|
Generalized Verma Module
In mathematics, generalized Verma modules are a generalization of a (true) Verma module, and are objects in the representation theory of Lie algebras. They were studied originally by James Lepowsky in the 1970s. The motivation for their study is that their homomorphisms correspond to invariant differential operators over generalized flag manifolds. The study of these operators is an important part of the theory of parabolic geometries. Definition Let \mathfrak be a semisimple Lie algebra and \mathfrak a parabolic subalgebra of \mathfrak. For any irreducible finite-dimensional representation V of \mathfrak we define the generalized Verma module to be the relative tensor product :M_(V):=\mathcal(\mathfrak)\otimes_ V. The action of \mathfrak is left multiplication in \mathcal(\mathfrak). If λ is the highest weight of V, we sometimes denote the Verma module by M_(\lambda). Note that M_(\lambda) makes sense only for \mathfrak-dominant and \mathfrak-integral weights (see weight) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highest Weight
In the mathematical field of representation theory, a weight of an algebra ''A'' over a field F is an algebra homomorphism from ''A'' to F, or equivalently, a one-dimensional representation of ''A'' over F. It is the algebra analogue of a multiplicative character of a group. The importance of the concept, however, stems from its application to representations of Lie algebras and hence also to representations of algebraic and Lie groups. In this context, a weight of a representation is a generalization of the notion of an eigenvalue, and the corresponding eigenspace is called a weight space. Motivation and general concept Given a set ''S'' of n\times n matrices over the same field, each of which is diagonalizable, and any two of which commute, it is always possible to simultaneously diagonalize all of the elements of ''S''.In fact, given a set of commuting matrices over an algebraically closed field, they are simultaneously triangularizable, without needing to assume that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weyl Group
In mathematics, in particular the theory of Lie algebras, the Weyl group (named after Hermann Weyl) of a root system Φ is a subgroup of the isometry group of that root system. Specifically, it is the subgroup which is generated by reflections through the hyperplanes orthogonal to the roots, and as such is a finite reflection group. In fact it turns out that ''most'' finite reflection groups are Weyl groups. Abstractly, Weyl groups are finite Coxeter groups, and are important examples of these. The Weyl group of a semisimple Lie group, a semisimple Lie algebra, a semisimple linear algebraic group, etc. is the Weyl group of the root system of that group or algebra. Definition and examples Let \Phi be a root system in a Euclidean space V. For each root \alpha\in\Phi, let s_\alpha denote the reflection about the hyperplane perpendicular to \alpha, which is given explicitly as :s_\alpha(v)=v-2\frac\alpha, where (\cdot,\cdot) is the inner product on V. The Weyl group W of \Phi is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homomorphism
In algebra, a homomorphism is a structure-preserving map between two algebraic structures of the same type (such as two groups, two rings, or two vector spaces). The word ''homomorphism'' comes from the Ancient Greek language: () meaning "same" and () meaning "form" or "shape". However, the word was apparently introduced to mathematics due to a (mis)translation of German meaning "similar" to meaning "same". The term "homomorphism" appeared as early as 1892, when it was attributed to the German mathematician Felix Klein (1849–1925). Homomorphisms of vector spaces are also called linear maps, and their study is the subject of linear algebra. The concept of homomorphism has been generalized, under the name of morphism, to many other structures that either do not have an underlying set, or are not algebraic. This generalization is the starting point of category theory. A homomorphism may also be an isomorphism, an endomorphism, an automorphism, etc. (see below). Each of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
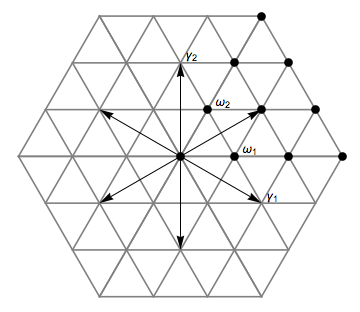
Fundamental Weight
In the mathematical field of representation theory, a weight of an algebra ''A'' over a field F is an algebra homomorphism from ''A'' to F, or equivalently, a one-dimensional representation of ''A'' over F. It is the algebra analogue of a multiplicative character of a group. The importance of the concept, however, stems from its application to representations of Lie algebras and hence also to representations of algebraic and Lie groups. In this context, a weight of a representation is a generalization of the notion of an eigenvalue, and the corresponding eigenspace is called a weight space. Motivation and general concept Given a set ''S'' of n\times n matrices over the same field, each of which is diagonalizable, and any two of which commute, it is always possible to simultaneously diagonalize all of the elements of ''S''.In fact, given a set of commuting matrices over an algebraically closed field, they are simultaneously triangularizable, without needing to assume that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Weyl Chamber
