|
GRB 790305b
GRB 790305b is an event that took place on 5 March 1979. It was an extremely bright burst that was successfully localized to supernova remnant N49 in the Large Magellanic Cloud. This event is now interpreted as a magnetar giant flare, more related to SGR flares than "true" gamma-ray bursts. It is the first observed SGR megaflare, a specific type of short GRB. It has been associated with the magnetar PSR B0525-66. The event On 5 March 1979, Soviet spacecraft Venera 11 and Venera 12, then drifting through the Solar System, were hit by a blast of gamma radiation at approximately 10:51 EST. This contact raised the radiation readings on both the probes from a normal 100 counts per second to over 200,000 counts a second, in only a fraction of a millisecond. This burst of gamma rays quickly continued to spread. Eleven seconds later, Helios 2, a NASA probe, which was in orbit around the Sun, was saturated by the blast of radiation. It soon hit Venus, and the Pioneer Venus Orbite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMC N49
N49 or LMC N49 (PKS 0525-66, PKS B0525-661, PKS J0525-6604, SNR J052559-660453), also known as Brasil Nebula,Sky & Telescope, august 2004, page 12 is the brightest supernova remnant in the Large Magellanic Cloud, approximately 160,000 light-years from Earth. Its form has been assessed to be roughly 5,000 years old. The latest pictures of N49 by the Chandra X-ray Observatory have revealed a bullet-shaped object traveling at about 5 million miles an hour away from a bright X-ray and gamma-ray point source, probably a neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field, known as a soft gamma repeater A soft gamma repeater (SGR) is an astronomical object which emits large bursts of gamma-rays and X-rays at irregular intervals. It is conjectured that they are a type of magnetar or, alternatively, neutron stars with fossil disks around them. His .... A particularly strong gamma-ray burst from LMC N49 was detected on March 5, 1979. References * Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
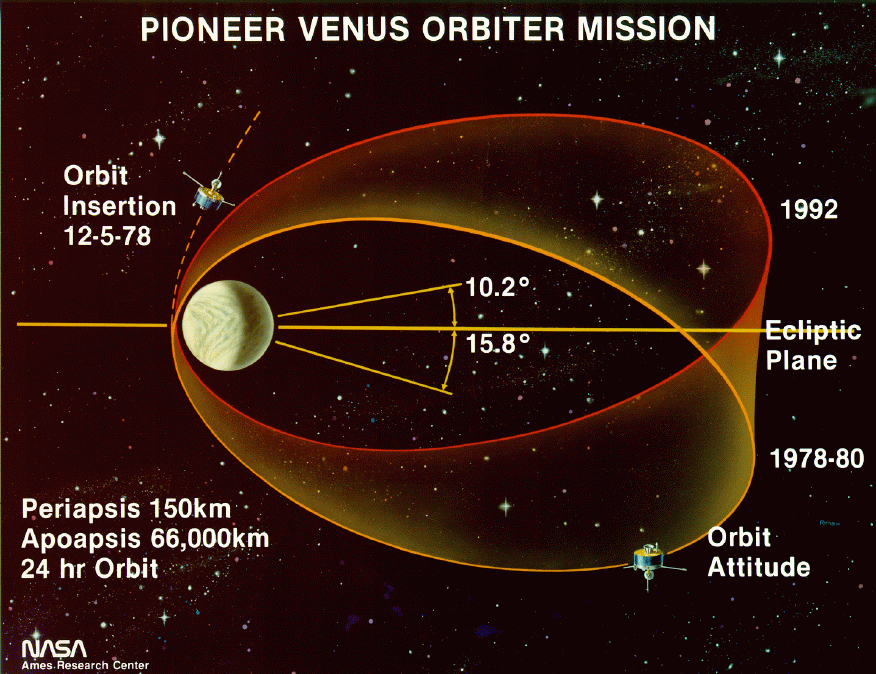
Pioneer Venus Orbiter
The Pioneer Venus Orbiter, also known as Pioneer Venus 1 or Pioneer 12, was a mission to Venus conducted by the United States as part of the Pioneer Venus project. Launched in May 1978 atop an Atlas-Centaur rocket, the spacecraft was inserted into an elliptical orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978. It returned data on Venus until October 1992. Launch and arrival at Venus The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was launched by an Atlas SLV-3D Centaur-D1AR rocket, which flew from Launch Complex 36A at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 13:13:00 on May 20, 1978, and deployed the Orbiter into heliocentric orbit for its coast to Venus. Venus orbit insertion occurred on December 4, 1978. Spacecraft Manufactured by Hughes Aircraft Company, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter was based on the HS-507 bus. The spacecraft was a flat cylinder, in diameter and long. All instruments and spacecraft subsystems were mounted on the forward end of the cylinder, except the magnetometer, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorado (constellation)
Dorado () is a constellation in the southern sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the dolphinfish (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' in Spanish, although it has also been depicted as a swordfish. Dorado contains most of the Large Magellanic Cloud, the remainder being in the constellation Mensa. The South Ecliptic pole also lies within this constellation. Even though the name Dorado is not Latin but Spanish, astronomers give it the Latin genitive form ''Doradus'' when naming its stars; it is treated (like the adjacent asterism Argo Navis) as a feminine proper name of Greek origin ending in -ō (like ''Io'' or ''Callisto'' or ''Argo''), which have a genitive ending ''-ūs''. History Dorado was one of twelve constellations named by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It appeared: * On a celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-ray Bursts
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. After an initial flash of gamma rays, a longer-lived "afterglow" is usually emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio). The intense radiation of most observed GRBs is thought to be released during a supernova or superluminous supernova as a high-mass star implodes to form a neutron star or a black hole. A subclass of GRBs appear to originate from the merger of binary neutron stars. The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 0525-66
SGR may refer to: * Heart Colchester and Heart Ipswich, radio stations in Suffolk, England both once known as SGR * Sagittarius (constellation) abbreviation * '' Scary Go Round'', a webcomic * Scientists for Global Responsibility, a United Kingdom group that promotes the ethical practice and use of science and technology * Segar LRT station in Bukit Panjang, Singapore (LRT station abbreviation) * Select Graphic Rendition (ANSI), an ANSI X3.64 escape sequence * Service Général du Renseignement et de la Sécurité, the French name of the Belgian General Information and Security Service * SGR (band), a ska band from New Jersey, United States * Shale Gouge Ratio, a mathematical algorithm aiming to predict the fault rock types for simple fault zones * The Shaw Group, a company which formerly used as its ticker symbol * Slade Green railway station in London, England (National Rail station code) * Smart Green Resilient (planning concept) abbreviation * Societa' di Gestione del Ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corresponding to the typical energy levels in nuclei with reasonably long lifeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
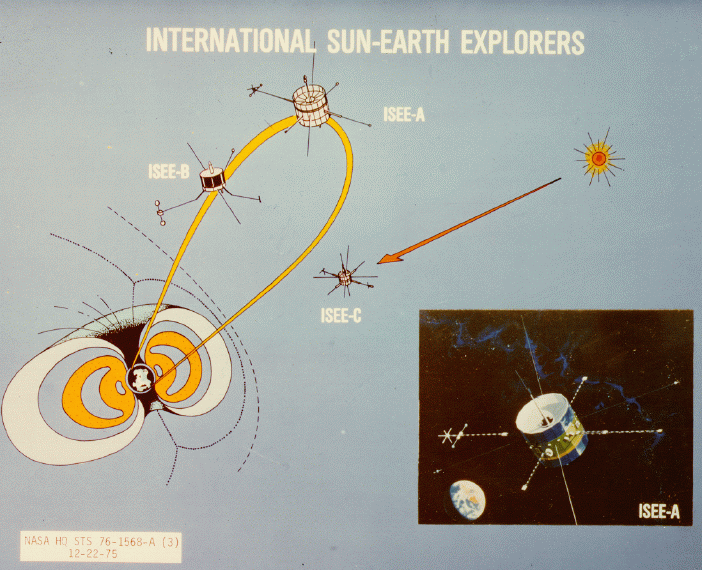
ISEE-3
The International Cometary Explorer (ICE) spacecraft (designed and launched as the International Sun-Earth Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) satellite), was launched 12 August 1978, into a heliocentric orbit. It was one of three spacecraft, along with the mother/daughter pair of ISEE-1 and ISEE-2, built for the International Sun-Earth Explorer (ISEE) program, a joint effort by NASA and European Space Research Organisation, ESRO/European Space Agency, ESA to study the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind. ISEE-3 was the first spacecraft to be placed in a halo orbit at the Earth-Sun Lagrange point. Renamed ICE, it became the first spacecraft to visit a comet, passing through the plasma tail of comet 21P/Giacobini–Zinner, Giacobini-Zinner within about of the nucleus on 11 September 1985. NASA suspended routine contact with ISEE-3 in 1997, and made brief status checks in 1999 and 2008. On 29 May 2014, two-way communication with the spacecraft was reestablished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Observatory
Einstein Observatory (HEAO-2) was the first fully imaging X-ray telescope put into space and the second of NASA's three High Energy Astrophysical Observatories. Named HEAO B before launch, the observatory's name was changed to honor Albert Einstein upon its successfully attaining orbit. Project conception and design The HEAO Program, High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) program originated in the late 1960's within the Astronomy Missions Board at NASA, which recommended the launch of a series of satellite observatories dedicated to high-energy astronomy. In 1970, NASA requested proposals for experiments to fly on these observatories, and a team organized by Riccardo Giacconi, Herbert Gursky, George W. Clark, Elihu Boldt, and Robert Novick responded in October 1970 with a proposal for an x-ray telescope. NASA approved four missions in the HEAO program, with the x-ray telescope planned to be the third mission. One of the three missions of the HEAO program was cancelled in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognoz SO-M
Prognoz, also known as SO (Solar Object, first three satellites), SO-M (SO-modified, next seven satellites) and SO-M2 (last two satellites, also known as Interball) was a Soviet scientific research satellite programme. Twelve Prognoz satellites were launched between 14 April 1972 and 29 August 1996, by Molniya-M carrier rockets. The satellites were placed in High Earth orbits. First ten Prognoz spacescrafts were launched from Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome and last two from Site 43/3 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. The satellites were primarily used for Solar research, however the later satellites were used for other research, including research into the Big Bang theory, and Earth's magnetosphere.Encyclopedia Astronautica - Prognoz The tenth satellite was used as part of the |
Vela (satellite)
Vela was the name of a group of satellites developed as the Vela Hotel element of Project Vela by the United States to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union. Vela started out as a small budget research program in 1959. It ended 26 years later as a successful, cost-effective military space system, which also provided scientific data on natural sources of space radiation. In the 1970s, the nuclear detection mission was taken over by the Defense Support Program (DSP) satellites. In the late 1980s, it was augmented by the Navstar Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. The program is now called the Integrated Operational NuDet (Nuclear Detonation) Detection System ( IONDS). Deployment Twelve satellites were built, six of the Vela Hotel design and six of the Advanced Vela design. The Vela Hotel series was to detect nuclear tests in space, while the Advanced Vela series was to detect not only nuclear explosions in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |