|
Geg
Gheg (also spelled Geg; Gheg Albanian: ''gegnishtja'', Standard sq, gegërishtja) is one of the two major varieties of Albanian, the other being Tosk. The geographic dividing line between the two varieties is the Shkumbin River, which winds its way through central Albania. Gheg is spoken in northern and central Albania, Kosovo, northwestern North Macedonia, southeastern Montenegro and southern Serbia by the Albanian dialectal subgroup known as Ghegs.Joseph 2003, When Languages Collide: Perspectives on Language Conflict, Language Competition, and Language Coexistence, p. 266: "Northeastern Geg" Gheg does not have any official status as a written language in any country. Publications in Kosovo and North Macedonia are in Standard Albanian, which is based on Tosk. However, some authors continue to write in Gheg. History Before World War II, there had been no official attempt to enforce a unified Albanian literary language; both literary Gheg and literary Tosk were used. The comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghegs
The Ghegs (also spelled as Gegs; sq, Gegët) are one of two major dialectal subgroups of Albanians (the other being the Tosks) They are also differentiated by minor Culture, cultural, Albanian dialects, dialectal, Society, social and Religion, religious characteristics. The Ghegs live in Albania (north of the Shkumbin River, Shkumbin river), Kosovo, North Macedonia, Serbia and Montenegro. The Ghegs speak Gheg Albanian, one of the two main dialects of Albanian language. The social organization of the Ghegs was traditionally Tribal society, tribal, with several distinct tribal groups of Ghegs. The Ottoman Empire annexed and ruled the Tosk-inhabited south at the beginning of the 15th century, while the territory populated by Ghegs remained out of the reach of the regular Ottoman civil administration until the beginning of the 20th century. As a consequence, the Ghegs evolved isolated from the Tosks. Similarly, the Islamization of the Ghegs was incomplete, with a large area of northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
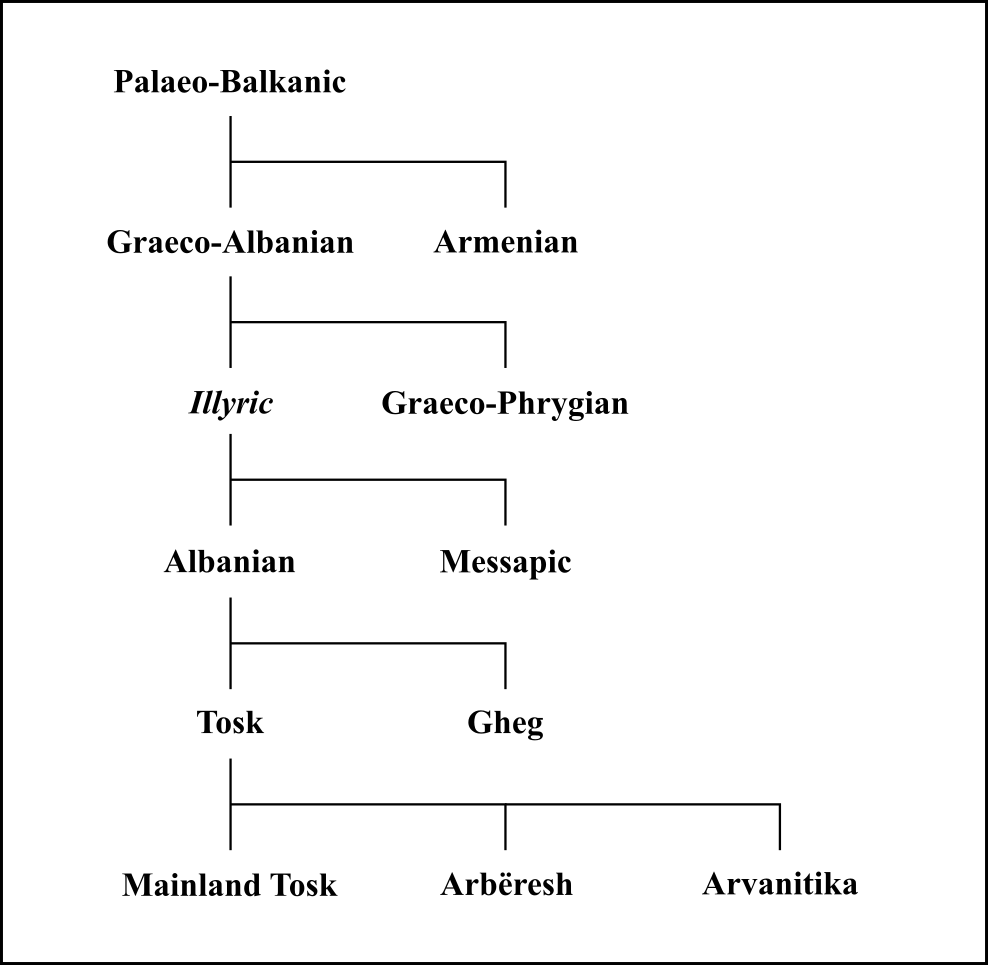
Albanian Language
Albanian ( endonym: or ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is spoken by the Albanians in the Balkans and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. With about 7.5 million speakers, it comprises an independent branch within the Indo-European languages and is not closely related to any other modern Indo-European language. Albanian was first attested in the 15th century and it is a descendant of one of the Paleo-Balkan languages of antiquity. For historical and geographical reasons,: "It is often thought (for obvious geographic reasons) that Albanian descends from ancient Illyrian (see above), but this cannot be ascertained as we know next to nothing about Illyrian itself." the prevailing opinion among modern historians and linguists is that the Albanian language is a descendant of a southern Illyrian dialect spoken in much the same region in classical times. Alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gheg Albanian
Gheg (also spelled Geg; Gheg Albanian: ''gegnishtja'', Standard sq, gegërishtja) is one of the two major varieties of Albanian, the other being Tosk. The geographic dividing line between the two varieties is the Shkumbin River, which winds its way through central Albania. Gheg is spoken in northern and central Albania, Kosovo, northwestern North Macedonia, southeastern Montenegro and southern Serbia by the Albanian dialectal subgroup known as Ghegs.Joseph 2003, When Languages Collide: Perspectives on Language Conflict, Language Competition, and Language Coexistence, p. 266: "Northeastern Geg" Gheg does not have any official status as a written language in any country. Publications in Kosovo and North Macedonia are in Standard Albanian, which is based on Tosk. However, some authors continue to write in Gheg. History Before World War II, there had been no official attempt to enforce a unified Albanian literary language; both literary Gheg and literary Tosk were used. The comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Albanian Language
The Proto-Albanian language is the unattested language from which Albanian later developed. Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European language that was closely related to Illyrian and Messapic,; which is sometimes also referred to as Albanoid. Proto-Albanian is reconstructed by way of the comparative method between the Tosk and Gheg dialects, as well as the treatment of loanwords, the most important of which are those from Latin (dated by De Vaan to the period 167 BCE to 400 CE) and from Slavic (dated from 600 CE onward). The evidence from loanwords allows linguists to construct in great detail the shape of native words at the points of major influxes of loans from well-attested languages. Proto-Albanian is broken up into different stages which are usually delimited by the onset of contact with different well-attested languages. Its earliest stages are dated to the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korçë
Korçë (; sq-definite, Korça) is the eighth most populous city of the Republic of Albania and the seat of Korçë County and Korçë Municipality. The total population is 75,994 (2011 census), in a total area of . It stands on a plateau some above sea level, surrounded by the Morava Mountains. The area of the Old Bazaar, including Mirahori Mosque, is considered as the urban core of the city. Founded by a local Ottoman Albanian lord, Ilias Bey Mirahori, the urban area of Korçë dates back to the late 15th century and the beginning of the 16th century, however its actual physiognomy was realized in the 19th century, during a period that corresponds with the rapid growth and development of the city. The Old Bazaar has played a dominant role in Albania's market history. Korçë is the largest city of eastern Albania and an important cultural and industrial centre. Name Korçë is named differently in other languages: rup, Curceaua, Curceao or Curciau; Serbian, Bulgaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirana
Tirana ( , ; aln, Tirona) is the capital and largest city of Albania. It is located in the centre of the country, enclosed by mountains and hills with Dajti rising to the east and a slight valley to the northwest overlooking the Adriatic Sea in the distance. Due to its location at the Plain of Tirana and the close proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, the city is particularly influenced by a Mediterranean seasonal climate. It is among the wettest and sunniest cities in Europe, with 2,544 hours of sun per year. Tirana was founded as a city in 1614 by the Ottoman Albanian general Sylejman Pasha Bargjini and flourished by then around the Old Mosque and the ''türbe''. The area that today corresponds to the city's territory has been continuously inhabited since the Iron Age. It was inhabited by Illyrians, and was most likely the core of the Illyrian Kingdom of the Taulantii, which in Classical Antiquity was centred in the hinterland of Epidamnus. Following the Illyrian Wars it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosk Albanian
Tosk ( sq-definite, toskërishtja) is the southern group of dialects of the Albanian language, spoken by the ethnographic group known as Tosks. The line of demarcation between Tosk and Gheg (the northern variety) is the Shkumbin River. Tosk is the basis of the standard Albanian language. Major Tosk-speaking groups include the Myzeqars of Myzeqe, Labs of Labëria, Chams of Çamëria, Arvanites of Greece and the Arbëreshë of Italy, as well as the original inhabitants of Mandritsa in Bulgaria. In North Macedonia, there were approximately 3000 speakers in the early 1980s. Tosk features * Rhotacism: Proto-Albanian ''*-n-'' becomes ''-r-'' (e.g. ''rëra'' "sand") * Tosk dialects preserve groups ''mb'', ''ngj'' and ''nd'' assimilated to ''m'', ''nj'' and ''n'' in Geg. * Proto-Albanian ''*ō'' becomes ''va''. * Nasal vowels: There is a lack of nasal vowels in Tosk (e.g. ''sy'' "eye") and Late Proto-Albanian ''*â'' plus a nasal becomes ''ë'' (e.g. ''nëntë'' "nine"). * e-vow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Communism
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika Popullore Socialiste e Shqipërisë, links=no) was the Marxist–Leninist government, Marxist–Leninist one party state that existed in Albania from 1946 to 1992 (the official name of the country was the People's Republic of Albania from 1946 until 1976 and the Republic of Albania from 1991 until its dissolution in 1992). From 1944 to 1946, the state of Albania was known as the Democratic Government of Albania. During this time period, the country was ruled by Enver Hoxha and the Party of Labour of Albania. They ruled Albania by establishing a Stalinism, Albanian stalinist style of state administration and adhering to policies which stressed Albanian nationalism, national unity and Self-sufficiency, self-reliance. Travel and visa restrictions made Albania one of the most difficult countries to visit or travel from. Former President Ilir Meta called it the "North Korea of Europe" during an interview with Euronews. Being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istrian Albanian
Istrian Albanian was a Gheg variety of the Albanian language, spoken in the village of Katun History From the 13th to the 17th century the depopulation of the Istrian Peninsula prompted the Republic of Venice to repopulate the region with settlers, which among others included Albanians. The coalescence of the various dialects spoken by the settlers led to the formation of the Istrian Albanian dialect. The only surviving text of the dialect was written by the local scholar Pietro Stancovich Pietro Mattia Stancovich (Petar Matija Stanković) (Barban, February 24, 1771 – Barban, September 12, 1852) was an Italian priest, historian and inventor, born in Istria. Biography He studied theology in Padua, was ordained in Pula and th ... in the 1830s. Stankovich recorded a version of the Parable of the Prodigal Son and a vocabulary list of the dialect. References Albanian dialects History of Istria Extinct languages of Europe {{ie-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arshi Pipa
Arshi Pipa (28 July 1920 – 20 July 1997) was an Albanian-American philosopher, writer, poet and literary critic. Biography Arshi Pipa was born on 28 July 1920 in Shkodër and attended school there until 1938. Pipa received a BA equivalent degree ("Laurea") in philosophy at the University of Florence in 1942. After he completed his studies he was a teacher of Italian language in different schools in Albania. He was imprisoned for ten years (1946–56) in Communist Albania because he antagonized the communist regime with his recitation of a verse from a "Song of the Flea" by Goethe found in a translation of ''Faust''. After he was released from prison (his original sentence was 20 years, but after amnesty it was cut to 10) he escaped to Yugoslavia and lived in Sarajevo during the period 1957–9. In 1959 he emigrated to the United States where he taught at Adelphi College, Georgetown University, Columbia University, and UC Berkeley. Then, from 1966 to 1989, he was a profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shijak
Shijak ( sq-definite, Shijaku) is a town and a municipality in Durrës County, west-central Albania. The municipality was formed at the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities Gjepalaj, Maminas, Shijak and Xhafzotaj, that became municipal units. The seat of the municipality is the town Shijak. The total population is 27,861 (2011 census), in a total area of 92.24 km2. The population of the former municipality at the 2011 census was 7,568. Overview Shijak is located 11 km away from the city of Durrës, and 31 km from the city of Tirana. The former municipality had a surface area of about 5 km2, and a reported population of around 12,853 people as of 2007. In reality the population is smaller as many people who claim residency in Shijak actually reside permanently elsewhere. With this taken into account the actual population size is estimated to be around 6,000–7,000 people. Population size has grown at a rate of around 1% per yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishëm
Ishëm is a former municipality in the Durrës County, northwestern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Durrës. The population at the 2011 census was 5,001. Ishëm Castle is located in the municipal unit. Famous peoples *Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |