|
General Semantics
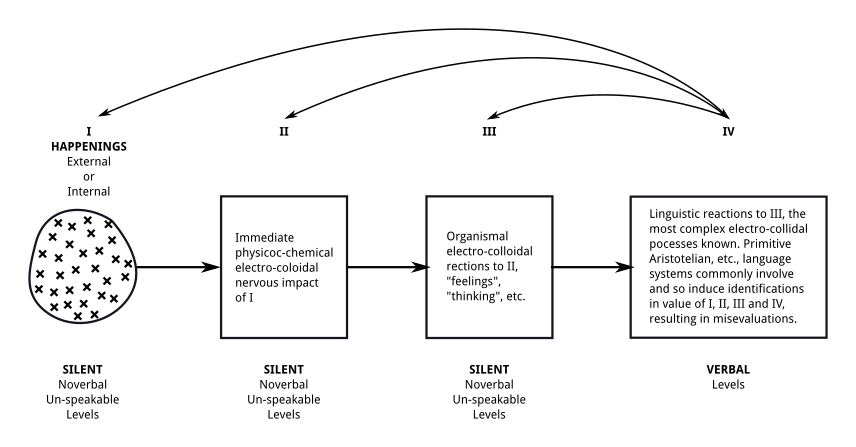
General semantics is concerned with how events translate to perceptions, how they are further modified by the names and labels we apply to them, and how we might gain a measure of control over our own cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses. Proponents characterize general semantics as an antidote to certain kinds of delusional thought patterns in which incomplete and possibly warped mental constructs are projected onto the world and treated as reality itself. After partial launches under the names ''human engineering'' and ''humanology'', Polish-American originator Alfred Korzybski (1879–1950) fully launched the program as ''general semantics'' in 1933 with the publication of ''Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics''. In ''Science and Sanity'', general semantics is presented as both a theoretical and a practical system whose adoption can reliably alter human behavior in the direction of greater sanity. In the 1947 preface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Korzybski
Alfred Habdank Skarbek Korzybski (, ; July 3, 1879 – March 1, 1950) was a Polish-American independent scholar who developed a field called general semantics, which he viewed as both distinct from, and more encompassing than, the field of semantics. He argued that human knowledge of the world is limited both by the human nervous system and the languages humans have developed, and thus no one can have direct access to reality, given that the most we can know is that which is filtered through the brain's responses to reality. His best known dictum is " The map is not the territory". Early life and career Born in Warsaw, Vistula Country, which was then part of the Russian Empire, Korzybski belonged to an aristocratic Polish family whose members had worked as mathematicians, scientists, and engineers for generations. He learned the Polish language at home and the Russian language in schools, and having a French and German governess, he became fluent in four languages as a child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvin Bridges
Calvin Blackman Bridges (January 11, 1889 – December 27, 1938) was an American scientist known for his contributions to the field of genetics. Along with Alfred Sturtevant and H.J. Muller, Bridges was part of Thomas Hunt Morgan's famous "Fly Room" at Columbia University. Early life Calvin Blackman Bridges was born in Schuyler Falls, New York in 1889 to the parents of Leonard Bridges and Charlotte Blackman. Tragically, Calvin's mother died when he was two years old, and his father died a year later, leaving the young Calvin an orphan. Bridges was subsequently taken in and raised by his grandmother. It took Bridges several years to complete high school, graduating when he was 20 years old. Despite this setback, he moved on to be an outstanding student at Columbia University in New York City, which he attended both undergraduate and postgraduate school. While taking a zoology class at Columbia, Bridges met Thomas Hunt Morgan. This started a relationship which would eventually l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellensburg, Washington
Ellensburg is a city in and the county seat of Kittitas County, Washington, United States. It is located just east of the Cascade Range near the junction of Interstate 90 and Interstate 82 Interstate 82 (I-82) is an Interstate Highway in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States that travels through parts of Washington and Oregon. It runs from its northwestern terminus at I-90 in Ellensburg, Washington, to its southeaste .... The population was 18,666 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. and was estimated to be 19,596 in 2021. The city is located along the Yakima River in the Kittitas Valley, an agricultural region that extends east towards the Columbia River. The valley is a major producer of timothy hay, which is processed and shipped internationally. Ellensburg is also the home of Central Washington University (CWU). Ellensburg, originally named Ellensburgh for the wife of town founder John Alden Shoudy, was founded in 1871 and grew rapidly in the 1880 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciousness untouched by the mind ('' Chitta'') and mundane suffering (''Duḥkha''). There is a wide variety of schools of yoga, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism,Stuart Ray Sarbacker, ''Samādhi: The Numinous and Cessative in Indo-Tibetan Yoga''. SUNY Press, 2005, pp. 1–2.Tattvarthasutra .1 see Manu Doshi (2007) Translation of Tattvarthasutra, Ahmedabad: Shrut Ratnakar p. 102. and traditional and modern yoga is practiced worldwide. Two general theories exist on the origins of yoga. The linear model holds that yoga originated in the Vedic period, as reflected in the Vedic textual corpus, and influenced Buddhism; according to author Edward Fitzpatrick Crangle, this model is mainly supported by Hindu scholars. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Gardner
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writings of Lewis Carroll, L. Frank Baum, and G. K. Chesterton.Martin (2010) He was also a leading authority on Lewis Carroll. ''The Annotated Alice'', which incorporated the text of Carroll's two Alice books, was his most successful work and sold over a million copies. He had a lifelong interest in magic and illusion and in 1999, MAGIC magazine named him as one of the "100 Most Influential Magicians of the Twentieth Century". He was considered the doyen of American puzzlers. He was a prolific and versatile author, publishing more than 100 books. Gardner was best known for creating and sustaining interest in recreational mathematicsand by extension, mathematics in generalthroughout the latter half of the 20th century, principally through his "Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methods include questioning, critical discussion, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Newton's 1687 ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'' later became classified as a book of physics. In the 19th century, the growth of modern research universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Objects
In metaphysics, the distinction between abstract and concrete refers to a divide between two types of entities. Many philosophers hold that this difference has fundamental metaphysical significance. Examples of concrete objects include plants, human beings and planets while things like numbers, sets and propositions are abstract objects. There is no general consensus as to what the characteristic marks of concreteness and abstractness are. Popular suggestions include defining the distinction in terms of the difference between (1) existence inside or outside space-time, (2) having causes and effects or not, (3) having contingent or necessary existence, (4) being particular or universal and (5) belonging to either the physical or the mental realm or to neither. Despite this diversity of views, there is broad agreement concerning most objects as to whether they are abstract or concrete. So under most interpretations, all these views would agree that, for example, plants are concrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universals
In metaphysics, a universal is what particular things have in common, namely characteristics or qualities. In other words, universals are repeatable or recurrent entities that can be instantiated or exemplified by many particular things. For example, suppose there are two chairs in a room, each of which is green. These two chairs both share the quality of " chairness", as well as greenness or the quality of being green; in other words, they share a "universal". There are three major kinds of qualities or characteristics: types or kinds (e.g. mammal), properties (e.g. short, strong), and relations (e.g. father of, next to). These are all different types of universals. Paradigmatically, universals are '' abstract'' (e.g. humanity), whereas particulars are ''concrete'' (e.g. the personhood of Socrates). However, universals are not necessarily abstract and particulars are not necessarily concrete. For example, one might hold that numbers are particular yet abstract objects. Likew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Kähler
Erich Kähler (; 16 January 1906 – 31 May 2000) was a German mathematician with wide-ranging interests in geometry and mathematical physics, who laid important mathematical groundwork for algebraic geometry and for string theory. Education and life Erich Kähler was born in Leipzig, the son of a telegraph inspector Ernst Kähler. Inspired as a boy to be an explorer after reading books about Sven Hedin that his mother Elsa Götsch had given to him, the young Kähler soon focused his passion for exploration on astronomy. He is said to have written a 50-page thesis on fractional differentiation while still in high school, hoping that it would earn him a PhD. His teachers replied that he would have to attend university courses first. Kähler enrolled in the University of Leipzig in 1924. He read Galois theory, met the mathematician Emil Artin, and did research under the supervision of Leon Lichtenstein. Still fascinated by celestial mechanics, Kähler wrote a dissertation entitle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Fairchild
David Grandison Fairchild (April 7, 1869 – August 6, 1954) was an American botanist and plant explorer. Fairchild was responsible for the introduction of more than 200,000 exotic plants and varieties of established crops into the United States, including soybeans, pistachios, mangos, nectarines, dates, bamboos, and flowering cherries. Certain varieties of wheat, cotton, and rice became especially economically important. Early life and education Fairchild was born in Lansing, Michigan and was raised in Manhattan, Kansas. He was a member of the Fairchild family, descendants of Thomas Fairchild of Stratford, Connecticut. He graduated from Kansas State College of Agriculture (B.A. 1888, M.S. 1889) where his father, George Fairchild, was president. He continued his studies at Iowa State and at Rutgers with his uncle, Byron Halsted, a noted biologist. He received an honorary D.Sc. degree from Oberlin College in 1915. Career Barbour Lathrop, a wealthy world traveler, persuaded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence B
Clarence may refer to: Places Australia * Clarence County, New South Wales, a Cadastral division * Clarence, New South Wales, a place near Lithgow * Clarence River (New South Wales) * Clarence Strait (Northern Territory) * City of Clarence, a local government body and municipality in Tasmania * Clarence, Western Australia, an early settlement * Electoral district of Clarence, an electoral district in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly Canada * Clarence, Ontario, a hamlet in the city of Clarence-Rockland * Clarence Township, Ontario * Clarence, Nova Scotia * Clarence Islands, Nunavut, Canada New Zealand * Clarence, New Zealand, a small town in Marlborough * Waiau Toa / Clarence River United States * Clarence Strait, Alaska * Clarence, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Clarence, Iowa, a city * Clarence Township, Barton County, Kansas * Clarence, Louisiana, a village * Clarence Township, Michigan * Clarence, Missouri, a city * Clarence, New York, a town ** Clarence (CDP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alanson White
William Alanson White (24 January 1870 – 7 March 1937) was an American neurologist and psychiatrist. Biography He was born in Brooklyn, New York to parents Alanson White and Harriet Augusta Hawley White. He attended public school in Brooklyn. A young White was influenced by philosopher Herbert Spencer; After White's death, one writer recalled that White "was never seriously shaken from Spencer's hopeful evolutionary catechism, which at the age of 13 he had accepted as the key to all knowledge". At 15, White entered Cornell, studying there from 1885 to 1889. In 1891, White graduated with an M.D. from the Long Island College Hospital. After serving as an intern for a year, for nine years he was an assistant physician at the Binghamton (New York) State Hospital. There he collaborated with Boris Sidis. On October 1, 1903, White became superintendent of the "Government Hospital for the Insane", later named St. Elizabeths Hospital, in Washington, D.C. There he spent the rest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |