|
Geiparvarin
Geiparvarin is a coumarin derivative found in the leaves of the Australian Willow (''Geijera parviflora''). It is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, espe .... Several analogues of geiparvarin have been studied for antitumor properties. References Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Coumarins Phenol ethers Enones Alkene derivatives {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemical class and considered as a lactone. Coumarin is a colorless crystalline solid with a sweet odor resembling the scent of vanilla and a bitter taste. It is found in many plants, where it may serve as a chemical defense against predators. By inhibiting synthesis of vitamin K, a related compound is used as the prescription drug warfarin – an anticoagulant – to inhibit formation of blood clots, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Etymology Coumarin is derived from ''coumarou'', the French word for the tonka bean. The word ''tonka'' for the tonka bean is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geijera Parviflora
''Geijera parviflora'', commonly known as wilga, is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to inland parts of eastern Australia. It has drooping branches, linear to narrow lance-shaped leaves, small white flowers in loose panicles and spherical fruit containing a shiny black seed. Other vernacular names include Australian willow, native willow, sheepbush and dogwood. Description ''Geijera parviflora'' is a shrub or tree that typically grows to a height of and has drooping branches and leaves often reaching ground level, but these are often grazed by sheep. The leaves are glossy dark green, linear to lance-shaped, long and wide on a petiole long. The leaves give off a strong smell when crushed. The flowers are arranged in loose panicles long, each flower on a pedicel about long. The sepals are long, the petals white and long. The smell of the flowers has been described as foetid, but also as citrus-scented and attracts insects. Flowering oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Journal Of Chemistry
The ''Australian Journal of Chemistry - an International Journal for Chemical Science'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by CSIRO Publishing. It was established in 1948 and covers all aspects of chemistry. The editors-in-chief are George Koutsantonis (University of Western Australia) and John Wade (University of Melbourne). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * CAB Abstracts *Chemical Abstracts Service *Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * EBSCO databases *Ei Compendex *Science Citation Index *Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 1.32. See also * ''Environmental Chemistry'' (journal) *List of scientific journals in chemistry A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
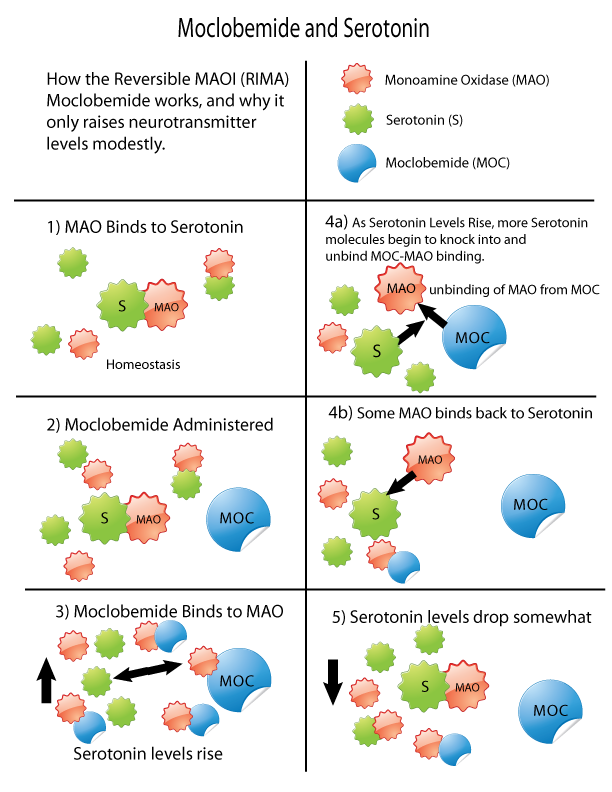
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog (chemistry)
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions *Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Record (other) *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical **Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science **Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation *Magazine, non-academic or scholarly periodicals in general **Trade magazine, a magazine of interest to those of a particular profession or trade **Literary magazine, a magazine devoted to literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumarins
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain , forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemical class and considered as a lactone. Coumarin is a colorless crystalline solid with a sweet odor resembling the scent of vanilla and a bitter taste. It is found in many plants, where it may serve as a chemical defense against predators. By inhibiting synthesis of vitamin K, a related compound is used as the prescription drug warfarin – an anticoagulant – to inhibit formation of blood clots, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Etymology Coumarin is derived from ''coumarou'', the French word for the tonka bean. The word ''tonka'' for the tonka bean is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French Guia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |