|
Gauthildr Algautsdóttir
Gauthildr Algautsdóttir (Swedish: Göthild Algotsdotter) (7th century), according to the '' Heimskringla'', was the daughter of the Geatish king Algaut and the wife of Ingjald Ill, a semi-legendary king of Sweden. She was the mother of Olof Trätälja, the last Yngling ruler of Sweden and Åsa who married Gudröd, a legendary king of Skåne. See also * Geatland *Geats The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of th ... Sources * Ynglinga saga {{DEFAULTSORT:Gauthildr Algautsdottir 7th-century women Geats Legendary Norsemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derived from the first two words of one of the manuscripts (''kringla heimsins'', "the circle of the world"). ''Heimskringla'' is a collection of sagas about Swedish and Norwegian kings, beginning with the saga of the legendary Swedish dynasty of the Ynglings, followed by accounts of historical Norwegian rulers from Harald Fairhair of the 9th century up to the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla in 1177. The exact sources of the Snorri's work are disputed, but they include earlier kings' sagas, such as Morkinskinna, Fagrskinna and the 12th-century Norwegian synoptic histories and oral traditions, notably many skaldic poems. He explicitly names the now lost work '' Hryggjarstykki'' as his source for the events of the mid-12th century. Alth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geatish King
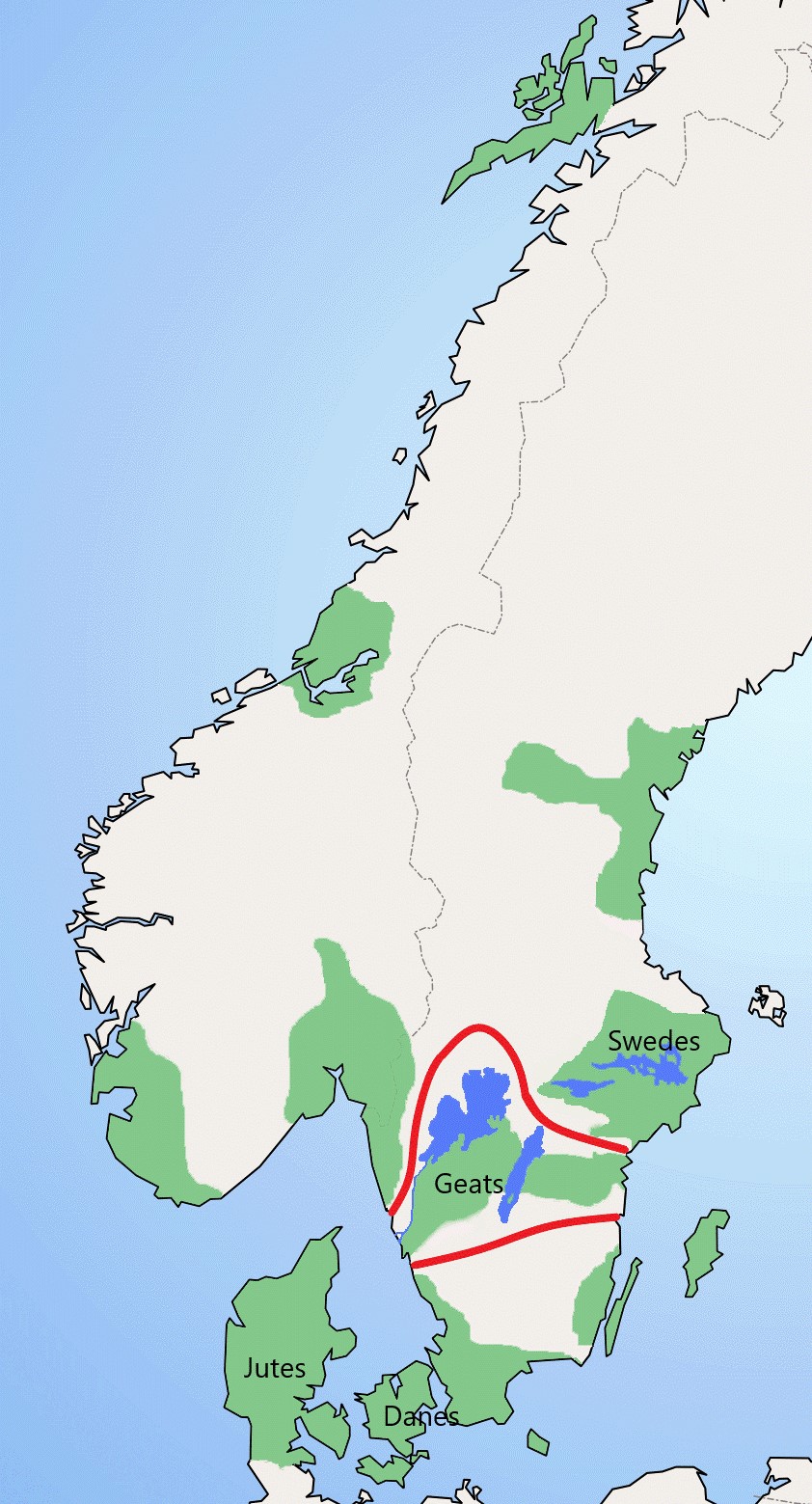
Geatish kings ( la, Rex Getarum/Gothorum; sv, Götakungar), ruling over the provinces of Götaland (Gautland/Geatland), appear in several sources for early Swedish history. Today, most of them are not considered historical. This list follows the generally accepted identification between the names Götar ( modern Swedish), Gautar (Old Norse) and Geatas ( Old English), which is based both on tradition, literary sources and on etymology. However, unlike some translations it does not identify this tribe with the Goths. Both Old Norse and Old English records clearly separate the Geats from the Goths, while still depicting them as closely related to each other. From the Middle Ages until 1974, the king of Sweden claimed the title King of the Geats as "King of Sweden and Geats/Goths" or "Rex Sweorum et Gothorum". Danish monarchs used the similar title " King of the Goths" from 1362 until 1972. Legendary kings Some names appear in Norse mythology and in Germanic legend and in at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algaut
Algaut (or ''Algöt'') was a Geatish king who ruled West Götaland according to the '' Heimskringla''. Snorri Sturluson Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of the ... relates that he was burnt to death by his son-in-law, the Swedish king Ingjald Ill-ruler. Kings of the Geats People whose existence is disputed {{Sweden-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingjald
Ingjald illråde or Ingjaldr hinn illráði (''Ingold Illruler'' or ''Illready'') was a semi-legendary Swedish king of the House of Ynglings, son and successor of King Anund, and the father and predecessor of King Olof Trätälja. As with many of the 5th-7th century Yngling Kings of Sweden, his historicity is contested. Ingjald is mentioned in medieval historiographical sources including '' Ynglinga saga'', '' Historia Norvegiæ'', '' Hervarar saga'', ''Upplendinga Konungum'', '' Þorsteins saga Víkingssonar'' and '' Íslendingabók''. The setting of ''Þorsteins saga Víkingssonar'' is roughly the 7th century. Johannes Magnus in his 16th-century list of kings places Ingjald (''Ingevallus, Ingellus'') in AD 883. ''Ynglinga saga'' Snorri Sturluson gave an extensive account on the life of Ingjald in the '' Ynglinga saga'' which is part of the ''Heimskringla''. Youth The ''Ynglinga saga'', a part of the ''Heimskringla'' relates that the viceroy of Fjädrundaland wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-legendary Kings Of Sweden
The legendary kings of Sweden () according to legends were rulers of Sweden and the Swedes who preceded Eric the Victorious and Olof Skötkonung, the earliest reliably attested Swedish kings. Though the stories of some of the kings may be embellished tales of local rulers or chiefs that actually existed. For example, Hygelac (500 A.D.) is believed to have historical basis due to his name being attested in Frankish, English, Danish and Icelandic sources. But the historicity of most legendary kings remains impossible to verify due to a lack of sources.Dick, Harrison 2011 http://blog.svd.se/historia/2011/10/13/varfor-jag-inte-tror-pa-sagokungar/ The modern Swedish monarchy considers Eric the Victorious to have been the first King of Sweden. In medieval Swedish lists of kings, the figure generally represented as the first king of Sweden is Olof Skötkonung, the first Christian king of Sweden and the first Swedish king to mint coins. The earlier kings are for the most part only att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olof Trätälja
Olaf Tree Feller ( Old Norse: ''Óláfr trételgja'', Swedish: ''Olof Trätälja'', Norwegian: ''Olav Tretelgja'', all meaning ''Olaf Woodwhittler'') was the son of the Swedish king Ingjald illråde, ruler of the House of Yngling in the 7th century according to '' Ynglingatal'', a Skaldic poem detailing the kings of that house. Heimskringla His mother was Gauthild, a princess of West Götaland, whose maternal grandfather was Olof the Sharp-sighted, the king of Nerike. His mother sent him to his foster-father Bove in West Götaland, where he grew up with his foster-brother Saxe who was surnamed Flette. When Olof heard of his father's death, he assembled the men who were willing to follow him and went to his kinsmen in Nerike, because after his father's atrocities, the Swedes had grown hostile towards the Ynglings. When the Swedes learnt that Olof and his kin had sought refuge in Nerike, they were attacked and had to head west through deep and mountainous forests (Kilsberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yngling
The Ynglings were a dynasty of kings, first in Sweden and later in Norway, primarily attested through the poem ''Ynglingatal''. The dynasty also appears as Scylfings (Old Norse ''Skilfingar'') in ''Beowulf''. When ''Beowulf'' and ''Ynglingatal'' were composed sometime in the eighth to tenth centuries, the respective scop and skald (poet) expected his audience to have a great deal of background information about these kings, which is shown in the allusiveness of the references. According to sources such as ''Ynglingatal'' and ''Íslendingabók'', the Fairhair dynasty in Oppland, Norway was in fact a branch of the Ynglings. Saxo Grammaticus held that Eric the Victorious, whom modern regnal lists usually begin with, and his descendents were also Ynglings, but this does not tally with Icelandic sources. The dynasty claimed descent from the gods Freyr and Njörðr, and other kings were likely mythical as well, whereas others may have been real: especially Egil, Ottar, Ale and Adils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times, . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skåne
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skåne County, created in 1997. Like the other former provinces of Sweden, Scania still features in colloquial speech and in cultural references, and can therefore not be regarded as an archaic concept. Within Scania there are 33 municipalities that are autonomous within the Skåne Regional Council. Scania's largest city, Malmö, is the third-largest city in Sweden, as well as the fifth-largest in Scandinavia. To the north, Scania borders the former provinces of Halland and Småland, to the northeast Blekinge, to the east and south the Baltic Sea, and to the west Öresund. Since 2000, a road and railway bridge, the Öresund Bridge, bridges the Sound and connects Scania with Denmark. Scania forms part of the transnational Øresund Region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
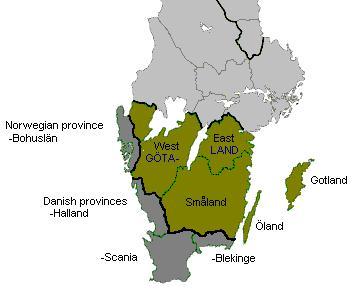
Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Geatland'', '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border. Götaland once consisted of petty kingdoms, and their inhabitants were called ''Gautar'' in Old Norse. However, the term mainly referred to the population of modern Västergötland. It is agreed that these were the same as the ''Geats'', the people of the hero Beowulf in England's national epic, ''Beowulf''. The modern state of Sweden started forming when some provinces of Götaland gradually became more and more politically intertwined with those of Svealand. This process can be traced back to at least the 11th century, and would continue for several hundred years. Other parts of modern Götaland were at that time either Danish or Norwegian. The province of Sm� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geats
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and '' Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |