|
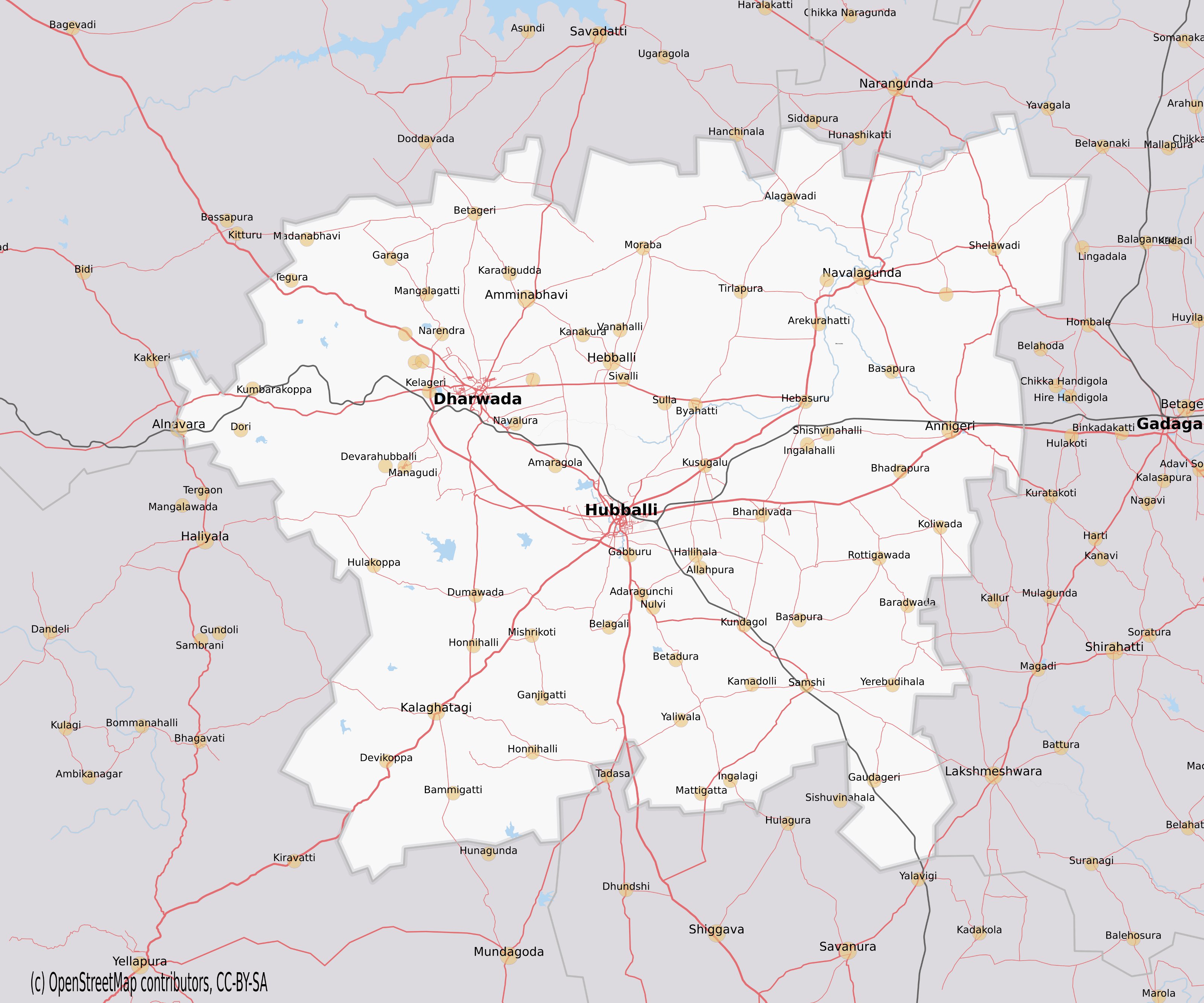
Garag
Garag is a village in the northern part of Karnataka of India. India.Village code= 649900 Garag, Dharwad, Karnataka It is located in the Dharwad taluk of Dharwad district in Karnataka. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India there were 2,152 households in Garag and a total population of 10,528 consisting of 5,388 males and 5,140 females. There were 1,281 children ages 0-6. Geography Garag is well known for its black soil farm lands. The famous stream Tupri Halla flows nearby. The stream flows only during rainy season. An artificial lake Bokyapur lake is also nearby. Water from Bokyapur lake was used for irrigating agricultural fields. Rare water fowls migrate to Bokyapur during winter months. Very close to the lake is an ancient Lord Hanuman temple which has a Halegannada inscription dating back to 10th or 11th century. National Flag of India The hand-woven khadi for the National Flag was initially manufactured at Garag, a small village in Dharwad district in North Karn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kittur
Kittur, historically as Kittoor, is a ''taluka'' in the Belagavi district of the Indian state of Karnataka. It was part of Bailhongal taluka but was declared as an independent taluka on 23October 2012 by the Chief Minister of Karnataka on the inauguration of Kittur Utsav. It is 177th Taluk of Karnataka State. It is a place of historical importance because of the armed rebellion of Kittur Chennamma (1778–1829), Rani of the State of Kittur against the British East India Company, during which a British Commissioner, St John Thackeray was killed. History On the outskirts of the town lie the ruins of the palace within a fort. The palace was the residence of the Rani Chennamma. In the 18th century, Kittur was ruled by the Marathas, until the Third Anglo-Maratha War, when it came under British suzerainty. Kittur was ruled by Mallasaraja in the early 19th century. His only son predeceased him, and subsequently, he was succeeded by his wife, Queen Chennamma. In connection with a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddharudha Swami
Siddharudha Swami was an Indian Hindu Guru: and Philosopher. Biography Sadguru Siddharudha Maharaj lived in the style of an ascetic throughout his life. He condemned practice of casteism and conceived divinity in everything that exists, as well as disagreeing with the common notion that Brahmins were the only ones entitled to liberation, firmly believing that everyone is equally entitled. Considered to be an incarnation of Shiva, one of the Trinity deities of Hinduism, Siddharudha renounced his home and his family ties at the very young age of 6 years, and set himself the goal of finding his Satguru or spiritual master. Siddharudha later surrendered himself, as a student, to the realized soul Shri Gajadandaswami, and served at his Ashram. According to the book ''Siddharoodh Charitra'' by Shivadas, Siddharudha was blessed by his guru and was asked to undertake a pilgrimage with the purpose of helping those in need, dispelling ignorance, and revealing the right path to spiritu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shishunala Sharif
Muhammad Sharif was an Indian social reformer, philosopher and poet. Birth and early life Santa Shishunala Sharifa was born on 7 March 1819 in Shishuvinahala, a village in Shigganvi (now Shiggaon) taluk (in Haveri district), Karnataka. He was the son of an Imam Saheb, who was a disciple of Hajaresha Qadri, whose dream was to unite Hinduism and Islam. Hajaresha Qadri used to give “Linga Deeksha”, or initiation by tying a linga around the neck of a disciple, as per the Lingayat tradition. His father used to teach him Ramayana, Mahabharata, and even the teachings of Allama Prabhu. Legend has it that Shishunala Sharifa was conceived with the blessings of Basavanna. Even when Sharifa was a boy, He was taught the tenets of both religions. In his birthplace Shishuvinahala, even today, both Hindus and Muslims revere him as a saint at the same temple. Meeting Govinda Bhatta Govinda Bhatta, a Brahmin, was famous in the region as an unconventional Master. He cared little for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belur Industrial Area
Belur Industrial Area (Abbreviation : BIA) is an industrial area of the Dharwad city in India and it is one of the biggest industrial areas in Karnataka. lies on the Dharwad-Belgaum Highway. It houses small, medium, and large-scale industries. The industrial area is known for engineering, electrical goods such as: CNC Machine tools, GDC dies & moulds transformer A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...s, motors and generators, textile (silk), hydraulics, machine tool industries and Rubber moulding industries. References {{reflist Industrial parks in India Neighborhoods in Dharwad Dharwad district Karnataka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Karnataka
North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 13 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra. Transport Bus * North Western Karnataka Road Transport Corporation NWKRTC, serves the north western part of Karnataka. * Kalyana Karnataka Road Transport Corporation KKRTC, serves the north eastern part of Karnataka Air Airports in the region are * Belgaum Airport * Hubli Airport * Jindal Vijaynagar Airport * Bidar Airport * Gulbarga Airport Airlines and destinations Belgaum Airport is an airport in Belgaum, a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Built in 1942 by the Royal Air Force (RAF), Belgaum Airport is the oldest airport in North Karnataka. The RAF used the ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halegannada
Old Kannada or Halegannada ( kn, ಹಳೆಗನ್ನಡ, Haḷegannaḍa) is the Kannada language which transformed from ''Purvada halegannada'' or ''Pre-old Kannada'' during the reign of the Kadambas of Banavasi (ancient royal dynasty of Karnataka 345−525 CE). The Modern Kannada language has evolved in four phases over the years. From the Purva Halegannada in the 5th century (as per early epigraphic records), to the Halegannada (Old Kannada) between the 9th and 11th century, the Nadugannada (Middle Kannada) between the 12th and 17th century (as evidenced by Vachana literature), it has evolved to the present day Hosagannada (Modern Kannada) from 18th century to present. Hosagannada (Modern Kannada) is the official language of the state of Karnataka and is one of the 22 official national languages of the Republic of India and is the native language of approximately 65% of Karnataka's population. Etymology Halegannada is derived from two Kannada terms, ''haḷe'' and ''Kanna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Hanuman