In the mathematical field of representation theory, a weight of an algebra ''A'' over a field F is an algebra homomorphism from ''A'' to F, or equivalently, a one-dimensional representation of ''A'' over F. It is the algebra analogue of a multiplicative character of a group. The importance of the concept, however, stems from its application to representations of Lie algebras and hence also to representations of algebraic and Lie groups. In this context, a weight of a representation is a generalization of the notion of an eigenvalue, and the corresponding eigenspace is called a weight space. Motivation and general concept Given a set ''S'' of n\times n matrices over the same field, each of which is diagonalizable, and any two of which commute, it is always possible to simultaneously diagonalize all of the elements of ''S''.In fact, given a set of commuting matrices over an algebraically closed field, they are simultaneously triangularizable, without needing to assume that they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borel Subalgebra
In mathematics, specifically in representation theory, a Borel subalgebra of a Lie algebra \mathfrak is a maximal solvable subalgebra. The notion is named after Armand Borel. If the Lie algebra \mathfrak is the Lie algebra of a complex Lie group, then a Borel subalgebra is the Lie algebra of a Borel subgroup. Borel subalgebra associated to a flag Let \mathfrak g = \mathfrak(V) be the Lie algebra of the endomorphisms of a finite-dimensional vector space ''V'' over the complex numbers. Then to specify a Borel subalgebra of \mathfrak g amounts to specify a flag of ''V''; given a flag V = V_0 \supset V_1 \supset \cdots \supset V_n = 0, the subspace \mathfrak b = \ is a Borel subalgebra, and conversely, each Borel subalgebra is of that form by Lie's theorem. Hence, the Borel subalgebras are classified by the flag variety of ''V''. Borel subalgebra relative to a base of a root system Let \mathfrak g be a complex semisimple Lie algebra, \mathfrak h a Cartan subalgebra and ''R'' the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Sum Of Modules
In abstract algebra, the direct sum is a construction which combines several modules into a new, larger module. The direct sum of modules is the smallest module which contains the given modules as submodules with no "unnecessary" constraints, making it an example of a coproduct. Contrast with the direct product, which is the dual notion. The most familiar examples of this construction occur when considering vector spaces (modules over a field) and abelian groups (modules over the ring Z of integers). The construction may also be extended to cover Banach spaces and Hilbert spaces. See the article decomposition of a module for a way to write a module as a direct sum of submodules. Construction for vector spaces and abelian groups We give the construction first in these two cases, under the assumption that we have only two objects. Then we generalize to an arbitrary family of arbitrary modules. The key elements of the general construction are more clearly identified by conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Action
Let W be the Weyl group of a semisimple Lie algebra \mathfrak (associate to fixed choice of a Cartan subalgebra \mathfrak). Assume that a set of simple roots in \mathfrak^* is chosen. The ''affine action'' (also called the ''dot action'') of the Weyl group on the space \mathfrak^* is :w\cdot \lambda:=w(\lambda+\delta)-\delta where \delta is the sum of all fundamental weights, or, equivalently, the half of the sum of all positive root In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vector space, vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and ...s. References * . Representation theory of Lie algebras {{algebra-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
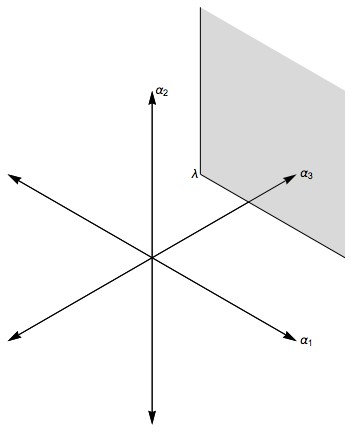
Root Reflection
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups (and some analogues such as algebraic groups) and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied. Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagrams, occurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory (such as singularity theory). Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. Definitions and examples As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, R2, as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors span the whole s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Root (root System)
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups (and some analogues such as algebraic groups) and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied. Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagrams, occurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory (such as singularity theory). Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. Definitions and examples As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, R2, as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors span the whole s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projection (mathematics)
In mathematics, a projection is a mapping of a set (or other mathematical structure) into a subset (or sub-structure), which is equal to its square for mapping composition, i.e., which is idempotent. The restriction to a subspace of a projection is also called a ''projection'', even if the idempotence property is lost. An everyday example of a projection is the casting of shadows onto a plane (sheet of paper): the projection of a point is its shadow on the sheet of paper, and the projection (shadow) of a point on the sheet of paper is that point itself (idempotency). The shadow of a three-dimensional sphere is a closed disk. Originally, the notion of projection was introduced in Euclidean geometry to denote the projection of the three-dimensional Euclidean space onto a plane in it, like the shadow example. The two main projections of this kind are: * The projection from a point onto a plane or central projection: If ''C'' is a point, called the center of projection, then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)