|
Gastornithiformes
Gastornithiformes were an extinct order of giant flightless fowl with fossils found in North America, Eurasia, and possibly Australia. Members of Gastornithidae were long considered to be a part of the order Gruiformes. However, the traditional concept of Gruiformes has since been shown to be an unnatural grouping. Beginning in the late 1980s and the first phylogenetic analysis of gastornithid relationships, consensus began to grow that they were close relatives of the lineage that includes waterfowl and screamers, the Anseriformes. Recognizing the apparent close relationship between gastornis and waterfowl, some researchers even classify them within the anseriform group itself. Others restrict the name Anseriformes only to the crown group formed by all modern species, and label the larger group including extinct relatives of anseriformes in the clade Anserimorphae (which this article and related pages have adopted). While the order is generally considered to be monotypic, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastornithiformes
Gastornithiformes were an extinct order of giant flightless fowl with fossils found in North America, Eurasia, and possibly Australia. Members of Gastornithidae were long considered to be a part of the order Gruiformes. However, the traditional concept of Gruiformes has since been shown to be an unnatural grouping. Beginning in the late 1980s and the first phylogenetic analysis of gastornithid relationships, consensus began to grow that they were close relatives of the lineage that includes waterfowl and screamers, the Anseriformes. Recognizing the apparent close relationship between gastornis and waterfowl, some researchers even classify them within the anseriform group itself. Others restrict the name Anseriformes only to the crown group formed by all modern species, and label the larger group including extinct relatives of anseriformes in the clade Anserimorphae (which this article and related pages have adopted). While the order is generally considered to be monotypic, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anserimorphae
The Odontoanserae is a proposed clade that includes the family Pelagornithidae (pseudo-toothed birds) and the clade Anserimorphae (the order Anseriformes and their stem-relatives). The placement of the pseudo-toothed birds in the evolutionary tree of birds has been problematic, with some supporting the placement of them near the orders Procellariformes and Pelecaniformes based on features in the sternum. In 2005 a cladistic analysis had found support in placing pseudo-toothed birds as the sister group to waterfowl. Evidence for this comes from shared characteristics in the skull such as lack of a crest on the underside of the palatine bone and two condyles on the mandibular process of the quadrate bone, with the middle condyle beakwards of the side condyle. In addition to that, both groups have similar features in their pelvic and pectoral regions. Furthermore, a 2013 study on the growth pattern and structure of the pseudoteeth in ''Pelagornis mauretanicus'' shows more support of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
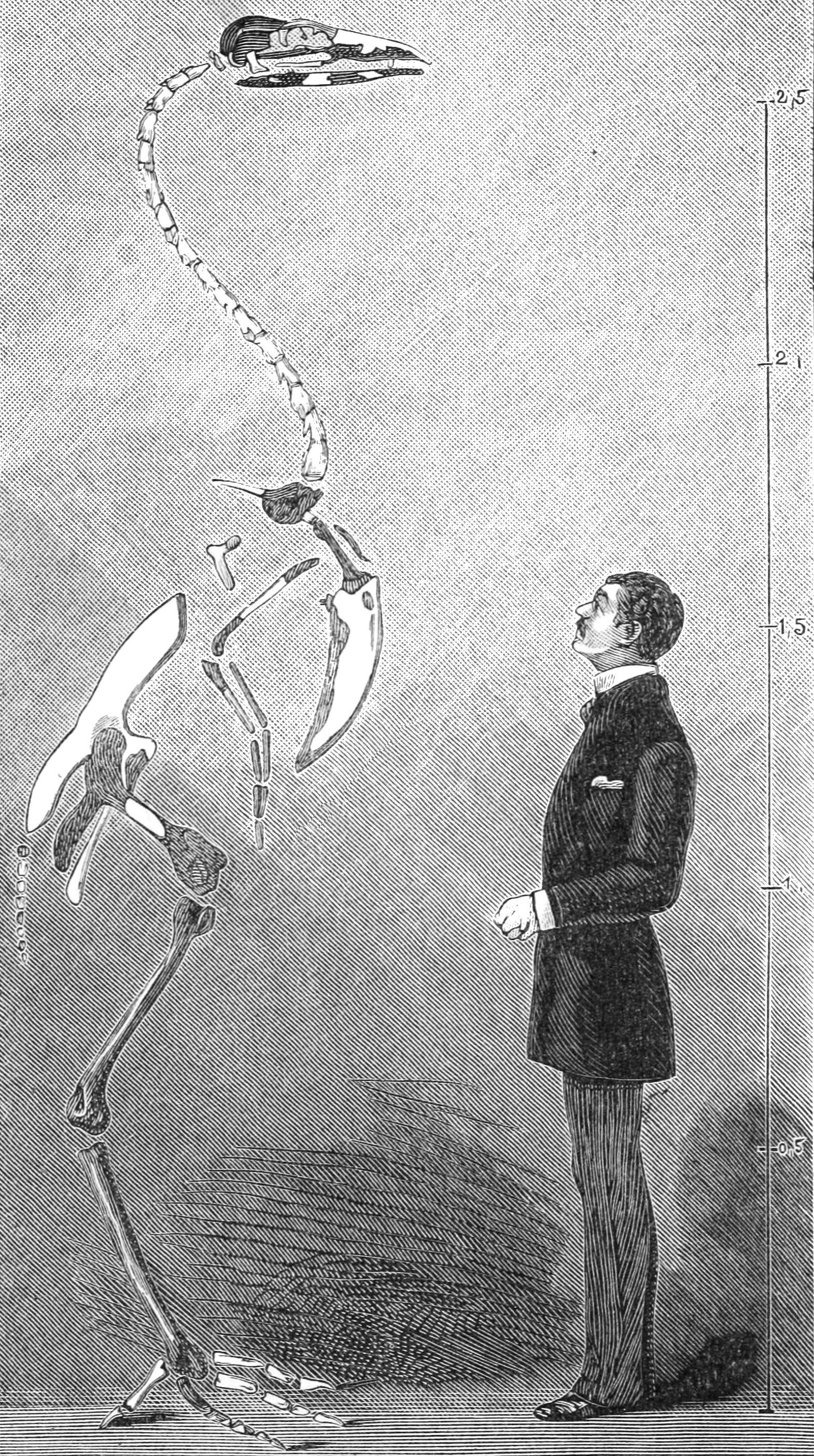
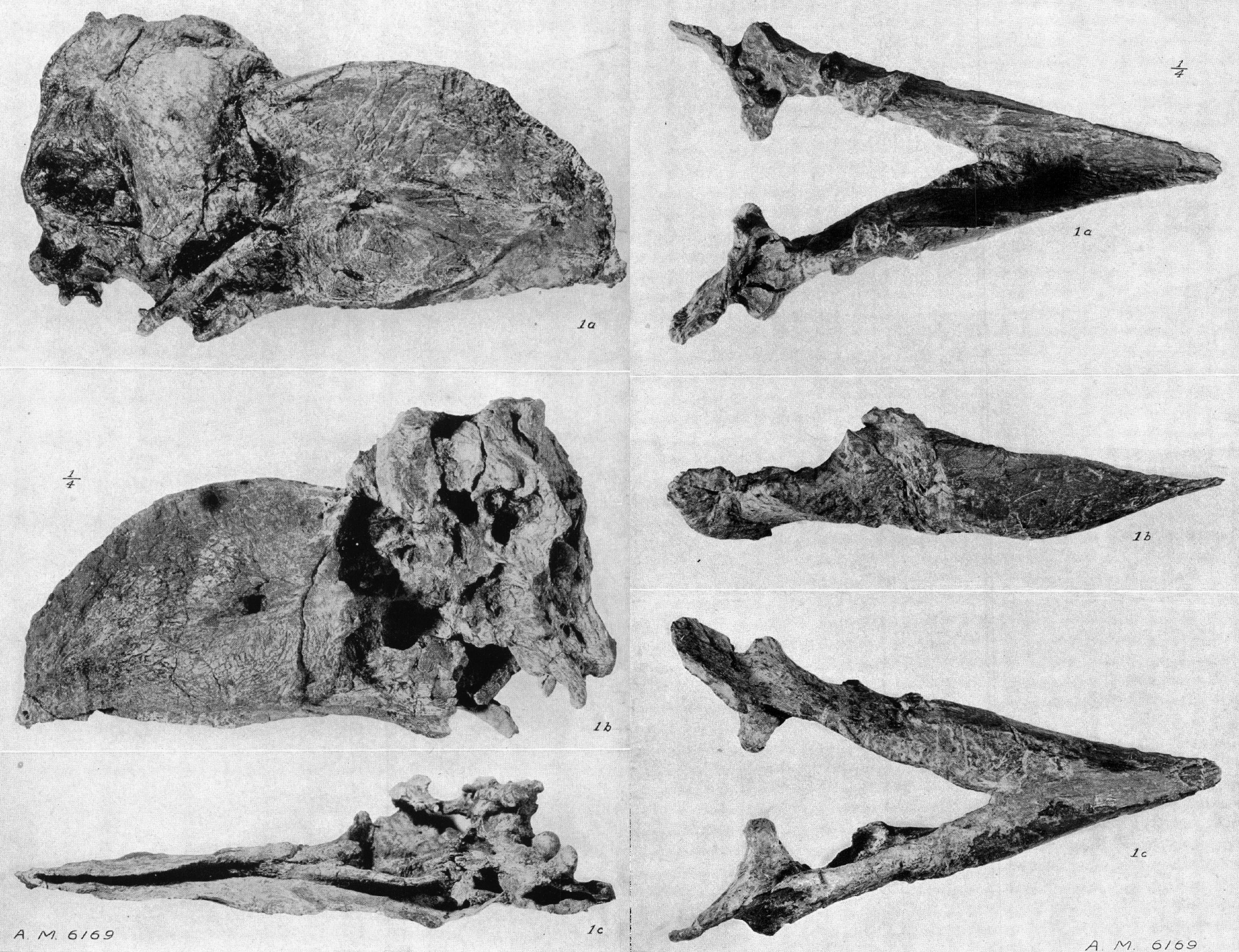
Gastornis
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large flightless birds that lived during the mid Paleocene to mid Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America, with the remains from North America originally assigned to the genus ''Diatryma''. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds, and have traditionally been considered to be predators of small mammals. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws in known ''Gastornis'' footprints and studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones have caused scientists to reinterpret these birds as herbivores that probably fed on tough plant material and seeds. ''Gastornis'' is generally agreed to be related to Galloanserae, the group containing waterfowl and gamebirds. History ''Gastornis'' was first described in 1855 from a fragmentary skeleton. It was named after Gaston Planté, described as a "studious young man full of zeal", who had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastornithidae
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large flightless birds that lived during the mid Paleocene to mid Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America, with the remains from North America originally assigned to the genus ''Diatryma''. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds, and have traditionally been considered to be predators of small mammals. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws in known ''Gastornis'' footprints and studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones have caused scientists to reinterpret these birds as herbivores that probably fed on tough plant material and seeds. ''Gastornis'' is generally agreed to be related to Galloanserae, the group containing waterfowl and gamebirds. History ''Gastornis'' was first described in 1855 from a fragmentary skeleton. It was named after Gaston Planté, described as a "studious young man full of zeal", who had disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
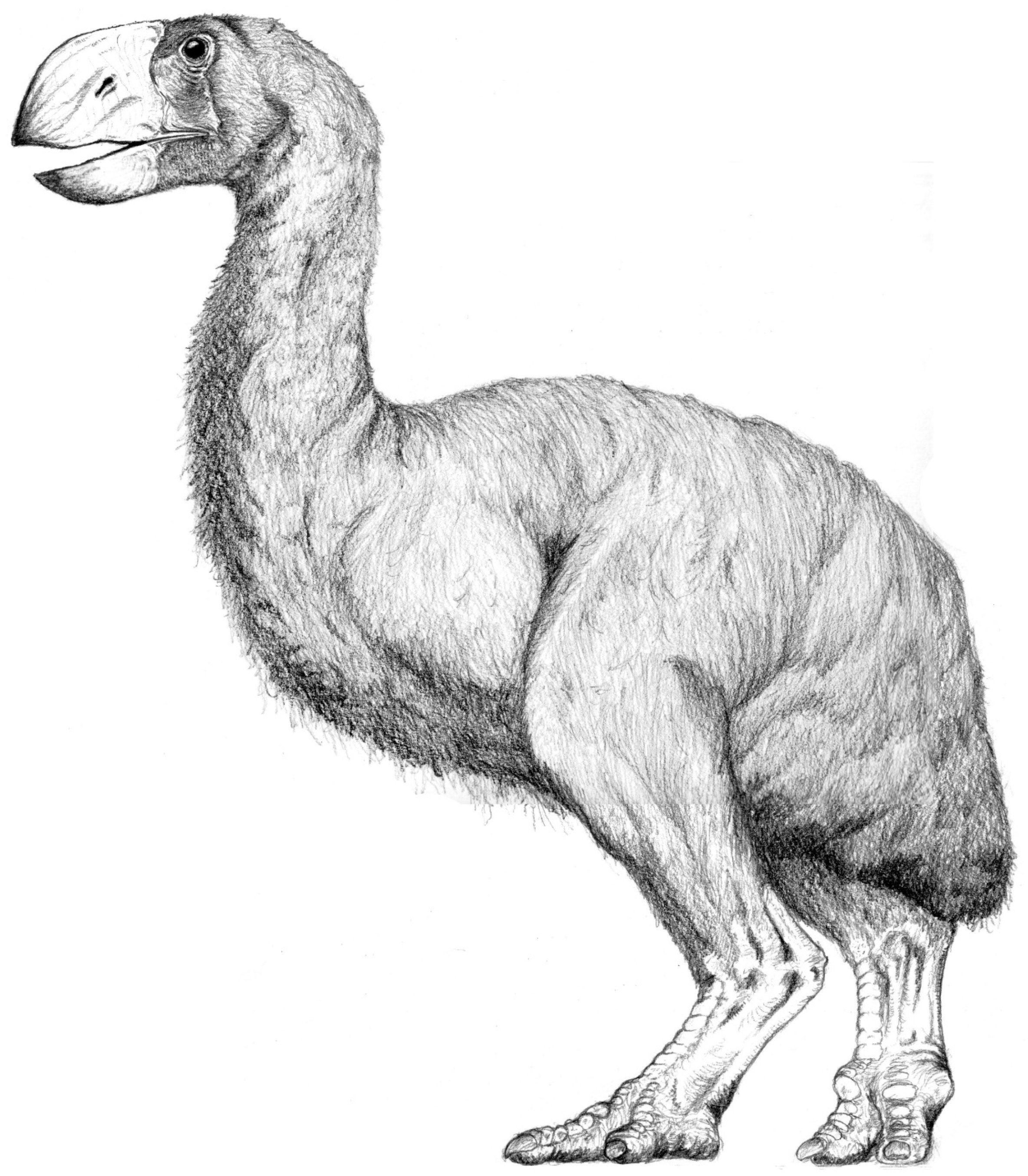
Gastornis Giganteus Restoration
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large flightless birds that lived during the mid Paleocene to mid Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America, with the remains from North America originally assigned to the genus ''Diatryma''. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds, and have traditionally been considered to be predators of small mammals. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws in known ''Gastornis'' footprints and studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones have caused scientists to reinterpret these birds as herbivores that probably fed on tough plant material and seeds. ''Gastornis'' is generally agreed to be related to Galloanserae, the group containing waterfowl and gamebirds. History ''Gastornis'' was first described in 1855 from a fragmentary skeleton. It was named after Gaston Planté, described as a "studious young man full of zeal", who had discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastornis Giganteus
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large flightless birds that lived during the mid Paleocene to mid Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America, with the remains from North America originally assigned to the genus ''Diatryma''. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds, and have traditionally been considered to be predators of small mammals. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws in known ''Gastornis'' footprints and studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones have caused scientists to reinterpret these birds as herbivores that probably fed on tough plant material and seeds. ''Gastornis'' is generally agreed to be related to Galloanserae, the group containing waterfowl and gamebirds. History ''Gastornis'' was first described in 1855 from a fragmentary skeleton. It was named after Gaston Planté, described as a "studious young man full of zeal", who had discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
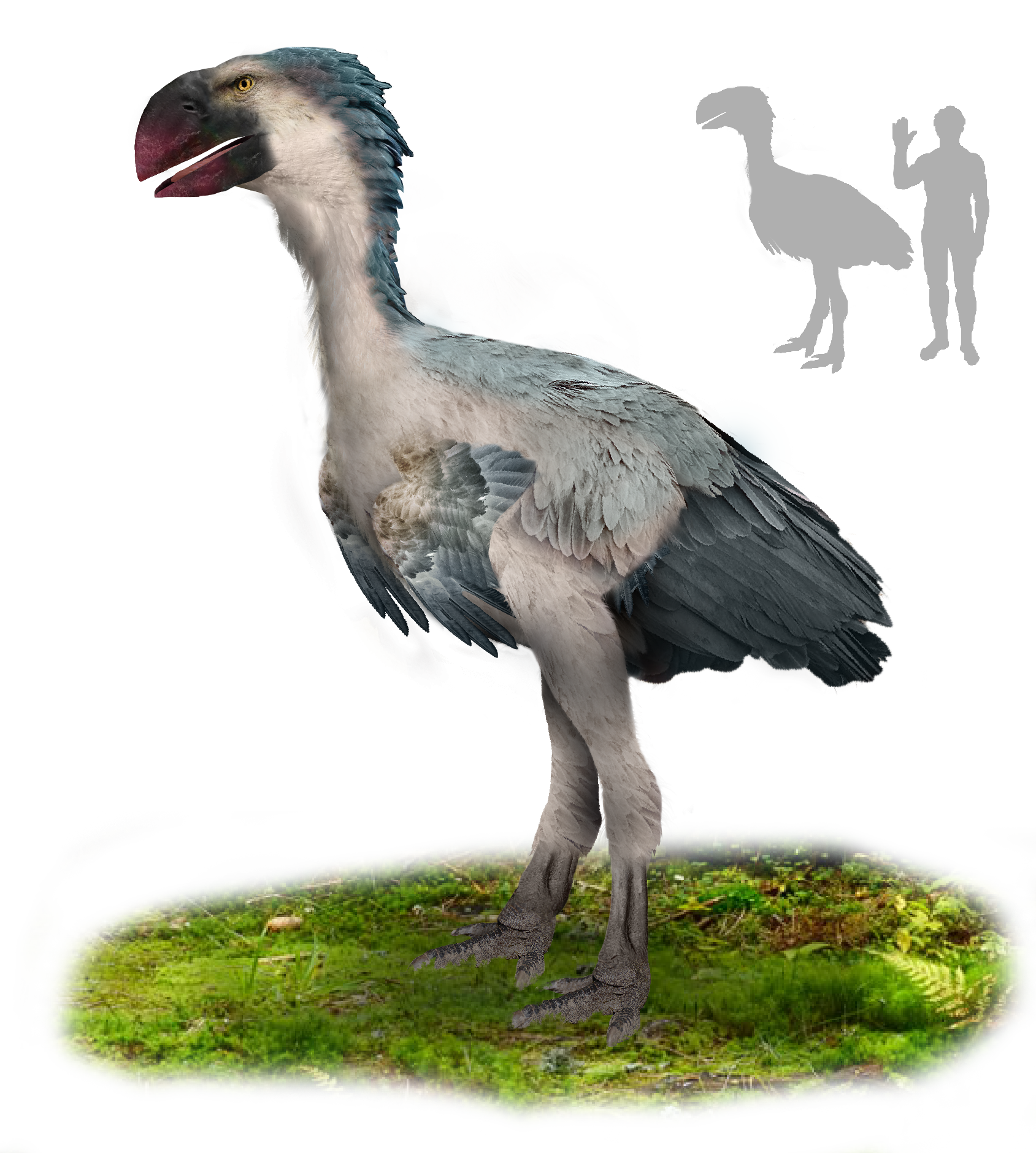
Brontornis
''Brontornis'' is an extinct genus of giant bird that inhabited Argentina during the Early to Middle Miocene. Its taxonomic position is highly controversial, with authors alternatively considering it to be a cariamiform, typically a phorusrhacid (terror bird) or an anserimorph. Taxonomy The first fossils of ''Brontornis burmeisteri'' were described by paleontologists Francisco Moreno and Alcides Mercerart in 1891, the fossils being a left femur, tibiotarsus, fibula, and tarsometatarsus all from the same individual found in the Lower-Middle Miocene strata of the Santa Cruz Formation in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina.Brodkorb, P. (1967). ''Catalogue of fossil birds: part 3 (Ralliformes, Ichthyornithiformes, Charadriiformes)''. University of Florida. In the same paper, two distal tibiotarsi from the same area were referred to ''Brontornis'' as well.Moreno, F. P., & Mercerat, A. (1891). ''Catálogo de los pájaros fósiles de la República Argentina conservados en el Museo de La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dromornithidae
Dromornithidae, known as mihirungs and informally as thunder birds or demon ducks, were a clade of large, flightless Australian birds of the Oligocene through Pleistocene Epochs. All are now extinct. They were long classified in Struthioniformes, but are now usually classified as galloanseres. Dromornithids were part of the Australian megafauna. One species, ''Dromornis stirtoni'', was tall. Only a single species, ''Genyornis newtoni'' survived into the Late Pleistocene. They are thought to have been herbivorous. The scientific name Dromornithidae derives from the Greek words , ("swift-running") and , ("bird"). Classification The family was named by Max Fürbringer in 1888, citing W. B. Clarke and Gerard Krefft, Owen's separation from ''" Dromaeus"'' and ''Dinornis'', and a note by von Haast allying ''Dromornis'' with ''Dromaeus''. What the nearest relatives of this group are is a controversial issue. For many years it was thought that dromornithids were related to ratite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegaviidae
Vegaviidae is an extinct family of ornithurines, often regarded as stem- anseriforms, which existed during the Late Cretaceous and possibly the Paleocene. Fossils attributed to the family have been found in Canada, Chile, New Zealand, and Antarctica. Previously the genera '' Neogaeornis'' and '' Polarornis'' were classified as stem-loons based on the similarities in the anatomy of the leg structure.Hope, S. (2002). "The Mesozoic radiation of Neornithes." Pp. 339-388 in Chiappe, L.M. and Witmer, L. (eds.), ''Mesozoic Birds: Above the Heads of Dinosaurs''.Carolina Acosta Hospitaleche, Javier N. Gelfo, New Antarctic findings of Upper Cretaceous and lower Eocene loons (Aves: Gaviiformes), Annales de Paléontologie Volume 101, Issue 4, October–December 2015, Pages 315–324 However, there were some criticism to these assertions as the material are from incomplete specimens from Antarctica lacking several important loon characteristics.Feduccia, A. (1999). ''The Origin and Evolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dromornis BW
''Dromornis'' is a genus of large to enormous prehistoric birds. The species were flightless, possessing greatly reduced wing structures but with large legs, similar to the modern ostrich or emu. They were likely to have been predominantly, if not exclusively, herbivorous browsers. The male of the largest species, ''Dromornis stirtoni'', is a contender for the tallest and heaviest bird, and possibly exhibited aggressive territorial behaviour. They belong to the clade dromornithid, extinct flightless birds known as mihirungs. Taxonomy The genus was erected to separate a new species, ''Dromornis australis'', from the previously described ''Dinornis'' (giant moas), another lineage of ancient large and flightless birds found in New Zealand that was earlier described by Richard Owen in 1843. A femur that was forwarded to England, probably a dromornithid and since lost, suggested an Australian genus, but Owen withheld publication for many years. The type specimen, another femur, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phorusrhacidae
Phorusrhacids, colloquially known as terror birds, are an extinct clade of large carnivorous flightless birds that were one of the largest species of apex predators in South America during the Cenozoic era; their conventionally accepted temporal range covers from 62 to 0.1 million years ( Ma) ago. They ranged in height from . Their closest modern-day relatives are believed to be the seriemas. '' Titanis walleri'', one of the larger species, is known from Texas and Florida in North America. This makes the phorusrhacids the only known large South American predator to migrate north in the Great American Interchange that followed the formation of the Isthmus of Panama land bridge (the main pulse of the interchange began about 2.6 Ma ago; ''Titanis'' at 5 Ma was an early northward migrant). It was once believed that ''T. walleri'' became extinct in North America around the time of the arrival of humans, but subsequent datings of ''Titanis'' fossils provided no evidence for their su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |