|
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Classification
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it was thought that viruses could not be made to fit Ernst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
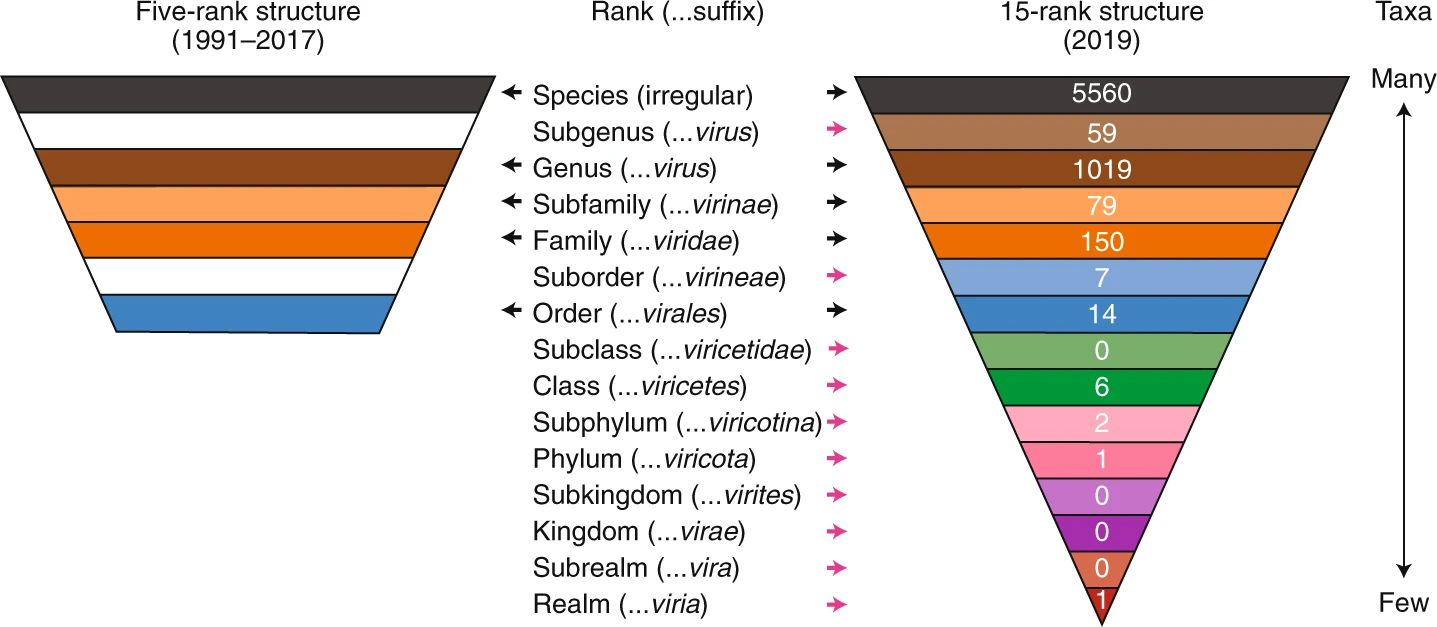
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two. Consider a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as comprising the tiger (''P. tigris''), lion (''P. leo''), jaguar (''P. onca''), and leopard (''P. pardus'') on the basis of common cranial features. Results of genetic analysis indicate that the snow leopard (formerly ''Uncia uncia'') also belongs to the genus ''Panthera'' (''P. uncia''), a classification that was accepted by IUCN Red List assessors in 2008. The tiger, lion, jaguar and leopard are the only cat species with anatomical structures that enable them to roar; the snow leopard cannot. The primary reason for this was formerly assumed to be the incomplete ossification of the hyoid bone. However, new studies show the ability to roar is due to other morphological features, especially of the larynx. Etymology The word ''panther'' derives from classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felidae
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the domestic cat ('' Felis catus''). Felidae species exhibit the most diverse fur pattern of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postzygotic Barrier
The mechanisms of reproductive isolation are a collection of evolutionary mechanisms, behaviors and physiological processes critical for speciation. They prevent members of different species from producing offspring, or ensure that any offspring are sterile. These barriers maintain the integrity of a species by reducing gene flow between related species.Strickberger, M. 1978. ''Genética''. Omega, Barcelona, España, p.: 874-879. .Futuyma, D. 1998. ''Evolutionary biology'' (3ª edición). Sinauer, Sunderland. The mechanisms of reproductive isolation have been classified in a number of ways. Zoologist Ernst Mayr classified the mechanisms of reproductive isolation in two broad categories: pre-zygotic for those that act before fertilization (or before mating in the case of animals) and post-zygotic for those that act after it.Mayr, E. 1963. ''Animal species and evolution''. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. The mechanisms are genetically controlled and can appear in species wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. By convention, sequences are usually presented from the 5' end to the 3' end. For DNA, the sense strand is used. Because nucleic acids are normally linear (unbranched) polymers, specifying the sequence is equivalent to defining the covalent structure of the entire molecule. For this reason, the nucleic acid sequence is also termed the primary structure. The sequence has capacity to represent information. Biological deoxyribonucleic acid represents the information which directs the functions of an organism. Nucleic acids also have a secondary structure and tertiary structure. Primary structure is sometimes mistakenly referred to as ''primary sequence''. Conversely, there is no parallel concept of secondary or tertiary sequence. Nucleotides Nucleic acids cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore can be considered a single effective population. It has been shown that it takes only "one migrant per generation" to prevent populations from diverging due to drift. Populations can diverge due to selection even when they are exchanging alleles, if the selection pressure is strong enough. Gene flow is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. Migrants change the distribution of genetic diversity among populations, by modifying allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). High rates of gene flow can reduce the genetic differentiation between the two groups, increasing homogeneity. For this reason, gene flow has been thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibit
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to: In biology * Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity * Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotransmitter * Lateral inhibition, a neural mechanism that increases contrast between active and (neighbouring) inactive neurons * Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, a synaptic potential that decreases the firing of a neuron In chemistry * Corrosion inhibitor, a substance that decreases the rate of metal oxidation * Reaction inhibitor, a substance that prevents or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction * Polymerisation inhibitor, a substance that inhibits unwanted polymerisation of monomers In psychology * Cognitive inhibition, the mind's ability to tune out irrelevant stimuli ** Inhibitory control, a cognitive process that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses * Inhibition of return, a feature of attention * Inhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(cropped).jpg)



.jpg)