|
Gabala Radar Station
Gabala Radar Station (; ) in some sources Gabala is spelled ''Qabala'', other names are Lyaki, Mingacevir and Mingechaur was a Daryal-type ( NATO Pechora) bistatic Passive electronically scanned array early warning radar, built by the Soviet Union in the Qabala district of the Azerbaijan SSR in 1985. It was operated by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces and closed at the end of 2012. The radar station had a range of up to , and was designed to detect missile launches as far as the Indian Ocean. The radar's surveillance covered Iran, Turkey, India, Iraq and the entire Middle East. It could detect the launch of missiles and track the whole trajectory to enable a ballistic missile defense system to intercept an offensive strike. The Radar Station hosted about 1,000 Russian servicemen with about 500 Azerbaijanis. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation and Azerbaijan negotiated the terms of the lease and in 2002 the two countries signed an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminum combined. Globally, the ready-mix concrete industry, the largest segment of the concrete market, is projected to exceed $600 billion in revenue by 2025. This widespread use results in a number of environmental impacts. Most notably, the production process for cement produces large volumes of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to net 8% of global emissions. Other environmental concerns include widespread illegal sand mining, impacts on the surrounding environment such as increased surface runoff or urban heat island effect, and potential public health implications from toxic ingredients. Significant research and development is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Defense
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and also the destruction of attacking missiles. Conceived as a defense against nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), its application has broadened to include shorter-ranged non-nuclear tactical and theater missiles. China, France, India, Iran, Israel, Italy, Russia, Taiwan, the United Kingdom and the United States have all developed such air defense systems. Missile defense categories Missile defense can be divided into categories based on various characteristics: type/range of missile intercepted, the trajectory phase where the intercept occurs, and whether intercepted inside or outside the Earth's atmosphere: Type/range of missile intercepted These types/ranges include strategic, theater and tactical. Each entails unique requirements for intercept, and a defensive system capable of intercepting one missile type frequently cannot intercept others. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pechora Radar Station
Pechora Radar Station ( rus, Печорская радиолокационная станция, Pechorskaya radiolokatsionnaya stantsiya) is an early warning radar near Pechora in the Komi Republic, northern Russia. It is a key part of the Russian early warning system against missile attack and was built by the Soviet Union, becoming operational in 1984. It is run by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. Daryal radar overview Pechora is a Daryal radar, a bistatic passive electronically scanned array early warning radar consisting of two separate large phased-array antennas separated by around to . The transmitter array is and the receiver is in size. The system is a VHF system operating at a wavelength of 1.5 to 2 meters (150 to 200 MHz). The claimed range of a Daryal installation is . Originally, at least seven Daryal facilities were planned, however, only the first two facilities completed, Pechora and Gabala, were ever operational. Two Daryal-U type wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit). : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
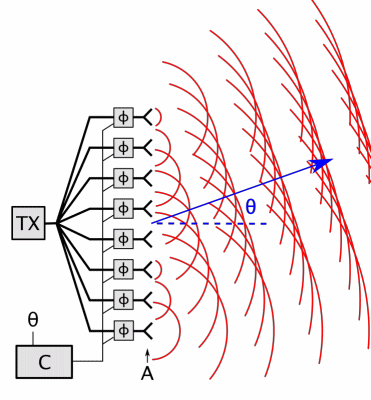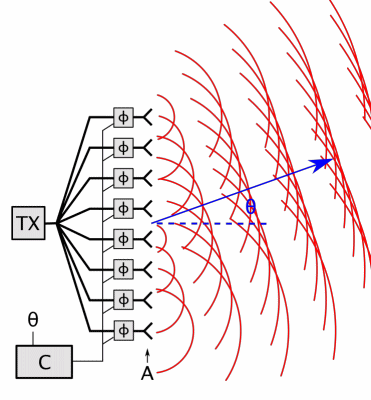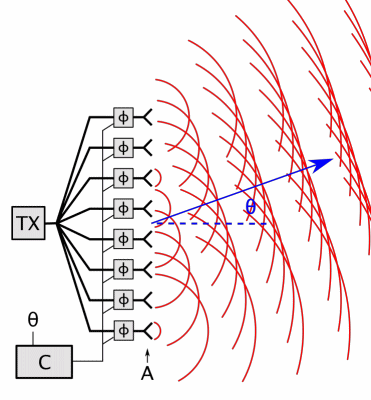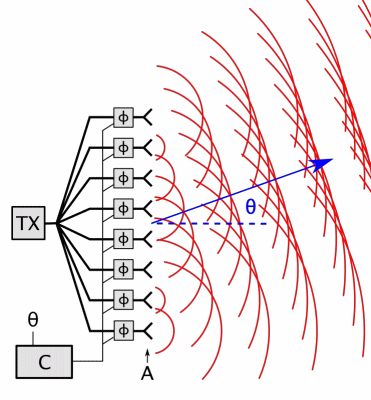
Phased-array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armavir Radar Station
Armavir Radar Station ( rus, Радиолокационная станция (РЛС) в Армавире) is an early warning radar station near Armavir in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is a key part of the Russian early warning system against missile attack and is run by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. There are two radars here - one faces south west and one south east. They provide radar coverage of the Middle East. The station is located on the former Baronovsky Airfield ( rus, аэродром Бароновский) south west of the village of Glubokiy and south west of Armavir. The station was described as starting to operate at the end of 2006 and then entering "experimental combat mode" in 2008. On the day in 2009 that Russia lost coverage from radars in Ukraine it was announced that it had "begun operations". In May 2012 it was announced that it would go on combat duty before the end of 2012. In December 2012 it was announced it will be in the first quarter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh Radar
Voronezh radars (russian: РЛС Воронеж) are the current generation of Russian early-warning radar, providing long distance monitoring of airspace against ballistic missile attack and aircraft monitoring. The first radar, in Lekhtusi near St Petersburg, became operational in 2009. There is a plan to replace older radars with the Voronezh by 2020. Their common name follows the pattern of Soviet radars in being named after a river, the Voronezh. The previous generation of radar was known as the Daryal (after Darial Gorge), Volga (after Volga River) and Daugava (Daugava River) and the generation before the Dnepr (Dnieper River), and Dnestr (Dniester River). The Voronezh radars are described as highly prefabricated meaning that they have a set up time of months rather than years and need fewer personnel than previous generations. They are also modular so that a radar can be brought into (partial) operation whilst being incomplete. Russia has used the launch of these new r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Security Treaty Organisation
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has its origins in the Soviet Armed Forces, which was replaced in 1992 by the United Armed Forces of the Commonwealth of Independent States, and was then itself replaced by the successor armed forces of the respective independent states. Similar to Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty and the Inter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance, Article 4 of the Collective Security Treaty (CST) establishes that an aggression against one signatory would be perceived as an aggression against all. The CSTO charter reaffirmed the desire of all participating states to abstain from the use or threat of force. Signatories are prohibited from joining other military alliances. Activities Exercises The CSTO holds yearly military command exercises for the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention. As the Soviet Union disintegrated, Belarus, Russia and Ukraine signed the Belovezh Accords on 8 December 1991, declaring that the Union had effectively ceased to exist and proclaimed the CIS in its place. On 21 December, the Alma-Ata Protocol was signed. The Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), which regard their membership in the Soviet Union as an illegal occupation, chose not to participate. Georgia withdrew its membership in 2008 following the Russo-Georgian War. Ukraine formally ended its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague Process (Armenian–Azerbaijani Negotiations)
The Prague Process was a series of negotiations between 2002 and 2007 over Nagorno-Karabakh between the Armenia Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...n and Azerbaijani foreign ministries. It was followed by the Madrid Principles. History It began in May, 2002, with the meeting of Personal Representatives of the Presidents of Armenia and Azerbaijan Deputy Foreign Minister Tatoul Markarian and Deputy Foreign Minister Araz Azimov at Stirin, outside Prague, under the Chairmanship of the OSCE Minsk Group. A second session talks was held in late July. The Prague Talks, as announced by the US State Department in September, 2002, would serve as a vehicle for continued communications between the parties as both Armenia and Azerbaijan hold presidential elections in 2003. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Oxford Reference Online'' also place Armenia in Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region; and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the Lachin corridor (under a Russian peacekeeping force) and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the capital, largest city and the financial center. Armenia is a unitary, multi-party, democratic nation-state with an ancient cultural heritage. The first Armenian state of Urartu was established in 860 BC, and by the 6th century BC it was replaced by the Satrapy of Armenia. The Kingdom of Armenia reached its height under Tigranes the Great in the 1st century BC and in the year 301 became the first state in the world to adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |