|
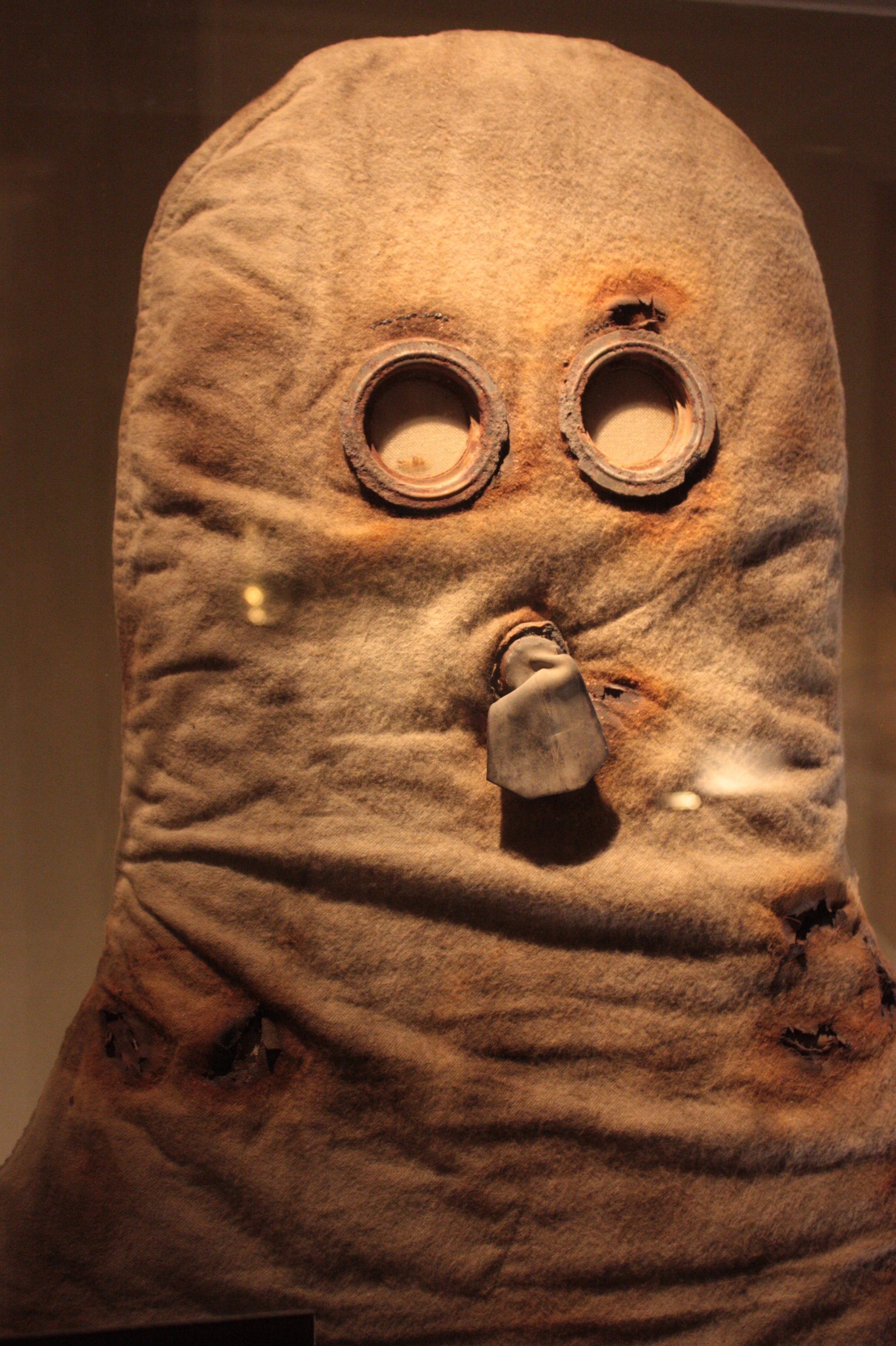
GP-5 Gas Mask
The GP-5 gas mask was historically used by the USSR for NBC protection. The mask has become a popular item in popular culture since and referenced widely in video games and films, as it is very cheap because it is the most produced gas mask ever. The GP-5 is a simple gas mask with protection around the entire head, and a single metal ringed filter for breathing. It was designed to protect against the ingress of toxic, radioactive substances and bacterial (biological) agents into the respiratory system, eyes and face of a person. It was produced in the period from 1961 to 1989 (although there were FPC GP-5's produced in 1990). Taking into account the identified shortcomings in the operation of the civilian gas mask GP-5, it was modernized, which was called the modernized civilian gas mask model 5 - GP-5M. Gas masks GP-5 were produced three times more than the population of the Soviet Union. It was in impressive quantities in almost all industries and in civil defense shelters, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Mask
A gas mask is a mask used to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne pollutants and toxic gases. The mask forms a sealed cover over the nose and mouth, but may also cover the eyes and other vulnerable soft tissues of the face. Most gas masks are also respirators, though the word ''gas mask'' is often used to refer to military equipment (such as a field protective mask), the scope used in this article. The gas mask only protects the user from digesting, inhaling, and contact through the eyes (many agents affect through eye contact). Most combined gas mask filters will last around 8 hours in a biological or chemical situation. Filters against specific chemical agents can last up to 20 hours. Airborne toxic materials may be gaseous (for example, chlorine or mustard gas), or particulates (such as biological agents). Many filters provide protection from both types. The first gas masks mostly used circular lenses made of glass, mica or cellulose acetate to allow vision. Glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
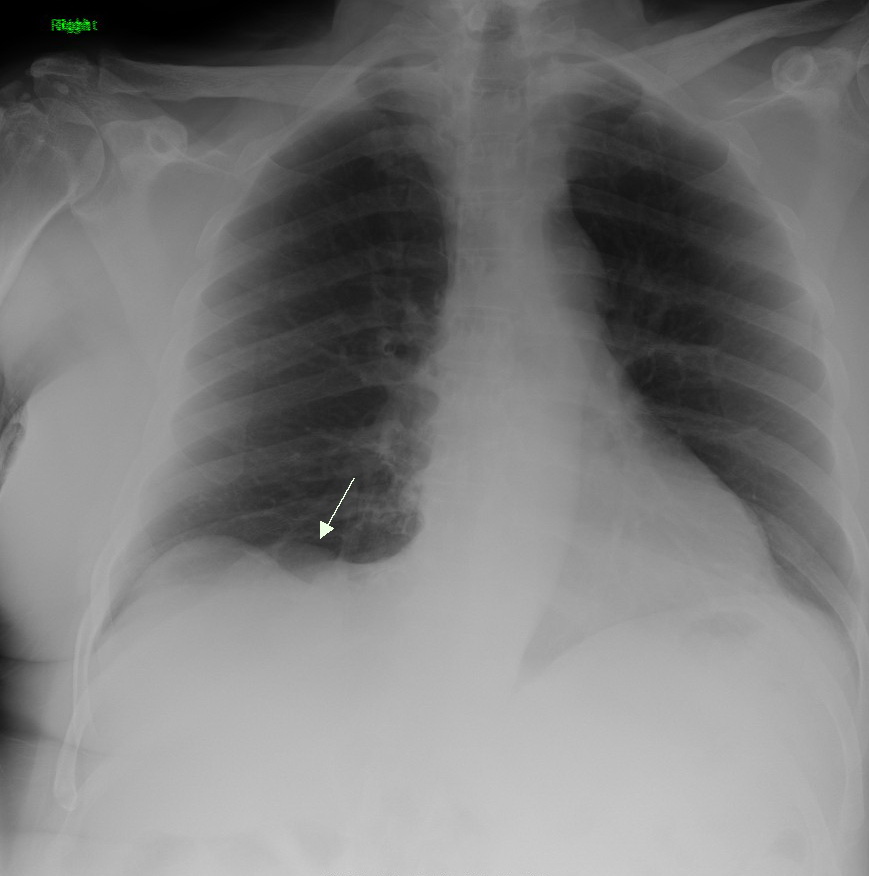
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobutane
Isobutane, also known as ''i''-butane, 2-methylpropane or methylpropane, is a chemical compound with molecular formula HC(CH3)3. It is an isomer of butane. Isobutane is a colourless, odourless gas. It is the simplest alkane with a tertiary carbon atom. Isobutane is used as a precursor molecule in the petrochemical industry, for example in the synthesis of isooctane. Production Isobutane is obtained by isomerization of butane. : Uses Isobutane is the principal feedstock in alkylation units of refineries. Using isobutane, gasoline-grade "blendstocks" are generated with high branching for good combustion characteristics. Typical products created with isobutane are 2,4-dimethylpentane and especially 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. Solvent In the Chevron Phillips slurry process for making high-density polyethylene, isobutane is used as a diluent. As the slurried polyethylene is removed, isobutane is "flashed" off, and condensed, and recycled back into the loop reactor for this purpose. Prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered Ring (chemistry), ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet of hydrogen". It was an accidental discovery while attempting to isolate potassium metal. By heating potassium carbonate with carbon at very high temperatures, he produced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethane
Ethane ( , ) is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production. Related compounds may be formed by replacing a hydrogen atom with another functional group; the ethane moiety is called an ethyl group. For example, an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group yields ethanol, the alcohol in beverages. History Ethane was first synthesised in 1834 by Michael Faraday, applying electrolysis of a potassium acetate solution. He mistook the hydrocarbon product of this reaction for methane and did not investigate it further. During the period 1847–1849, in an effort to vindicate the radical theory of organic chemistry, Hermann Kolbe and Edward Frankland produced ethane by the reductions of propionitrile (ethyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it poses technical challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases. It has also been detected on other plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia is both caust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing. The two cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms: N≡C‒ C≡N, although other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide (NCBr) (but see also ''Cyano radical''.) Cyanogen is the anhydride of oxamide: :H2NC(O)C(O)NH2 → NCCN + 2 H2O although oxamide is manufactured from cyanogen by hydrolysis: :NCCN + 2 H2O → H2NC(O)C(O)NH2 Preparation Cyanogen is typically generated from cyanide compounds. One laboratory method entails thermal decomposition of mercuric cyanide: :2 Hg(CN)2 → (CN)2 + Hg2(CN)2 Alternatively, one can combine solutions of copper(II) salts (such as copper(II) sulfate) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structure . It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its volatile nature. Structure and general properties Hydrogen cyanide is a linear molecule, with a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. The tautomer of HCN is HNC, hydrogen isocyanide. Hydrogen cyanide is weakly acidic with a p''K''a of 9.2. It partially ionizes in water solution to give the cyanide anion, CN−. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water, represented as HCN, is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The salts of the cyanide ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon commonly used to filter contaminants from water and air, among many other uses. It is processed (activated) to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area available for adsorption (which is not the same as absorption) or chemical reactions. Activation is analogous to making popcorn from dried corn kernels: popcorn is light, fluffy, and has a surface area that is much larger than the kernels. ''Activated'' is sometimes replaced by ''active''. Due to its high degree of microporosity, one gram of activated carbon has a surface area in excess of as determined by gas adsorption. Charcoal, before activation, has a specific surface area in the range of . An activation level sufficient for useful application may be obtained solely from high surface area. Further chemical treatment often enhances adsorption properties. Activated carbon is usually derived from waste products such as coconut husks; waste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






-3D-balls.png)