|
GNAS Complex Locus
GNAS complex locus is a gene locus in humans. Its main product is the heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunit Gs-α, a key component of G protein-coupled receptor-regulated adenylyl cyclase signal transduction pathways. GNAS stands for Guanine Nucleotide binding protein, Alpha Stimulating activity polypeptide. Gene This gene locus has a highly complex imprinted expression pattern. It gives rise to maternally-, paternally- and biallelically-expressed transcripts that are derived from four alternative promoters with distinct 5' exons. Some transcripts contain a differentially methylated region (DMR) within their 5' exons; such DMRs are commonly found in imprinted genes and correlate with transcript expression. An antisense transcript also exists, and this antisense transcript and one of the sense transcripts are paternally expressed, produce non-coding RNAs and may regulate imprinting in this region. In addition, one of the transcripts contains a second frame-shifted open read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
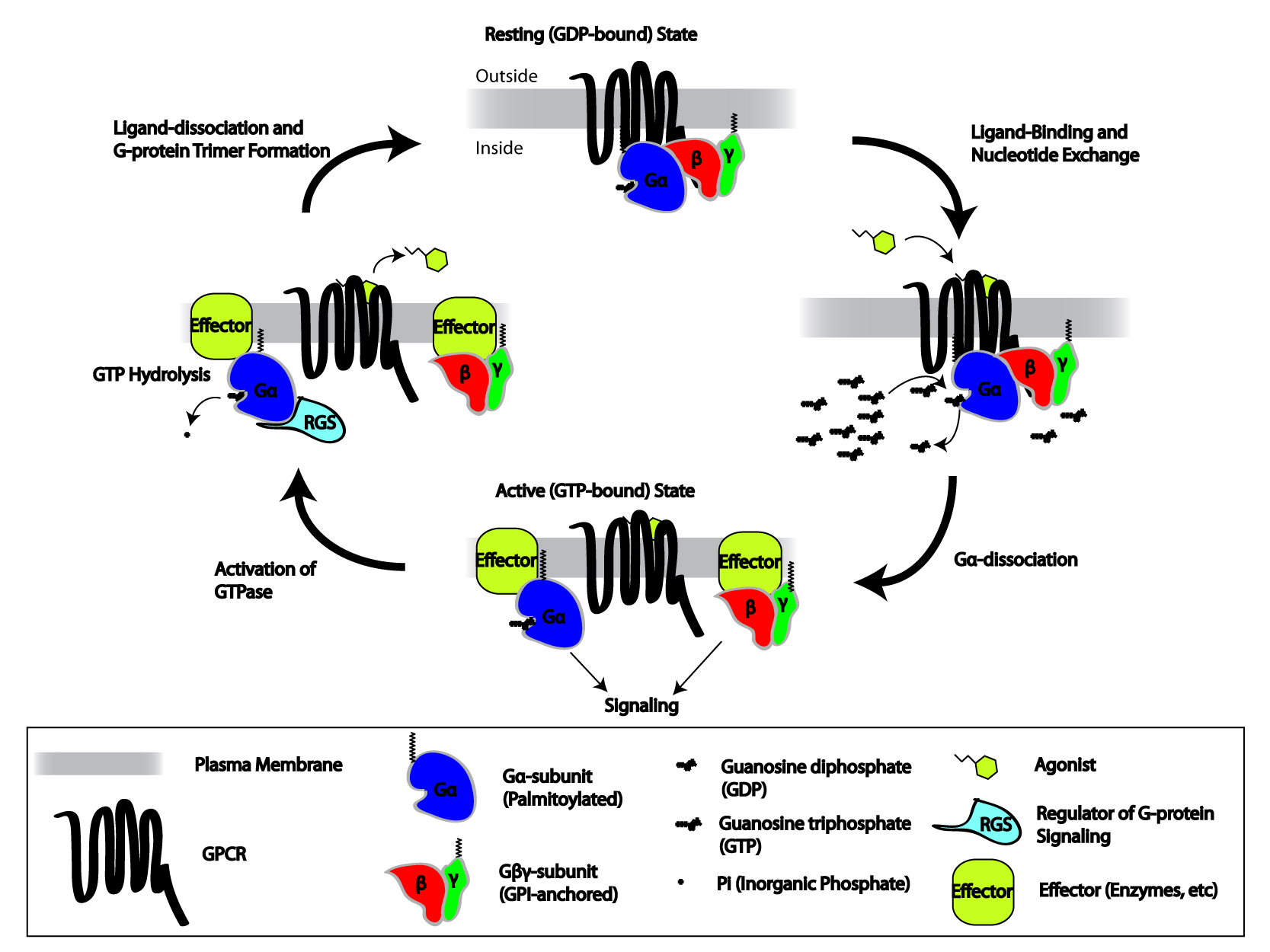
Heterotrimeric G-protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...s, directly. These G proteins are made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) Protein subunit, subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein. When ligands bind a GPCR, the GPCR acquires GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) abili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure Prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by computational biology; and it is important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Starting in 1994, the performance of current methods is assessed biannually in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D. Protein structure and terminology Proteins are chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. Many conformations of this chain are possible due to the rotation of the main chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at various locations in the interior of the cell. Adenylate cyclase is ''activated'' by a range of signaling molecules through the activation of adenylate cyclase stimulatory G ( Gs)-protein-coupled receptors. Adenylate cyclase is ''inhibited'' by agonists of adenyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Startle Reflex
In animals, including humans, the startle response is a largely unconscious defensive response to sudden or threatening stimuli, such as sudden noise or sharp movement, and is associated with negative affect.Rammirez-Moreno, David. "A computational model for the modulation of the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex". ''Biological Cybernetics'', 2012, p. 169 Usually the onset of the startle response is a startle reflex reaction. The startle reflex is a brainstem reflectory reaction (reflex) that serves to protect vulnerable parts, such as the back of the neck (whole-body startle) and the eyes (eyeblink) and facilitates escape from sudden stimuli. It is found across many different species, throughout all stages of life. A variety of responses may occur depending on the affected individual's emotional state, body posture, preparation for execution of a motor task, or other activities. The startle response is implicated in the formation of specific phobias. Startle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomegaly
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the heart is enlarged. As such, it is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity, heart valve disease, high blood pressure ( hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly can be serious depending on what part of the heart is enlarged, and can result in congestive heart failure. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death. Cardiomegaly may improve over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong treatment with medication. Having an immediate family member who has or had cardiomegaly may indicate that a person is more susceptible to getting this condition. Signs and symptoms For many people, cardiomegaly is asymptomatic. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial and the estimated in the general population is approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be |
Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia is a form of fibrous dysplasia affecting more than one bone. Fibrous dysplasia is a disorder where bone is replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to weak bones, uneven growth, and deformity. McCune-Albright syndrome includes polyostotic fibrous dysplasia as part of its presentation. When polyostotic fibrous dysplasia manifests in the long bones, limping results; when it manifests in the face, asymmetric growth of the face can result. One treatment that has been used is bisphosphonates. See also * Fibrous dysplasia of bone * Monostotic fibrous dysplasia * List of radiographic findings associated with cutaneous conditions References External links Genodermatoses {{Genodermatoses-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Osseous Heteroplasia
Progressive osseous heteroplasia is a cutaneous condition characterized by cutaneous or subcutaneous ossification. According to the Progressive Osseous Heteroplasia Association: It is associated with '' GNAS''. A telltale symptom of POH is osteoma cutis under the skin of a newborn. It was discovered in 1994 by physician Frederick Kaplan. Diagnosis Patients with POH have a distinctly different manifestation of symptoms than those with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), though heterotopic ossification appears in both diseases. They lack the congenital abnormality of the big toe that is a diagnostic feature for FOP. People with POH also have ossification of the skin during infancy, which does not occur in FOP. Also, the pattern of ossification differs in POH, spreading in an intramembranous fashion rather than endochondral. See also * Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva * Punctate porokeratosis * List of cutaneous conditions * Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism Pse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxoma
A myxoma (New Latin from Greek 'muxa' for mucus) is a myxoid tumor of primitive connective tissue. It is most commonly found in the heart (and is the most common primary tumor of the heart in adults) but can also occur in other locations. Types Table below: 1.SMA, smooth muscle actin. 2.MSA, muscle-specific actin. 3.EMA, epithelial membrane antigen. Symptoms and signs Symptoms associated with cardiac myxomas are typically due to the effect of the mass of the tumor obstructing the normal flow of blood within the chambers of the heart. Because pedunculated myxomas are somewhat mobile, symptoms may only occur when the patient is in a particular position. Some symptoms of myxoma may be associated with the release of interleukin 6 (IL-6) by the myxoma. High levels of IL-6 may be associated with a higher risk of embolism of the myxoma. Symptoms of a cardiac myxoma include: * Dyspnea on exertion * Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea * Fever * Weight loss (see cachexia) * Lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McCune–Albright Syndrome
McCune–Albright syndrome is a complex genetic disorder affecting the bone, skin and endocrine systems. It is a mosaic disease arising from somatic activating mutations in '' GNAS'', which encodes the alpha-subunit of the Gs heterotrimeric G protein. It was first described in 1937 by American pediatrician Donovan James McCune and American endocrinologist Fuller Albright. Signs and symptoms McCune–Albright syndrome is suspected when two or more of the following features are present: * Fibrous dysplasia * Hyperpigmented skin lesions with characteristic features, including jagged "coast of Maine" borders and tendency occur along the midline of the body. These lesions are historically termed café au lait macules, however the term "cafe-au-lait" only describes their appearance on lighter-skinned individuals. * Hyperfunctioning endocrine disease Patients may have one or many of these features, which may occur in any combination. As such, the clinical presentation of patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (PPHP) is an inherited disorder, named for its similarity to pseudohypoparathyroidism in presentation. It is more properly Albright hereditary osteodystrophy although without resistance of parathyroid hormone as frequently seen in that affliction. The term Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism is used to describe a condition where the individual has the phenotypic appearance of Pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a, but has (unexpected for the phenotype) normal labs including calcium and PTH. It can be considered a variant of Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, or Pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1A, as they present with the same constellation of signs and symptoms, including short stature, brachydactyly, subcutaneous calcification, and obesity. Presentation Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism can be best understood by comparing it to other conditions: Hormone resistance is not present in Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Short stature may be present. Obesity is les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |