|
Geology Of Japan
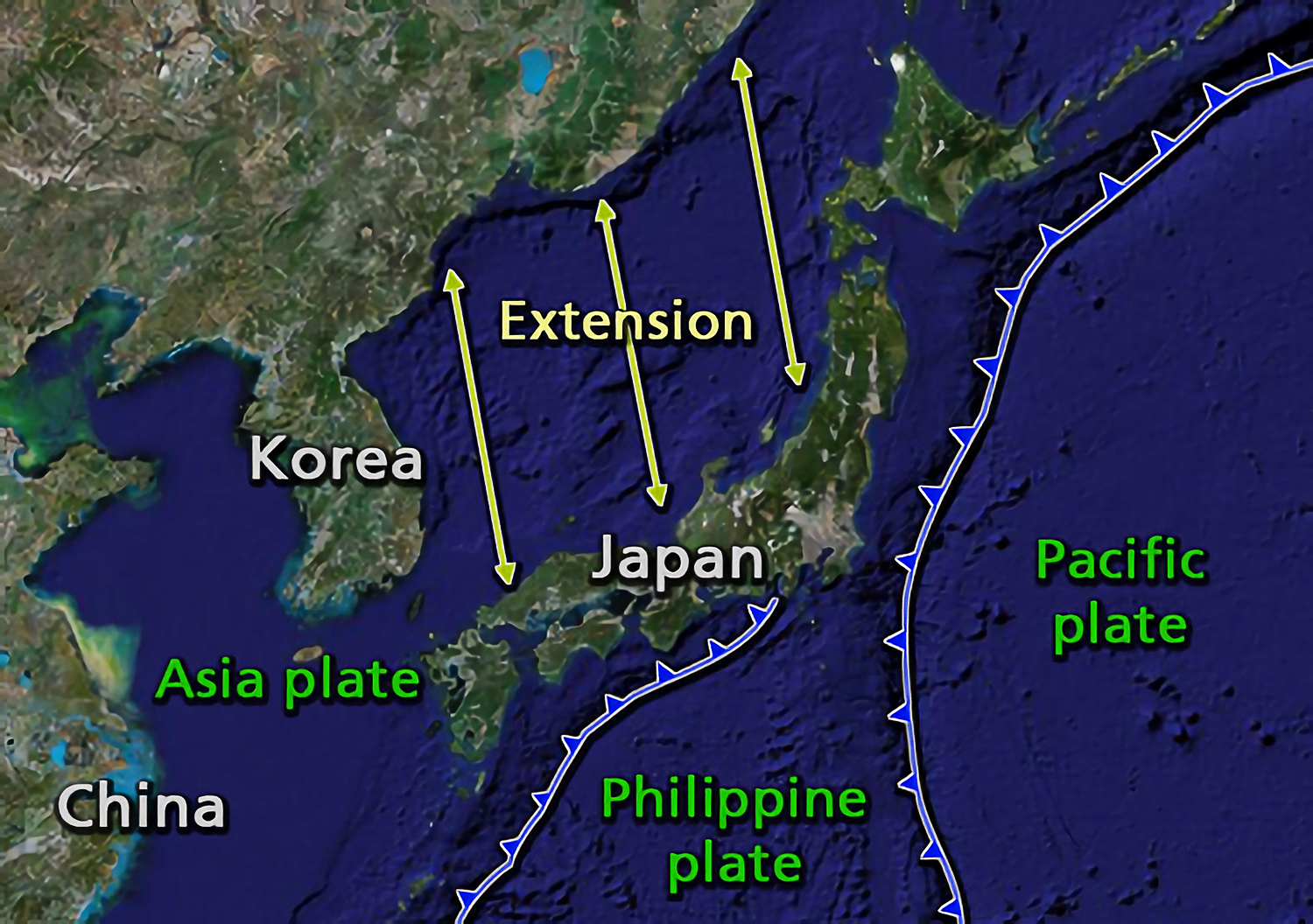
The islands of Japan are primarily the result of several large ocean movements occurring over hundreds of millions of years from the mid- Silurian to the Pleistocene, as a result of the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the continental Amurian Plate and Okinawa Plate to the south, and subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Okhotsk Plate to the north. Japan was originally attached to the eastern coast of the Eurasian continent. The subducting plates, being deeper than the Eurasian plate, pulled Japan eastward, opening the Sea of Japan around 15 million years ago. The Strait of Tartary and the Korea Strait opened much later. Japan is situated in a volcanic zone on the Pacific Ring of Fire. Frequent low intensity earth tremors and occasional volcanic activity are felt throughout the islands. Destructive earthquakes, often resulting in tsunamis, occur several times per century. The most recent major quakes include the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, the 2004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Separation
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Area is the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paired Metamorphic Belts
Paired metamorphic belts are sets of parallel linear rock units that display contrasting Metamorphic facies, metamorphic mineral assemblages. These paired belts develop along Convergent boundary, convergent plate boundaries where subduction is active. Each pair consists of one belt with a low-temperature, high-pressure metamorphic mineral assemblage, and another characterized by high-temperature, low-pressure metamorphic minerals. Historical background The concept of paired metamorphic belts was originally theorized by the Japanese geologist, Akiho Miyashiro in 1961. The parallel arrangement between the metamorphic belts and the similar ages of each belt, led Miyashiro to the idea that metamorphic belts formed together as pairs. The introduction of the paradigm of plate tectonics in the late 1960s, led to a better understanding of regional metamorphism and permitted the association between paired metamorphic belts and subduction zones. Conditions of formation The asymmetric defor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more Plate tectonics, lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, Orogeny, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and Deformation (geology), deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
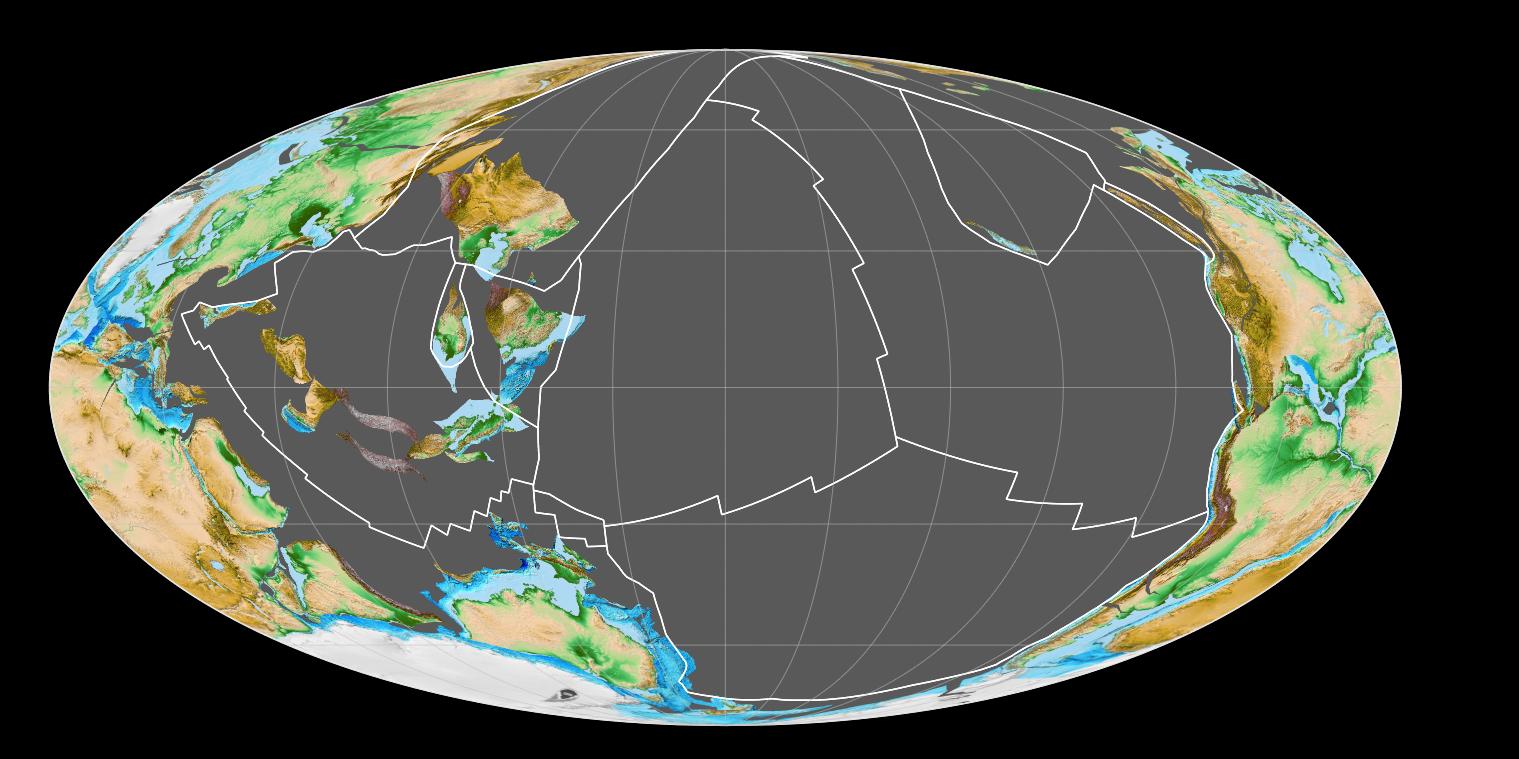
Panthalassa
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During the Paleozoic–Mesozoic transition 250 it occupied almost 70% of Earth's surface. Its ocean floor has completely disappeared because of the continuous subduction along the continental margins on its circumference. Panthalassa is also referred to as the Paleo-Pacific ("old Pacific") or Proto-Pacific because the Pacific Ocean is a direct continuation of Panthalassa. Formation The supercontinent Rodinia began to break up 870–845 probably as a consequence of a superplume caused by mantle slab avalanches along the margins of the supercontinent. In a second episode 750 the western half of Rodinia started to rift apart: western Kalahari and South China broke away from the western margins of Laurentia; and by 720 Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent. Rodinia formed at c. 1.23 Ga by accretion and collision of fragments produced by breakup of an older supercontinent, Columbia, assembled by global-scale 2.0–1.8 Ga collisional events.; Rodinia broke up in the Neoproterozoic with its continental fragments reassembled to form Pannotia 633–573 million years ago. In contrast with Pannotia, little is known yet about the exact configuration and geodynamic history of Rodinia. Paleomagnetic evidence provides some clues to the paleolatitude of individual pieces of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Relief Map Of Land And Seabed
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the most densely populated and urbanized. About three-fourths of the country's terrain is mountainous, concentrating its population of 123.2 million on narrow coastal plains. Japan is divided into 47 administrative prefectures and eight traditional regions. The Greater Tokyo Area is the most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Map Japan Basement
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Hanshin Earthquake
The , or Kobe earthquake, occurred on January 17, 1995, at 05:46:53 JST (January 16 at 20:46:53 UTC) in the southern part of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, including the region known as Hanshin. It measured 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum intensity of 7 on the JMA Seismic Intensity Scale (XI on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale). The tremors lasted for approximately 20 seconds. The focus of the earthquake was located 17 km beneath its epicenter, on the northern end of Awaji Island, 20 km away from the center of the city of Kobe. Approximately 6,434 people died as a result of this earthquake; about 4,600 of them were from Kobe. Among major cities, Kobe, with its population of 1.5 million, was the closest to the epicenter and hit by the strongest tremors. This was Japan's deadliest earthquake in the 20th century after the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923, which claimed more than 105,000 lives. Earthquake Most of the largest earthquakes in Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |