|
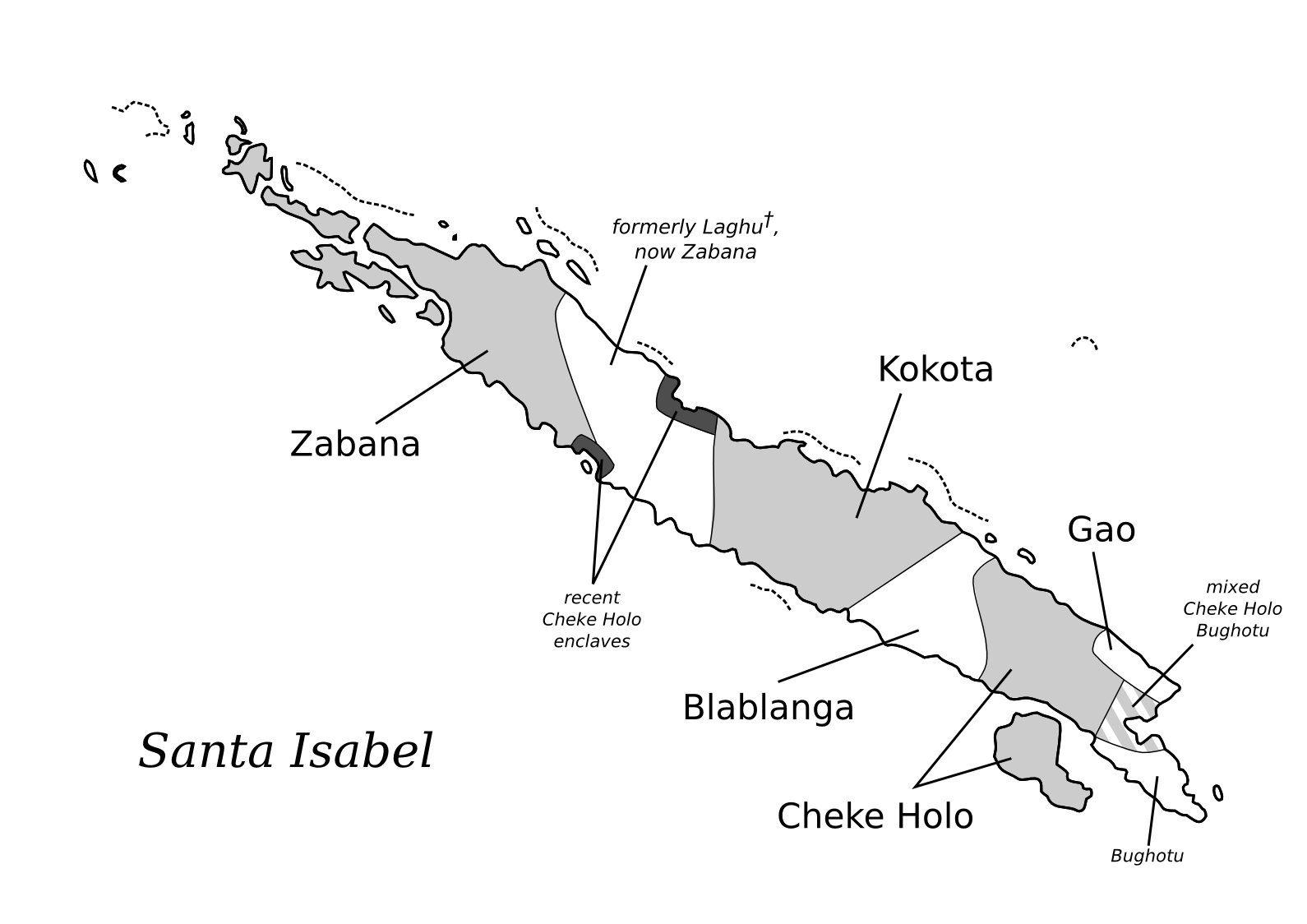
Gao Language
Gao (also called Nggao) is an endangered Oceanic language spoken in the Solomon Islands. Its speakers live on Santa Isabel Island. References External links * Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to ... open accescollection of recordingsin Gao. * Paradisec open accescollection of field noteson Gao vocabulary. Languages of the Solomon Islands Endangered Austronesian languages Ysabel languages Vulnerable languages {{Solomons-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands. The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BCE, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them. Though not named by Mendaña, it is believed that the islands were called ''"the Solomons"'' by those who later receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Isabel Island
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province. Location and geographic data Choiseul lies to the north-west, Malaita to the south-east. The Pacific Ocean lies to the north, and Guadalcanal (Isatabu) to the south. The highest point in Santa Isabel is Mount Sasari, . The Marutho river runs down Mount Sasari to the ocean at Hofi. Almost all the rivers or streams run from that centre point except for those at the other tip of the island on the Katova side. The administrative centre is Buala. The nearest airport is Fera Airport on neighbouring Fera Island. History The first European landing in the Solomon Islands archipelago was made at Santa Isabel Island, by the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña on 7 February 1568. It was charted as ''Santa Isabel de la Estrella'' (St. Elizabeth of the Star of Bethlehem in Spanish). A set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Solomonic Languages
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ysabel Languages
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Of The World's Languages In Danger
The UNESCO ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' is an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' as a title in print after a brief period of overlap before being transferred to an online only publication. History In 1992 the International Congress of Linguists (CIPL) meeting in Canada discussed the topic of endangered languages, as a result of which it formed the Endangered Languages Committee. It held an international meeting also in 1992 in Paris to place the topic before the world and initiate action. The meeting was considered important enough to come under the authority of UNESCO. At the instigation of Stephen Wurm the committee resolved to create a research center, the International Clearing House for Endangered Languages (ICHEL) and to publish the UNESCO ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' based on the data it collected, the title being derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradisec
The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to-reel field tapes, have a mass data store and use international standards for metadata description. PARADISEC is part of the worldwide community of language archives (Delaman and the Open Language Archives Community). PARADISEC's main motivation is to ensure that unique recordings of small languages are themselves preserved for the future, and that researchers consider the future accessibility to their materials for other researchers, community members, or anyone who has an interest in such materials. Vanishing voices As the number of small languages in the world is reduced by many factors (urbanisation, colonial policies, the speakers' desire to learn languages which give access to resources), the tapes which may be their only record beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Solomon Islands
Between 60 and 70 languages are spoken in the Solomon Islands Archipelago which covers a broader area than the nation state of Solomon Islands, and includes the island of Bougainville, which is an autonomous province of Papua New Guinea (PNG). The lingua franca of the archipelago is Pidgin, and the official language in both countries is English. Language families Most of the languages in the Solomon Islands are Austronesian languages. The Central Solomon languages such as Lavukaleve constitute an independent family. Two other language families are represented on Bougainville, which is geographically part of the Solomon Islands, if not within the national boundaries. The status of the Reefs – Santa Cruz languages were once thought to be non-Austronesian, but further research found them to be divergent Austronesian languages. The neighbouring languages of Vanikoro are also heavily relexified Austronesian languages. An indigenous sign language, Rennellese Sign Language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Austronesian Languages
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and invasive species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) IUCN Red List, Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have Environmental law, laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create Protected area, protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |