions of the act The basic purpose of the act was, as stated in its long title, "to amend the Law with respect to disqualification on account of sex", which it achieved in four short sections and one schedule. Its broad aim was achieved by section 1, which stated that: The Crown was given the power to regulate the admission of women to the civil service by Orders in Council, and judges were permitted to control the gender composition of juries. By section 2, women were to be admitted as solicitors after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the forces of the Irish Republic – the Irish Republican Army (IRA) – and British Crown forces. The Free State was established as a dominion of the British Empire. It comprised 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland. Northern Ireland, which was made up of the remaining six counties, exercised its right under the Treaty to opt out of the new state. The Free State government consisted of the Governor-General – the representative of the king – and the Executive Council (cabinet), which replaced both the revolutionary Dáil Government and the Provisional Government set up under the Treaty. W. T. Cosgrave, who had led both of these administrations since August 1922, became the first President of the Executive Council (prime minister). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |