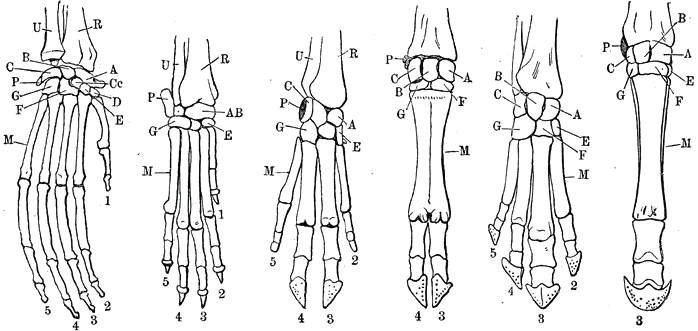|
Gait Abnormalities
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against it (which can apply to walking while underwater as well as on land). Due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
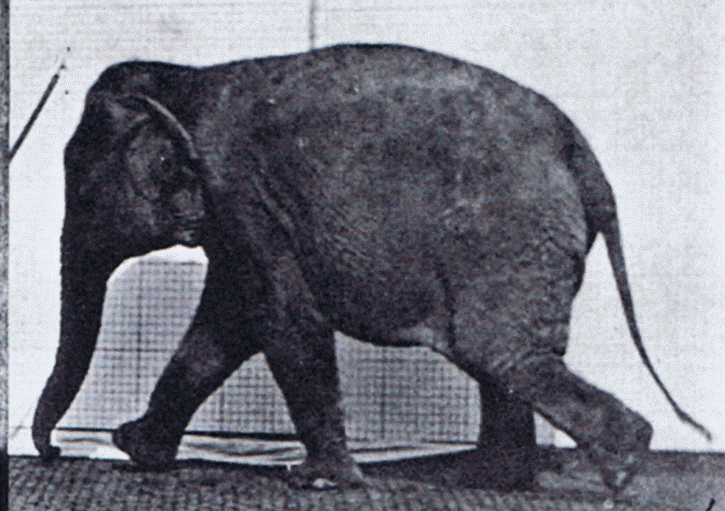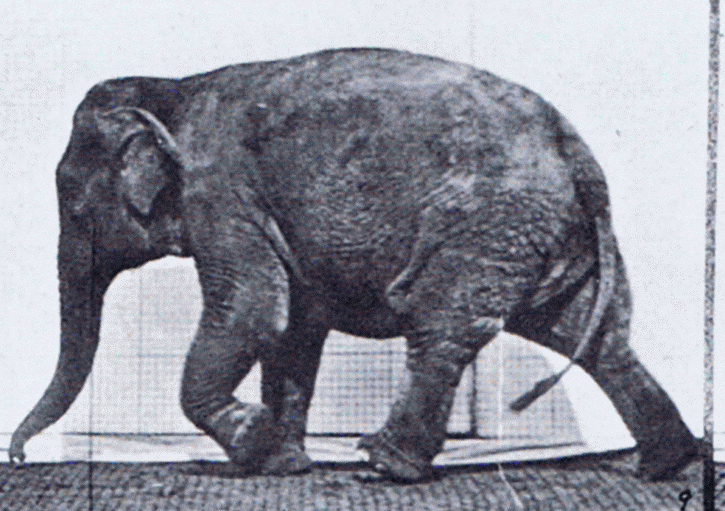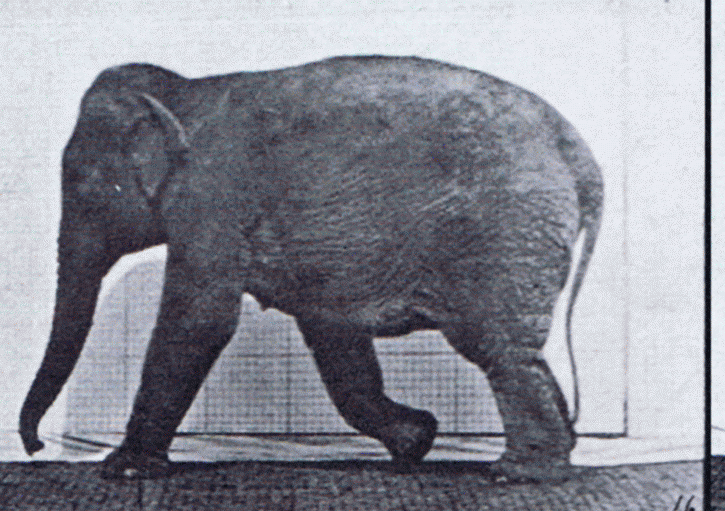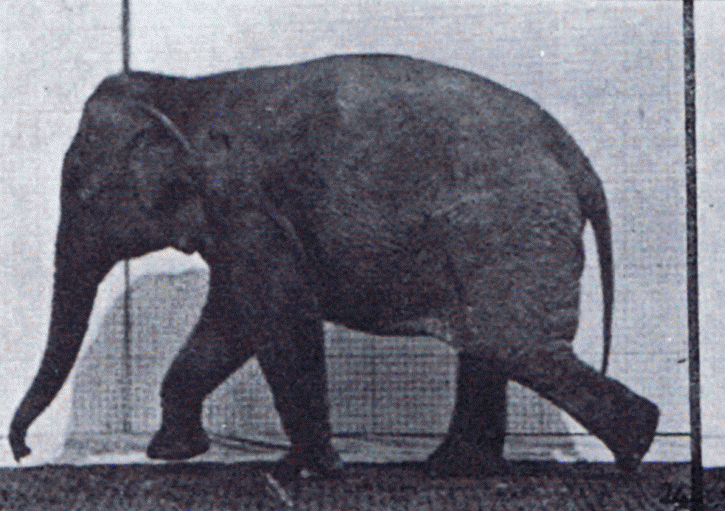
Elephant Walking
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term upper limb is often used. A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle or of a dolphin, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them. Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of birds and bats. Evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Tripod Gait
Alternating may refer to: Mathematics * Alternating algebra, an algebra in which odd-grade elements square to zero * Alternating form, a function formula in algebra * Alternating group, the group of even permutations of a finite set * Alternating knot, a knot or link diagram for which the crossings alternate under, over, under, over, as one travels along each component of the link * Alternating map, a multilinear map that is zero whenever any two of its arguments are equal * Alternating operator, a multilinear map in algebra * Alternating permutation, a type of permutation studied in combinatorics * Alternating series, an infinite series in which the signs of the general terms alternate between positive and negative Electronics * Alternating current, a flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction Other * Alternating turns, the process by which people in a conversation decide who is to speak next See also * Alternate bass * Alternative (other) Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
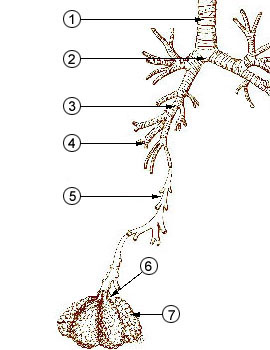
Breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or "external respiration", brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where "cellular respiration" takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary vital signs of life. Under normal conditions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscera
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
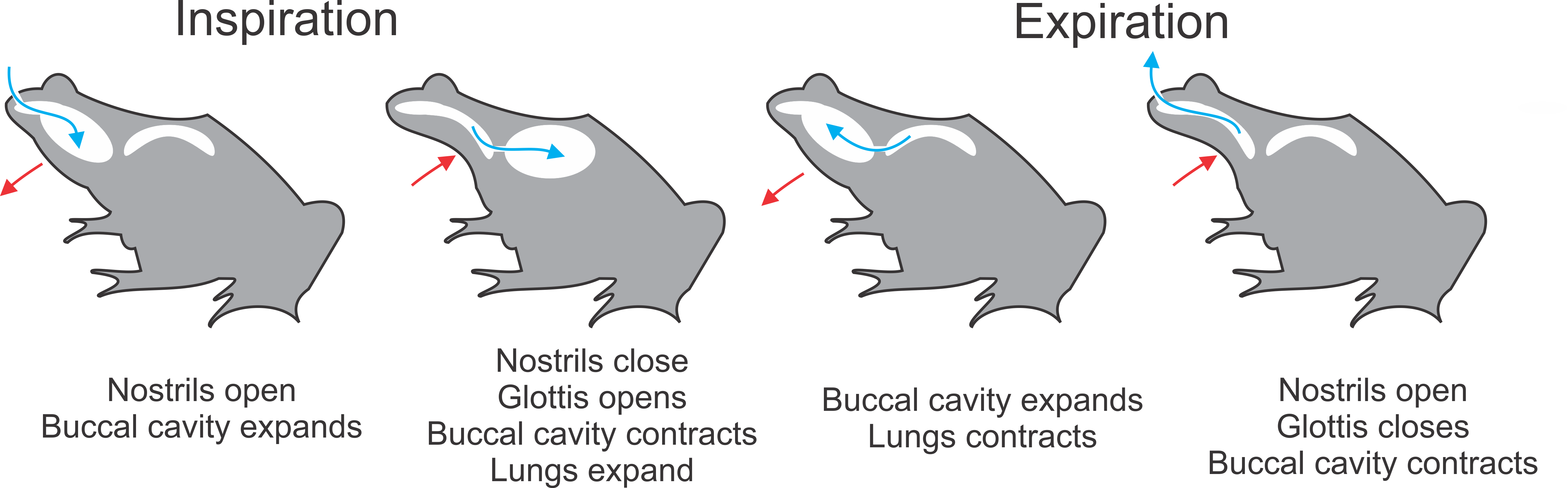
Buccal Pumping
Buccal pumping is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution of lung ventilation mechanisms in vertebrates. Experimental Biology Online 4, 11-28. http://www.brown.edu/Departments/EEB/brainerd_lab/pdf/Brainerd-1999-EBO.pdf It is the sole means of inflating the lungs in amphibians. There are two methods of buccal pumping, defined by the number of movements of the floor of the mouth needed to complete both inspiration and expiration. Four stroke Four-stroke buccal pumping is used by some basal ray-finned fish and aquatic amphibians such as ''Xenopus'' and ''Amphiuma''. This method has several stages. These will be described for an animal starting with lungs in a deflated state: First, the glottis (opening to the lungs) is closed, and the nostrils are opened. The floor of the mouth is then depresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor Lizards
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are recognized. Monitor lizards have long necks, powerful tails and claws, and well-developed limbs. The adult length of extant species ranges from in some species, to over in the case of the Komodo dragon, though the extinct varanid known as megalania (''Varanus priscus'') may have been capable of reaching lengths more than . Most monitor species are terrestrial, but arboreal and semiaquatic monitors are also known. While most monitor lizards are carnivorous, eating eggs, smaller reptiles, fish, birds, insects, and small mammals, some also eat fruit and vegetation, depending on where they live. Distribution The various species cover a vast area, occurring through Africa, the Indian subcontinent, to China, the Ryukyu Islands in southern Japan, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier's Constraint
Carrier's constraint is the observation that air-breathing vertebrates which have two lungs and flex their bodies sideways during locomotion find it very difficult to move and breathe at the same time, because the sideways flexing expands one lung and compresses the other, shunting stale air from lung to lung instead of expelling it completely to make room for fresh air. It was named by English paleontologist Richard Cowen for David R. Carrier, who wrote his observations on the problem in 1987. Consequences Most lizards move in short bursts, with long pauses for breath. Around the Late Triassic period, animals with Carrier's constraint were preyed on by bipedal species that evolved a more efficient stride. Solutions Workarounds Most snakes have only one lung, so Carrier's constraint does not apply. Monitor lizards increase their stamina by using bones and muscles in the throat and floor of the mouth to "gulp" air via gular pumping. Some other lizards, mainly agamids, use bipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
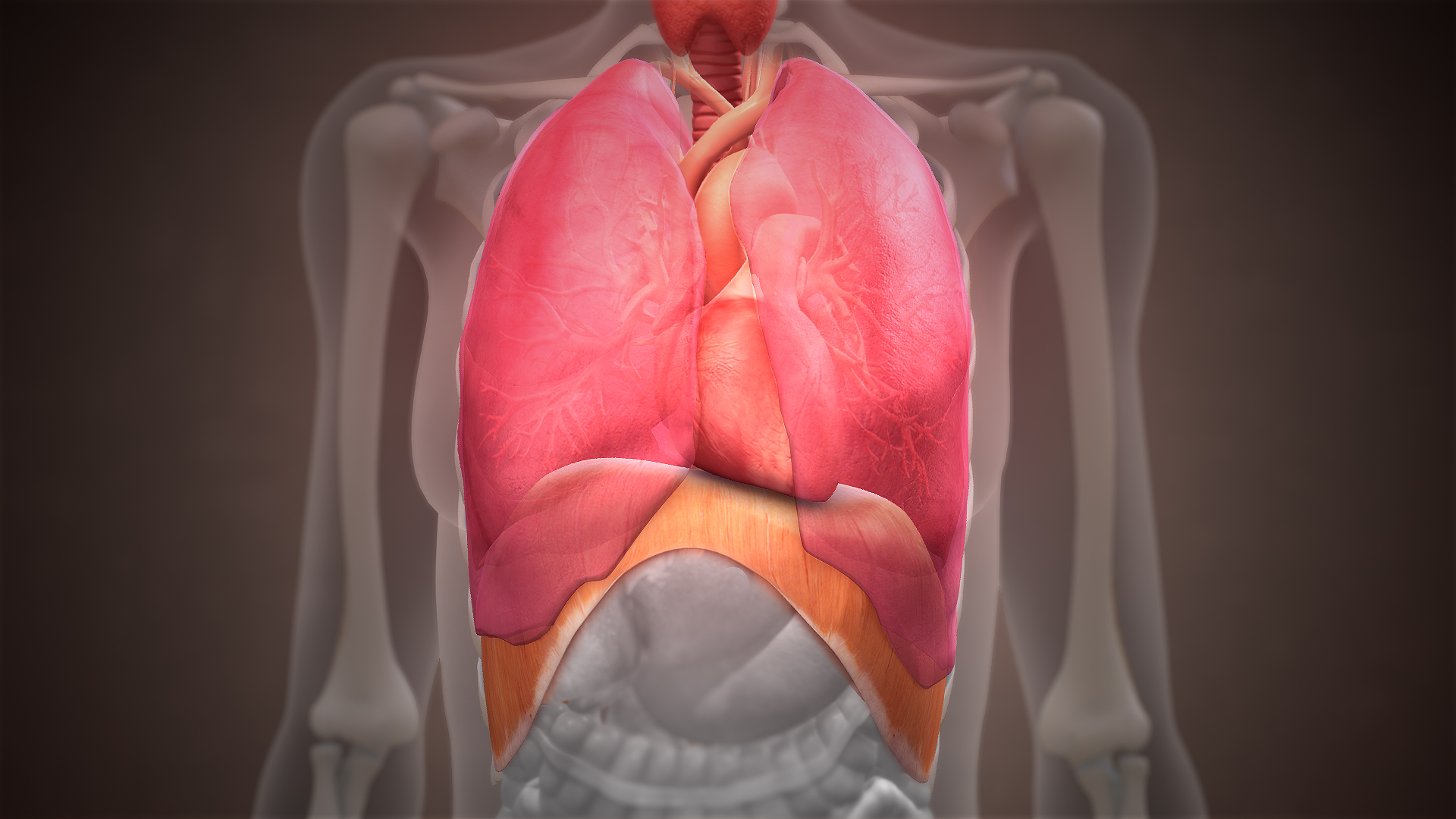
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventilation (physiology)
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or "external respiration", brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where "cellular respiration" takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary vital signs of life. Under normal conditions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_colourised.png)