Hanuman (; sa, हनुमान, ), also called Anjaneya (), is a Hindu god and a divine ''vanara'' companion of the god Rama. Hanuman is one of the central characters of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is an ardent devotee of Rama and one of the Chiranjivis. Hanuman is regarded to be the son of the wind-god Vayu, who in several stories played a direct role in Hanuman's birth, and considered to be an incarnation or son of Shiva in Shaivism. Hanuman is mentioned in several other texts, such as the epic ''Mahabharata'' and the various Puranas. Evidence of devotional worship to Hanuman is largely absent in these texts, as well as in most archeological sites. According to Philip Lutgendorf, an American Indologist, the theological significance of Hanuman and devotional dedication to him emerged about 1,000 years after the composition of the ''Ramayana'', in the 2nd millennium CE, after the arrival of Islamic rule in the Indian subcontinent.Paula Richman (2010), ''Review: Lutge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Census Of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India. The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was 'Our Census, Our future'. Spread across 28 states and 8 union territories, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharwad District
Dharwad is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India.The administrative headquarters of the district is the city of Dharwad, also known as Dharwar. Dharwad is located 425 km northwest of Bangalore and 421 km southeast of Pune, on the main highway between Chennai and Pune, the National Highway 4 (NH4). Before 1997 the district had an area of 13738 km2. In 1997, the new districts of Gadag and Haveri were carved out of Dharwad's former territory, and a portion of Dharwad district was combined with lands formerly part of three other districts to create the new district of Davanagere. History Historical studies show that people from early Paleolithic age inhabited Dharwad district. The district was ruled by various dynasties from the 5th century onwards, Important among them are Badami and Kalyan Chalukyas, Rastrakutas, Vijayanagar, Adilshahi, Mysore kingdom and Peshawas of Pune. Due to the rule of Peshwas, influence of Marathi is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taluk
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier terms, such as '' pargana'' (''pergunnah'') and ''thana''. In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, a newer unit called mandal (circle) has come to replace the system of tehsils. It is generally smaller than a tehsil, and is meant for facilitating local self-government in the panchayat system. In West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, community development blocks are the empowered grassroots administrative unit, replacing tehsils. As an entity of local government, the tehsil office (panchayat samiti) exercises certain fiscal and administrative power over the villages and municipalities within its jurisdiction. It is the ultimate execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |