|
Galling Lump
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material may appear gouged with balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface. Galling is most commonly found in metal surfaces that are in sliding contact with each other. It is especially common where there is inadequate lubrication between the surfaces. However, certain metals will generally be more prone to galling, due to the atomic structure of their crystals. For example, aluminium is a metal that will gall very easily, whereas annealed (softened) steel is slightly m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Thread Galling
External may refer to: * External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra * Externality, in economics, the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit * Externals, a fictional group of X-Men antagonists See also * *Internal (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushing (bearing)
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe. Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity. Design The design of a plain bearing depends on the type of motion the bearing must provide. The three types of motions possible are: * ''Journal'' (''friction'', ''radial'' or ''rotary'') ''bearing'': This is the most common type of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter. Measuring hardness There are three main types of hardness measurements: ''scratch' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductility
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing. It defines a material's suitability for certain manufacturing operations (such as cold working) and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload.. Some metals that are generally described as ductile include gold and copper. However, not all metals experience ductile failure as some can be characterized with brittle failure like cast iron. Polymers generally can be viewed as ductile materials as they typically allow for plastic deformation. Malleability, a similar mechanical property, is characterized by a material's ability to deform plastically without failure under compressive stress. Historically, materials were considered malleable if they were am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, plasticity, also known as plastic deformation, is the ability of a solid material to undergo permanent Deformation (engineering), deformation, a non-reversible change of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the material itself. In engineering, the transition from Elasticity (physics), elastic behavior to plastic behavior is known as Yield (engineering), yielding. Plastic deformation is observed in most materials, particularly metals, soils, Rock (geology), rocks, concrete, and foams. However, the physical mechanisms that cause plastic deformation can vary widely. At a crystalline scale, plasticity in metals is usually a consequence of dislocations. Such defects are relatively rare in most crystalline materials, but are numerous in some and part of their crystal structure; in such cases, plastic crystallinity can res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be described as the sharing of ''free'' electrons among a structure of positively charged ions ( cations). Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties of metals, such as strength, ductility, thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity, opacity, and luster. Metallic bonding is not the only type of chemical bonding a metal can exhibit, even as a pure substance. For example, elemental gallium consists of covalently-bound pairs of atoms in both liquid and solid-state—these pairs form a crystal structure with metallic bonding between them. Another example of a metal–metal covalent bond is the mercurous ion (). History As chemistry developed into a science, it became clear that metals formed the majority of the periodic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threaded Insert
A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thread on a material too thin to accept it, mold or cast threads into a work piece thereby eliminating a machining operation, or simplify changeover from unified to metric threads or vice versa. Types Thread inserts come in many varieties, depending on the application. Threaded inserts for plastics are used in plastic materials and applied with thermal insertion or ultrasonic welding machines. Manufacturers of ready-to-assemble furniture often ship the parts with threaded inserts and other kinds of knock-down fasteners pre-installed. People who use sheet metal or sandwich panel or honeycomb sandwich-structured composite often install threaded inserts to spread shear, tension, and torque loads over a larger area of the material. Captive n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spalling
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ball bearing). Spalling and spallation both describe the process of surface failure in which spall is shed. The terms ''spall'', ''spalling'', and ''spallation'' have been adopted by particle physicists; in neutron scattering instruments, neutrons are generated by bombarding a uranium (or other) target with a stream of atoms. The neutrons that are ejected from the target are known as "spall". Mechanical spalling Mechanical spalling occurs at high stress contact points, for example, in a ball bearing. Spalling occurs in preference to brinelling where the maximal shear stress occurs not at the surface, but just below, shearing the spall off. One of the simplest forms of mechanical spalling is plate impact, in which two waves of compression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Motor
A pneumatic motor (air motor), or compressed air engine, is a type of motor which does mechanical work by expanding compressed air. Pneumatic motors generally convert the compressed air energy to mechanical work through either linear or rotary motion. Linear motion can come from either a diaphragm or piston actuator, while rotary motion is supplied by either a vane type air motor, piston air motor, air turbine or gear type motor. Pneumatic motors have existed in many forms over the past two centuries, ranging in size from hand-held motors to engines of up to several hundred horsepower. Some types rely on pistons and cylinders; others on slotted rotors with vanes (vane motors) and others use turbines. Many compressed air engines improve their performance by heating the incoming air or the engine itself. Pneumatic motors have found widespread success in the hand-held tool industry, but are also used stationary in a wide range of industrial applications. Continual attempts are bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
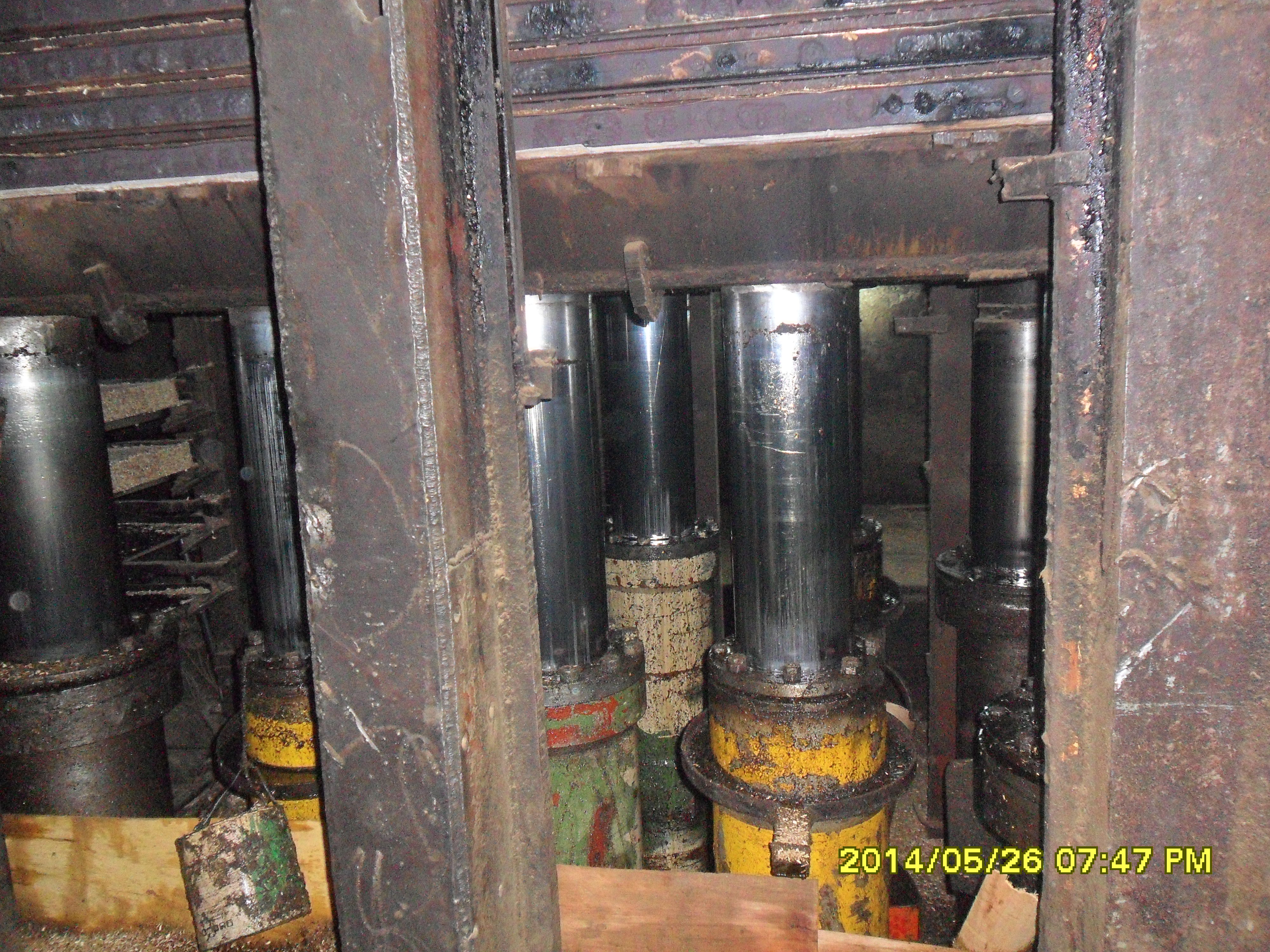
Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment (engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. Operation Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is incompressible. Typically oil is used as hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth. The barrel is closed on one end by the cylinder bottom (also called the cap) and the other end by the cylinder head (also called the gland) where the piston rod comes out of the cylinder. The piston has sliding rings and seals. The piston divides the inside of the cylinder into two chambers, the bottom chamber (cap end) and the piston rod side chamber (rod end/head-end). Flanges, trunnions, clevises, and lugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |