|
Gallows
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so that it is no longer sitting on the bottom, i.e., "weighing heanchor,” while avoiding striking the ship’s hull. In modern usage it has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term " gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevailed. Forms of hanging Gallows can take several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
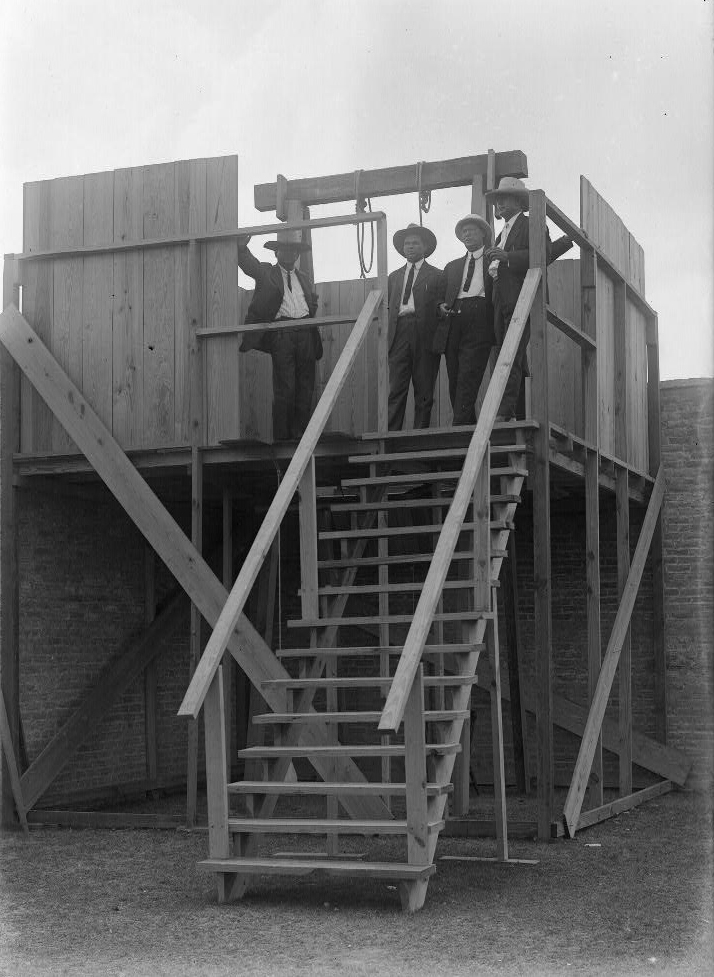
Gallows In Texas, 1916
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so that it is no longer sitting on the bottom, i.e., "weighing heanchor,” while avoiding striking the ship’s hull. In modern usage it has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term "gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevailed. Forms of hanging Gallows can take several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallows
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks of grain or minerals, usually positioned in markets or toll gates. The term was also used for a projecting framework from which a ship's anchor might be raised so that it is no longer sitting on the bottom, i.e., "weighing heanchor,” while avoiding striking the ship’s hull. In modern usage it has come to mean almost exclusively a scaffold or gibbet used for execution by hanging. Etymology The term " gallows" was derived from a Proto-Germanic word '' galgô'' that refers to a "pole", "rod" or "tree branch". With the beginning of Christianization, Ulfilas used the term ''galga'' in his Gothic Testament to refer to the cross of Christ, until the use of the Latin term (crux = cross) prevailed. Forms of hanging Gallows can take several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanging
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging in this sense is "specifically to put to death by suspension by the neck", though it formerly also referred to crucifixion and death by impalement in which the body would remain "hanging". Hanging has been a common method of capital punishment since medieval times, and is the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging was in Homer's ''Odyssey'' (Book XXII). In this specialised meaning of the common word ''hang'', the past and past participle is ''hanged'' instead of ''hung''. Hanging is a common method of suicide in which a person applies a ligature to the neck and brings about unconsciousness and then death by suspension or partial suspension. Methods of judicial hanging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanging From The Miseries And Misfortunes Of War By Jacques Callot
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging in this sense is "specifically to put to death by suspension by the neck", though it formerly also referred to crucifixion and death by impalement in which the body would remain "hanging". Hanging has been a common method of capital punishment since medieval times, and is the primary execution method in numerous countries and regions. The first known account of execution by hanging was in Homer's ''Odyssey'' (Book XXII). In this specialised meaning of the common word ''hang'', the past and past participle is ''hanged'' instead of ''hung''. Hanging is a common method of suicide in which a person applies a ligature to the neck and brings about unconsciousness and then death by suspension or partial suspension. Methods of judicial hanging The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutland County Museum
Rutland County Museum is located in Oakham, Rutland, in the old Riding School of the Rutland Fencible Cavalry which was built in 1794–95. The museum, opened in 1969, houses a collection of objects relating to local rural and agricultural life, social history and archaeology. Temporary exhibitions are shown alongside the permanent displays. Admission to the museum is free. Collection The Museum's original collections were those transferred to it when it was set up by the former Rutland County Council in 1967. These were the rural life collection of E G Bolton from Casterton Secondary Modern School and the mainly archaeological collection from Oakham School. Over the years the Museum has grown and it now has an extensive rural life collection which includes farm tools, tractors, wagons and a wide range of rural tradesmen's tools. In addition it also houses domestic and social history items, along with a large collection of archaeological material from around Rutland. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
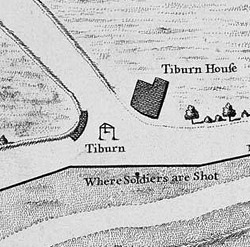
Tyburn Gallows
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street), the junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For this reason, for many centuries, the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment, it having been the principal place for execution of London criminals and convicted traitors, including many religious martyrs. It was also known as 'God's Tribunal', in the 18th century. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream',Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. but Tyburn Brook should not be confused with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arson In Royal Dockyards
Arson in royal dockyards was a criminal offence in the United Kingdom and the British Empire. It was among the last offences that were punishable by execution in the United Kingdom. The crime was created by the Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 (12 Geo. 3 c.24) passed by the Parliament of Great Britain and was designed to protect Royal Dockyards and vessels from arson attacks. It remained one of the few capital offences after reform of the death penalty in 1861, and remained in effect even after the death penalty was permanently abolished for murder in 1969. However, it was then eliminated by the Criminal Damage Act 1971. Passage The Dockyards etc. Protection Act 1772 was passed in order to protect Royal Navy ships, dockyards, and stores from damage. At the time, ships were built of flammable oak wood and tar, and the naval yards were full of these supplies. Punishment for violating the act was a death sentence. The first section created the offence of arson in the royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphyxiation
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that can induce asphyxia, all of which are characterized by the inability of a person to acquire sufficient oxygen through breathing for an extended period of time. Asphyxia can cause coma or death. In 2015, about 9.8 million cases of unintentional suffocation occurred which resulted in 35,600 deaths. The word asphyxia is from Ancient Greek "without" and , "squeeze" (throb of heart). Causes Situations that can cause asphyxia include but are not limited to: airway obstruction, the constriction or obstruction of airways, such as from asthma, laryngospasm, or simple blockage from the presence of foreign materials; from being in environments where oxygen is not readily accessible: such as underwater, in a low oxygen atmosphere, or in a vacuum; e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is to score more goals than the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into a rectangular framed goal defended by the opposing side. Traditionally, the game has been played over two 45 minute halves, for a total match time of 90 minutes. With an estimated 250 million players active in over 200 countries, it is considered the world's most popular sport. The game of association football is played in accordance with the Laws of the Game, a set of rules that has been in effect since 1863 with the International Football Association Board (IFAB) maintaining them since 1886. The game is played with a football that is in circumference. The two teams compete to get the ball into the other team's goal (between the posts and under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John The Painter
James Aitken (28 September 1752 – 10 March 1777), also known as John the Painter, was a mercenary who committed acts of sabotage in Royal Navy naval dockyards during the American Revolutionary War in 1776–77. Early life Aitken was born in Edinburgh in 1752, the son of a whitesmith and the eighth of twelve children. The early death of his father allowed Aitken to enter the charitable school for impoverished children at George Heriot's Hospital, which was founded to care for the "puir, faitherless bairns" ( Scots: poor, fatherless children) of Edinburgh. Upon leaving school at age 14, he tried his hand at a variety of low-paying trades, including painter apprenticeship in 1767, before finding that the world of criminal activity offered him more immediate rewards. He admitted in his testament to being a highwayman, burglar, shoplifter, robber, and (on at least one occasion) a rapist: ... I made the best of my way through Winchester to Basingstoke, intending to return t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
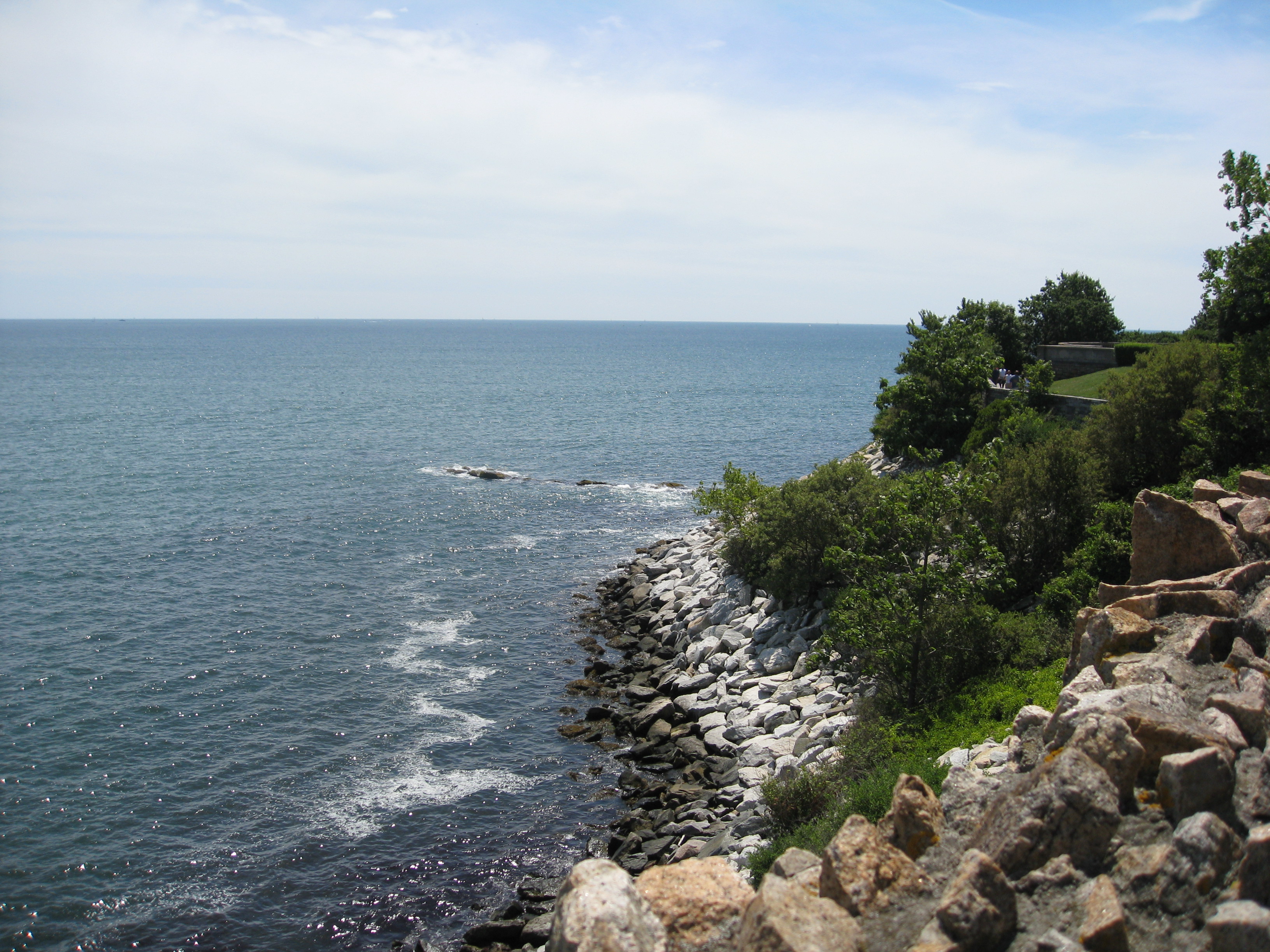
Intertidal Zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species of life, such as seastars, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the ''littoral zone'' or '' seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The well-known area also includes steep rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast mudflats). The area can be a narrow strip, as in Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in the intertidal zone are adapted to an environment of harsh extremes, living in water p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.jpeg)
