|
Gallus (biology)
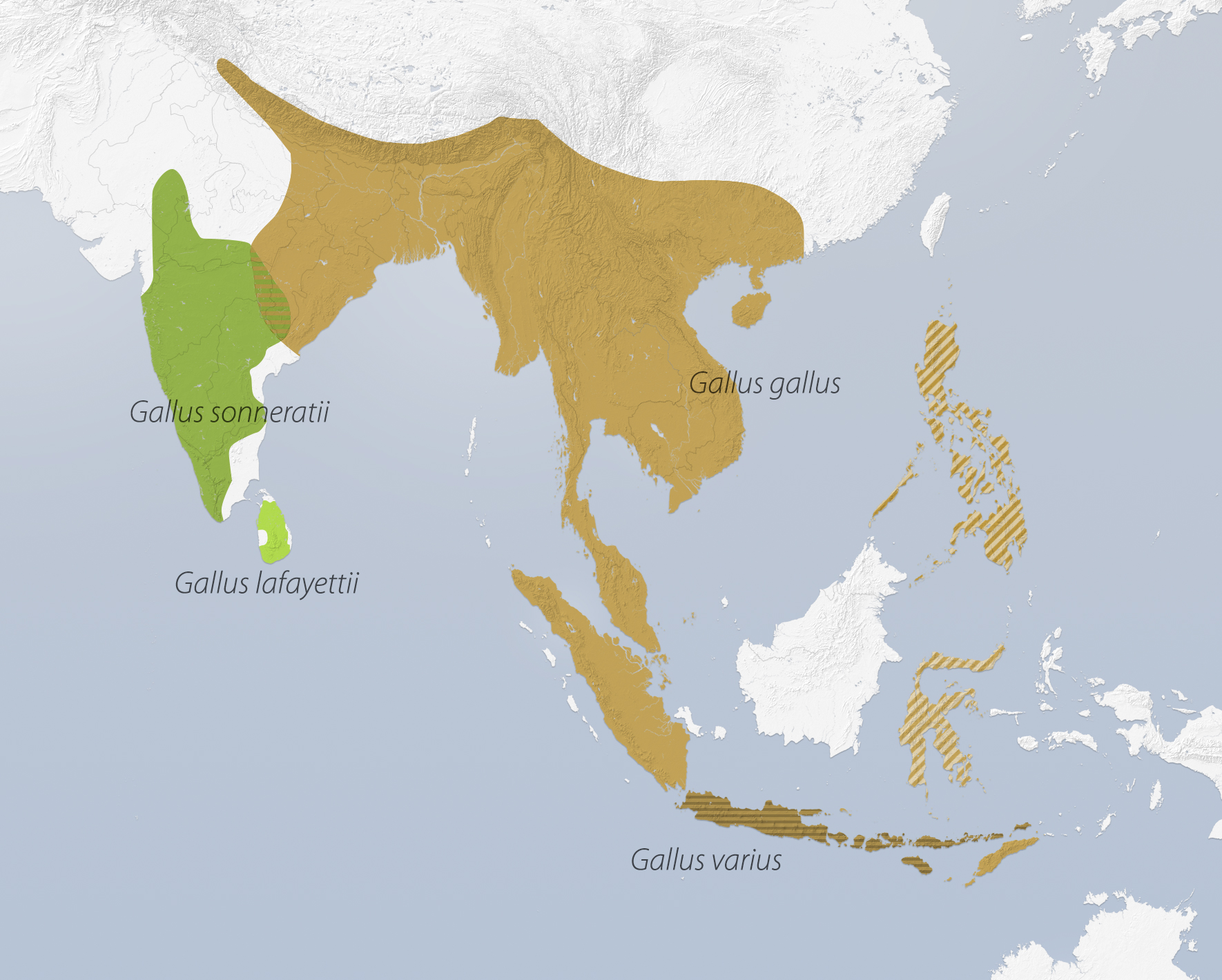
Junglefowl are the only four living species of bird from the genus ''Gallus'' in the bird order Galliformes, and occur in parts of South and Southeast Asia. They diverged from their common ancestor about 4–6 million years ago. Although originating in Asia, remains of junglefowl bones have also been found in regions of Chile, which date back to 1321–1407 CE, providing evidence of possible Polynesian migration through the Pacific Ocean. These are large birds, with colourful plumage in males, but are nevertheless difficult to see in the dense vegetation they inhabit. As with many birds in the pheasant family, the male takes no part in the incubation of the egg or rearing of the precocial young. These duties are performed by the drab and well-camouflaged female. Females and males do not form pair bonds; instead, the species has a polygynandrous mating system in which each female will usually mate with several males. Aggressive social hierarchies exist among both females a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Junglefowl
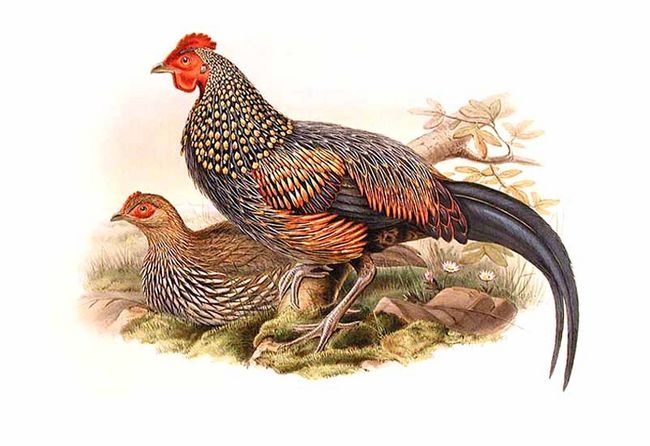
The gray junglefowl (''Gallus sonneratii''), also known as Sonnerat's junglefowl, is one of the wild ancestors of the Chicken, domestic chicken together with the red junglefowl and other junglefowls. The species epithet commemorates the French explorer Pierre Sonnerat. Local names include ''Komri'' in Rajasthan, ''Geera kur'' or ''Parda komri'' in Gondi language, Gondi, ''Jangli Murghi'' in Hindi, ''Raan kombdi'' in Marathi language, Marathi, ''Kattu Kozhi'' in Tamil language, Tamil and Malayalam, ''Kaadu koli'' in Kannada and ''Tella adavi kodi'' in Telugu language, Telugu. Description The male has a black cape with ochre spots and the body plumage on a grey ground colour is finely patterned. The elongated neck feathers are dark and end in a small, hard, yellowish plate; this peculiar structure making them popular for making high-grade Artificial fly, artificial flies. The male has red wattles and combs but not as strongly developed as in the red junglefowl. Legs of males a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Junglefowl
The gray junglefowl (''Gallus sonneratii''), also known as Sonnerat's junglefowl, is one of the wild ancestors of the Chicken, domestic chicken together with the red junglefowl and other junglefowls. The species epithet commemorates the French explorer Pierre Sonnerat. Local names include ''Komri'' in Rajasthan, ''Geera kur'' or ''Parda komri'' in Gondi language, Gondi, ''Jangli Murghi'' in Hindi, ''Raan kombdi'' in Marathi language, Marathi, ''Kattu Kozhi'' in Tamil language, Tamil and Malayalam, ''Kaadu koli'' in Kannada and ''Tella adavi kodi'' in Telugu language, Telugu. Description The male has a black cape with ochre spots and the body plumage on a grey ground colour is finely patterned. The elongated neck feathers are dark and end in a small, hard, yellowish plate; this peculiar structure making them popular for making high-grade Artificial fly, artificial flies. The male has red wattles and combs but not as strongly developed as in the red junglefowl. Legs of males a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Junglefowl
The green junglefowl (''Gallus varius''), also known as Javan junglefowl, forktail or green Javanese junglefowl, is the most distantly related and the first to diverge at least 4 million years ago among the four species of the junglefowl. Hybridization with domestic chicken has also been reported. Green junglefowl is a medium-sized (up to 75 cm long) bird in the pheasant Family (biology), family Phasianidae. Description The colouration of the green junglefowl is sexually dimorphic. The male's plumage is dark and blackish at a distance. A closer view reveals an iridescent mantle of gleaming scales reminiscent in colour and pattern to those seen in the ocellated turkey and green peafowl. Each scale is vivid blue at its base and moves through various shades of gold and bronzed green. Specialized plumes framing the throat of the male green junglefowl are highly light-reflective and appear violet at the proximal and sky blue at the distal edges. The lesser coverts of the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Junglefowl
The red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus'') is a tropical bird in the family Phasianidae. It ranges across much of Southeast Asia and parts of South Asia. It was formerly known as the Bankiva or Bankiva Fowl. It is the species that gave rise to the chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus''); the grey junglefowl, Sri Lankan junglefowl and green junglefowl have also contributed genetic material to the gene pool of the chicken. Evidence from the molecular level derived from whole-genome sequencing revealed that the chicken was domesticated from red junglefowl about 8,000 years ago, with this domestication event involving multiple maternal origins. Since then, their domestic form has spread around the world where they are kept by humans for their meat, eggs, and companionship. Taxonomy and systematics Numerous subspecies of ''Gallus gallus'' exist, including: * ''G. g. gallus'' – from India, Bangladesh, Southeast Asia * ''G. g. bankiva'' – from Java and Sumatra * ''G. g. jabouill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Zoological Nomenclature
The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is an organization dedicated to "achieving stability and sense in the scientific naming of animals". Founded in 1895, it currently comprises 26 commissioners from 20 countries. Organization The ICZN is governed by the "Constitution of the ICZN", which is usually published together with the ICZN Code. Members are elected by the Section of Zoological Nomenclature, established by the International Union of Biological Sciences (IUBS). The regular term of service of a member of the Commission is six years. Members can be re-elected up to a total of three full six-year terms in a row. After 18 continuous years of elected service, a break of at least three years is prescribed before the member can stand again for election. Activities Since 2014, the work of the Commission is supported by a small secretariat based at the National University of Singapore, in Singapore. Previously, the secretariat was based in London and fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phasianus
The "typical" pheasant genus ''Phasianus'' in the family Phasianidae consists of two species. The genus name is Latin for pheasant. Taxonomy The genus ''Phasianus'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. The genus name is Latin for "pheasant". The word is derived from the Ancient Greek φἀσιἀνος, ''phāsiānos'', meaning "(bird) of the Phasis". The birds were found by the Argonauts on the banks of the River Phasis (now the Rioni) in Colchis on the east coast of the Black Sea (now western Georgia). The type species of the genus is the common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus''). Species The genus contains just two species. The common pheasant (''P. colchicus'') has about 30 recognised subspecies forming five or six distinct groups; one is only found on the island of Taiwan off the southern coast of continental China, and the rest on the Asian mainland, reaching west to the Caucasus. Some subspecies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Pheasant
The common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus'') is a bird in the pheasant family (biology), family (Phasianidae). The genus name comes from Latin ''phasianus'', "pheasant". The species name ''colchicus'' is Latin for "of Colchis" (modern day Georgia (country), Georgia), a country on the Black Sea where pheasants became known to Europeans. Although ''Phasianus'' was previously thought to be closely related to the genus ''Gallus'', the genus of junglefowl and domesticated chickens, recent studies show that they are in different subfamilies, having diverged over 20 million years ago. It is native to Asia and parts of Europe like the northern foothills of the Caucasus and the Balkans. It has been widely introduced elsewhere as a game bird. In parts of its range, namely in places where none of its relatives occur such as in Europe, where it is naturalised, it is simply known as the "pheasant". Ring-necked pheasant is both the name used for the species as a whole in North America and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomenclature, was partially developed by the Bauhin brothers, Gaspard and Johann, Linnaeus was first to use it consistently throughout his book. The first edition was published in 1735. The full title of the 10th edition (1758), which was the most important one, was ' or translated: "System of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera and species, with characters, differences, synonyms, places". The tenth edition of this book (1758) is considered the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In 1766–1768 Linnaeus published the much enhanced 12th edition, the last under his authorship. Another again enhanced work in the same style and titled "'" was published by Johann Friedrich Gmelin between 1788 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-9858%2C_crop.jpg)




.jpg)

.png)
_(2).jpg)
