|
Gay Purges (Canada)
Occurring between the 1950s and the 1990s, the Gay Purges were a series of mass discrimination and expulsion of Canadian workers in the civil service, Royal Canadian Mounted Police and armed forces due to their suspected homosexuality. During the early stages of the Cold War, increased surveillance and interference from the Soviet Union resulted in the Canadian government and military to become increasingly worried about the loyalty of their employees. In the late 1940s and early 1950s, the RCMP was charged with investigating the loyalties, and later the reliability of character, of civil servants and Canadian armed forces members. The Canadian government determined that homosexuality was a "character defect," and security risk as homosexuals could be possible targets for blackmail by the Soviets. In response to the Canadian government and military's concerns, the RCMP began a purge to investigate and discover homosexuality in areas of the Canadian workforce that were deemed imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Civil Service
The Public Service of Canada (known as the Civil Service of Canada prior to 1967) is the civilian workforce of the Government of Canada's departments, agencies, and other public bodies. While the Government of Canada has employed civil servants to support its functions since Confederation in 1867, positions were initially filled through patronage until 1908, when the Laurier government enacted the ''Public Service Amendment Act'', which established the merit-based appointment system which governs hiring within the federal public service today. As of 2020, the Public Service employs 319,601 people, and is Canada's largest single employer. There are 137 distinct organizations within the Public Service, including 23 ministerial (line) departments, 3 service agencies, 17 departmental corporations, 50 departmental agencies, 12 special operating agencies, and 6 agents of Parliament. While Crown corporations are owned by the federal government, employees are generally not considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit Machine (homosexuality Test)
The "fruit machine" was a device developed in Canada by Frank Robert Wake, a psychology professor with Carleton University in the 1950s that was supposed to be able to identify gay men (derogatorily referred to as " fruits"). The subjects were made to view pornography; the device then measured the diameter of the pupils of the eyes (pupillary response test), perspiration, and pulse for a supposed erotic response. The machine was employed in Canada in the 1950s and 1960s during a campaign to eliminate all gay men from the civil service, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP), and the military. A substantial number of workers did lose their jobs. Although funding for the project was cut off in the late 1960s, the investigations continued, and the RCMP collected files on 9,000 people who had been investigated. The machine used a chair similar to that used by dentists. It had a pulley with a camera going towards the pupils, with a black box located in front of it that displaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBT History In Canada
This article gives a broad overview of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) history in Canada. LGBT activity was considered a crime from the Former colonies and territories in Canada, colonial period in Canada until 1969, when Bill C-150 was passed into law. However, there is still discrimination despite anti-discrimination law. For a more detailed listing of individual incidents in Canadian LGBT history, see also Timeline of LGBT history in Canada. 17th century New France's first-ever criminal trial for the crime of homosexuality took place in September 1648, when a military drummer stationed at the French garrison in Montreal, Ville-Marie, New France was sentenced to the gallows for sodomy by the local Sulpician Order, Sulpician priests."Looking ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everett Klippert
George Everett Klippert (September 6, 1926 – August 7, 1996) was the last person in Canada to be arrested, charged, prosecuted, convicted, and imprisoned for gross indecency before the decriminalization of homosexual acts in 1969; the reform was a direct result of the Klippert case. Klippert, originally from Kindersley, Saskatchewan, was raised in Calgary, Alberta. In 1960 he was convicted on eighteen charges of gross indecency and sentenced to four years' imprisonment. Upon his release, he moved to northern Canada. He was working as a mechanic in Pine Point, Northwest Territories, in 1965 when he was picked up by police for questioning in connection with a case of suspected arson. Although he was found not to have had any involvement in the fire, Klippert voluntarily admitted to having had recent consensual homosexual relations with four different adult men. He was subsequently arrested and charged with four counts of "gross indecency". A court-ordered psychiatrist assess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Kinsman
Gary William Kinsman (born 1955) is a Canadian sociologist. Born in Toronto, he is one of Canada's leading academics on lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender issues."Gary Kinsman's book Canadian War on Queers takes on gay issues in government" . '''', 17 March 2010. In 1987, he wrote one of the key Canadian texts on [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada In The Cold War
Canada in the Cold War was one of the western powers playing a central role in the major alliances. It was an ally of the United States, but there were several foreign policy differences between the two countries over the course of the Cold War. Canada was a founding member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949, the North American Aerospace Defence Command (NORAD) in 1958, and played a leading role in United Nations peacekeeping operations—from the Korean War to the creation of a permanent UN peacekeeping force during the Suez Crisis in 1956. Subsequent peacekeeping interventions occurred in the Congo (1960), Cyprus (1964), the Sinai (1973), Vietnam (with the International Control Commission), Golan Heights, Lebanon (1978), and Namibia (1989–1990). Canada did not follow the American lead in all Cold War actions, sometimes resulting in tensions between the two countries. For instance, Canada refused to join the Vietnam War; in 1984, the last nuclear weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library And Archives Canada
Library and Archives Canada (LAC; french: Bibliothèque et Archives Canada) is the federal institution, tasked with acquiring, preserving, and providing accessibility to the documentary heritage of Canada. The national archive and library is the fifth largest library in the world. The LAC reports to the Parliament of Canada through the Minister of Canadian Heritage. The LAC traces its origins to the Dominion Archives, formed in 1872, and the National Library of Canada, formed in 1953. The former was later renamed as the Public Archives of Canada in 1912, and the National Archives of Canada in 1987. In 2004, the National Archives of Canada and the National Library of Canada were merged to form Library and Archives Canada. History Predecessors The Dominion Archives was founded in 1872 as a division within the Department of Agriculture tasked with acquiring and transcribing documents related to Canadian history. In 1912, the division was transformed into an autonomous organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
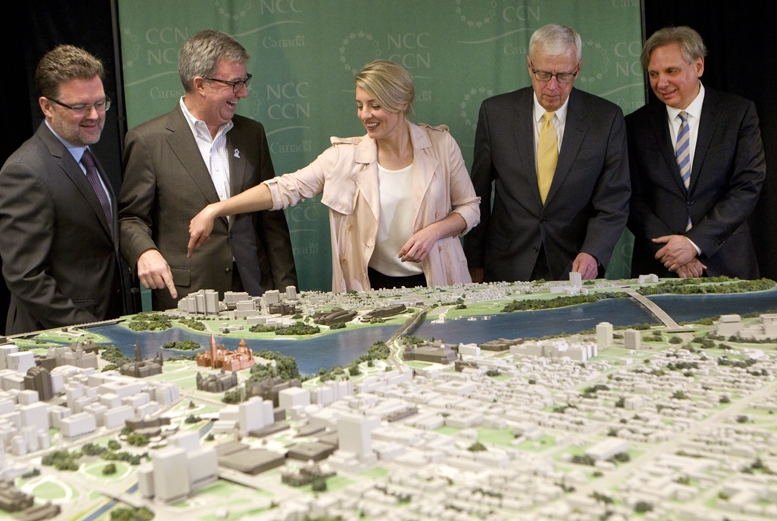
LGBTQ2+ National Monument
The LGBTQ2+ National Monument is a planned public monument in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, dedicated to the history of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer and two-spirit communities in Canada. The monument was launched by the LGBT Purge Fund, an organization created from the 2018 settlement of the class action suit against the Government of Canada by victims of the purges of LGBTQ employees from the federal civil service in the 1960s. In 2020 the fund and the National Capital Commission announced the planned site, a parkland site on Wellington Street between Library and Archives Canada and the Portage Bridge, and launched a design competition for artists and architects to submit proposals. In November 2021, the five shortlisted designs were unveiled.Matt Hickman"Canada’s LGBTQ2+ National Monument is moving ahead, and here are the shortlisted proposals" ''The Architect's Newspaper'', November 16, 2021. They included The Lens, by Fathom Studio, Two Row Architect and MVRDV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Capital Commission
The National Capital Commission (NCC; french: Commission de la capitale nationale, CCN) is the Crown corporation responsible for development, urban planning, and conservation in Canada's Capital Region (Ottawa, Ontario and Gatineau, Quebec), including administering most lands and buildings owned by the Government of Canada in the region. The NCC is the capital's largest property owner, owning and managing over 11% of all lands in the Capital Region. It also owns over 1,600 properties in its real estate portfolio, including the capital's six official residences; commercial, residential and heritage buildings; and agricultural facilities. The NCC reports to the Parliament of Canada through whichever minister in the Cabinet of Canada is designated responsible for the ''National Capital Act'', currently the Minister of Public Services and Procurement. History Ottawa Improvement Commission (1899–1927) Through the 19th century, the character of what is known today as the Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
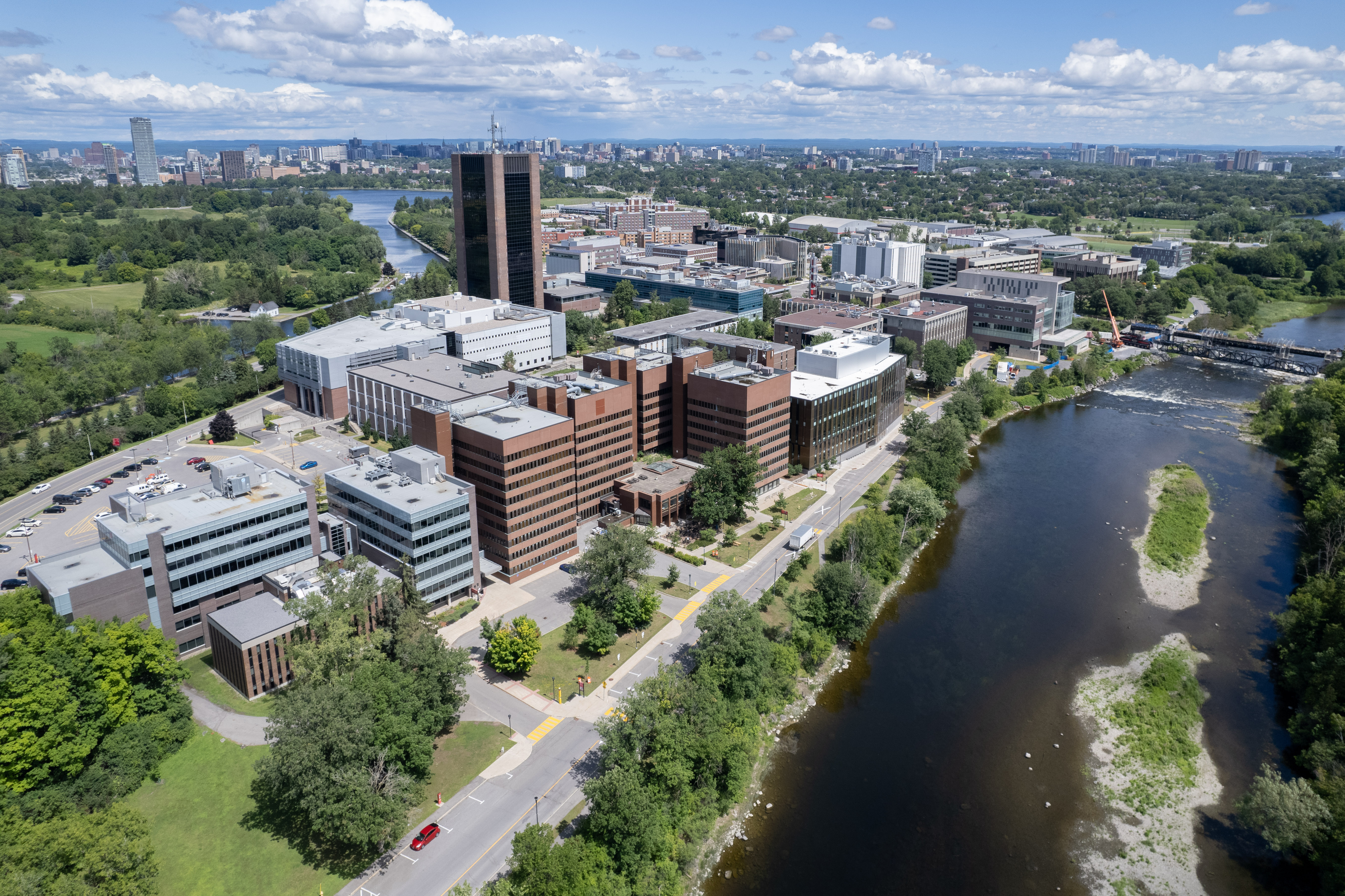
Carleton University
Carleton University is an English-language public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Founded in 1942 as Carleton College, the institution originally operated as a private, non-denominational evening college to serve returning World War II veterans. Carleton was chartered as a university by the provincial government in 1952 through ''The Carleton University Act,'' which was then amended in 1957, giving the institution its current name. The university is named for the now-dissolved Carleton County, which included the city of Ottawa at the time the university was founded. Carleton County, in turn, was named in honour of Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester, who was Governor General of The Canadas from 1786 to 1796. The university moved to its current campus in 1959, growing rapidly in size during the 1960s as the Ontario government increased support for post-secondary institutions and expanded access to higher education. Carleton offers a diverse range of academic program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
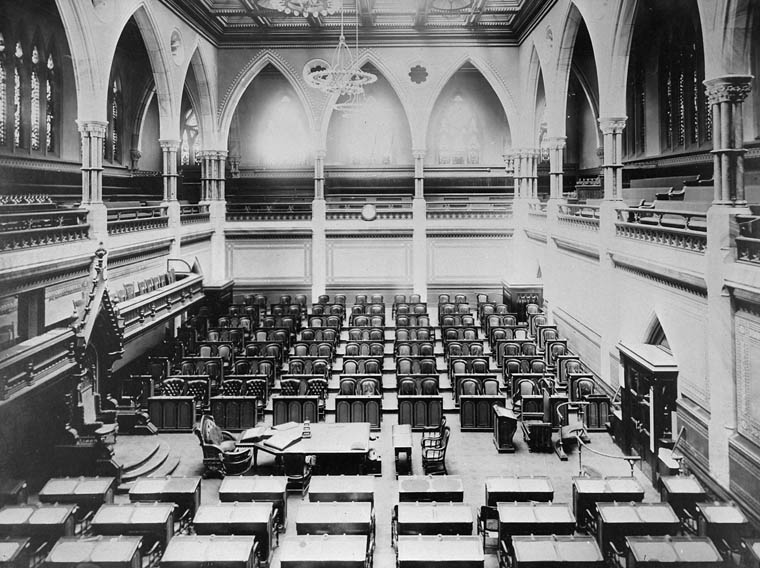
House Of Commons Of Canada
The House of Commons of Canada (french: Chambre des communes du Canada) is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada. The House of Commons is a democratically elected body whose members are known as members of Parliament (MPs). There have been 338 MPs since the most recent electoral district redistribution for the 2015 federal election, which saw the addition of 30 seats. Members are elected by simple plurality ("first-past-the-post" system) in each of the country's electoral districts, which are colloquially known as ''ridings''. MPs may hold office until Parliament is dissolved and serve for constitutionally limited terms of up to five years after an election. Historically, however, terms have ended before their expiry and the sitting government has typically dissolved parliament within four years of an election according to a long-standing convention. In any case, an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelle Douglas
Michelle D. Douglas (born December 30, 1963) is a Canadian human rights activist who launched a landmark legal challenge in the Federal Court of Canada against the military's discriminatory policies against LGBTQ+ service members.'' The Current'', May 9, 2005. Douglas herself served as an officer in the Canadian Armed Forces from 1986 to 1989. She was honourably discharged from the military in 1989 under the military's discriminating " LGBT Purge". LGBT purge legal challenge After graduating from Carleton University with a major in law in 1985, Douglas joined the Canadian Forces in 1986. She was soon promoted to the Special Investigations Unit—where she was the first woman to be promoted to the Unit as an officer. Absurdly, it was also the Unit responsible for running the "LGBT Purge" for the armed forces. In 1988, she came under investigation and was transferred to another position before losing her security clearance. Despite having an exemplary service record and repeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |