|
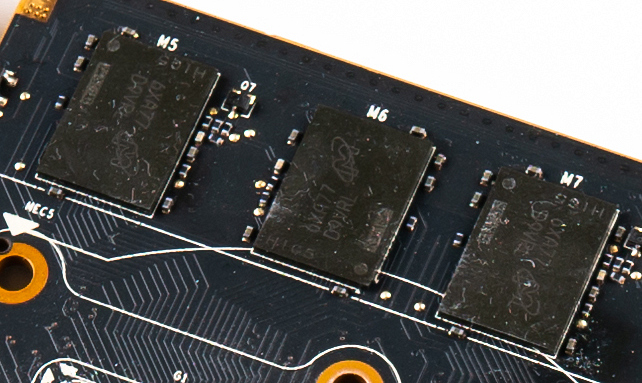
GDDR
Graphics DDR SDRAM (GDDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) specifically designed for applications requiring high bandwidth, e.g. graphics processing units (GPUs). GDDR SDRAM is distinct from the more widely known types of DDR SDRAM, such as DDR4, although they share some of the same features—including double data rate data transfers. , GDDR SDRAM has been succeeded by GDDR2, GDDR3, GDDR4, GDDR5, GDDR5X, GDDR6, and GDDR6X. Generations File:ATI Radeon X1300 256MB - Hynix HY5DU561622CTP-5-5390.jpg, Hynix GDDR SDRAM File:SAMSUNG@QDDR3-SDRAM@256MBit@K5J55323QF-GC16 Stack-DSC01234-DSC01284 - ZS-retouched.jpg, A Samsung GDDR3 256MBit package File:Sapphire Ultimate HD 4670 512MB - Qimonda HYB18H512321BF-10-93577.jpg, A 512 MBit Qimonda GDDR3 SDRAM package File:SAMSUNG@QDDR3-SDRAM@256MBit@K5J55323QF-GC16 Stack-DSC01340-DSC01367 - ZS-retouched.jpg, Inside a Samsung GDDR3 256MBit package DDR SGRAM GDDR was initially known as DDR SGRAM (double dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR5X
Graphics Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM). Overview Like its predecessor, GDDR4, GDDR5 is based on DDR3 SDRAM memory, which has double the data lines compared to DDR2 SDRAM. GDDR5 also uses 8-bit wide prefetch buffers similar to GDDR4 and DDR3 SDRAM. GDDR5 SGRAM conforms to the standards which were set out in the GDDR5 specification by the JEDEC. SGRAM is single-ported. However, it can open two memory pages at once, which simulates the dual-port nature of other VRAM technologies. It uses an 8N-prefetch architecture and DDR interface to achieve high performance operation and can be configured to operate in ×32 mode or ×16 (clamshell) mode which is detected during device initialization. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR5
Graphics Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM). Overview Like its predecessor, GDDR4, GDDR5 is based on DDR3 SDRAM memory, which has double the data lines compared to DDR2 SDRAM. GDDR5 also uses 8-bit wide prefetch buffers similar to GDDR4 and DDR3 SDRAM. GDDR5 SGRAM conforms to the standards which were set out in the GDDR5 specification by the JEDEC. SGRAM is single-ported. However, it can open two memory pages at once, which simulates the dual-port nature of other VRAM technologies. It uses an 8N-prefetch architecture and DDR interface to achieve high performance operation and can be configured to operate in ×32 mode or ×16 (clamshell) mode which is detected during device initialization. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR5 SDRAM
Graphics Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM). Overview Like its predecessor, GDDR4, GDDR5 is based on DDR3 SDRAM memory, which has double the data lines compared to DDR2 SDRAM. GDDR5 also uses 8-bit wide prefetch buffers similar to GDDR4 and DDR3 SDRAM. GDDR5 SGRAM conforms to the standards which were set out in the GDDR5 specification by the JEDEC. SGRAM is single-ported. However, it can open two memory pages at once, which simulates the dual-port nature of other VRAM technologies. It uses an 8N-prefetch architecture and DDR interface to achieve high performance operation and can be configured to operate in ×32 mode or ×16 (clamshell) mode which is detected during device initialization. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR6 SDRAM
Graphics Double Data Rate 6 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR6 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR5. Just like GDDR5X it uses QDR (quad data rate) in reference to the write command clock (WCK) and ODR (Octal Data Rate) in reference to the command clock (CK). Overview The finalized specification was published by JEDEC in July 2017. GDDR6 offers increased per-pin bandwidth (up to 16 Gbit/s) and lower operating voltages (1.35 V), increasing performance and decreasing power consumption relative to GDDR5X. Commercial implementation At Hot Chips 2016, Samsung announced GDDR6 as the successor of GDDR5X. Samsung later announced that the first products would be 16 Gbit/s, 1.35 V chips. In January 2018, Samsung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR6
Graphics Double Data Rate 6 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR6 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR5. Just like GDDR5X it uses QDR (quad data rate) in reference to the write command clock (WCK) and ODR (Octal Data Rate) in reference to the command clock (CK). Overview The finalized specification was published by JEDEC in July 2017. GDDR6 offers increased per-pin bandwidth (up to 16 Gbit/s) and lower operating voltages (1.35 V), increasing performance and decreasing power consumption relative to GDDR5X. Commercial implementation At Hot Chips 2016, Samsung announced GDDR6 as the successor of GDDR5X. Samsung later announced that the first products would be 16 Gbit/s, 1.35 V chips. In January 2018, Samsung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR6X
Graphics Double Data Rate 6 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR6 SDRAM) is a type of Synchronous dynamic random-access memory#Synchronous graphics RAM .28SGRAM.29, synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in Video card, graphics cards, Video game console, game consoles, and High-throughput computing, high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR5. Just like GDDR5X it uses QDR (quad data rate) in reference to the write command clock (WCK) and ODR (Octal Data Rate) in reference to the command clock (CK). Overview The finalized specification was published by JEDEC in July 2017. GDDR6 offers increased per-pin bandwidth (up to 16 Gbit/s) and lower operating voltages (1.35 V), increasing performance and decreasing power consumption relative to GDDR5X. Commercial implementation At Hot Chips 2016, Samsung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
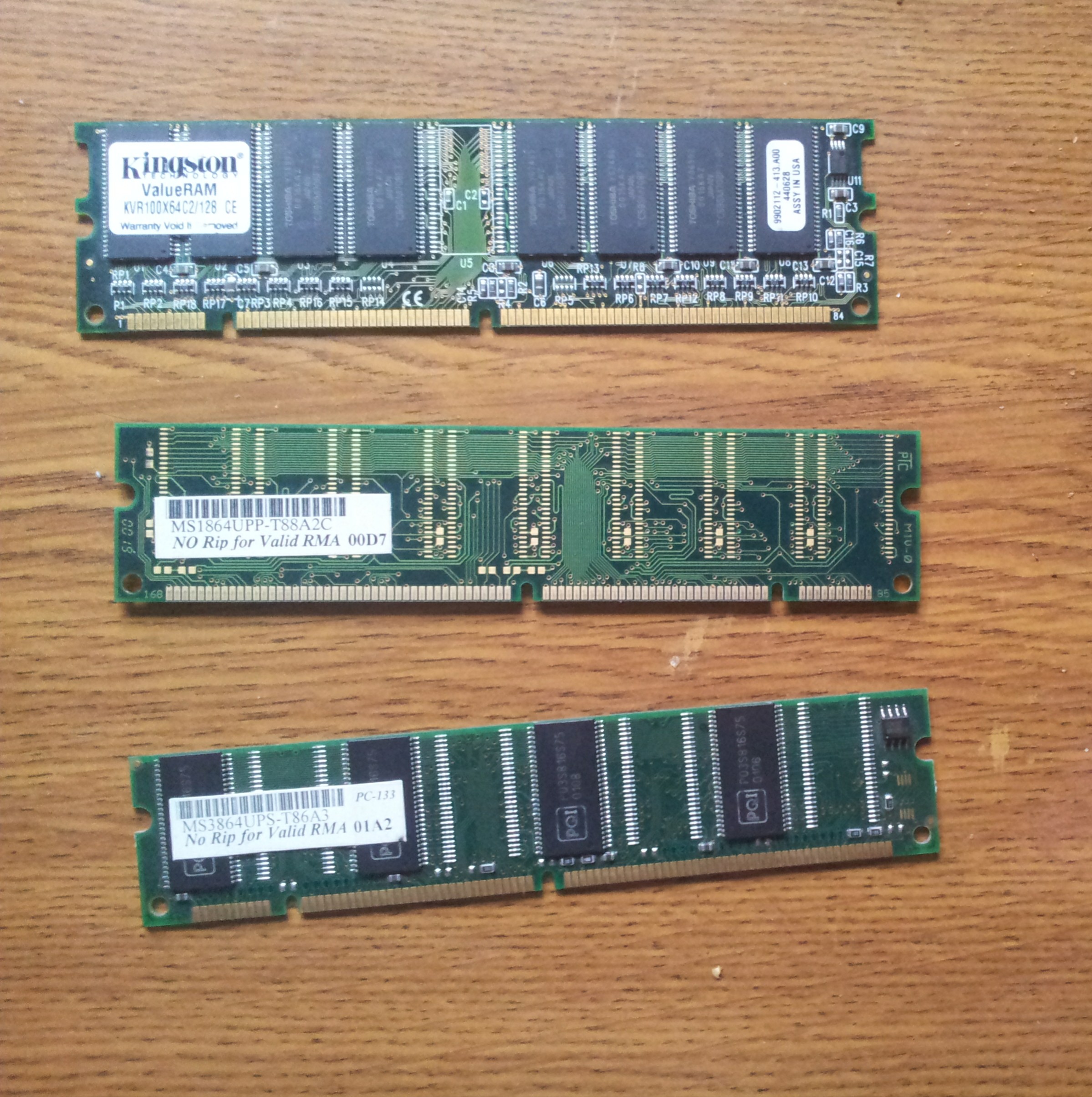
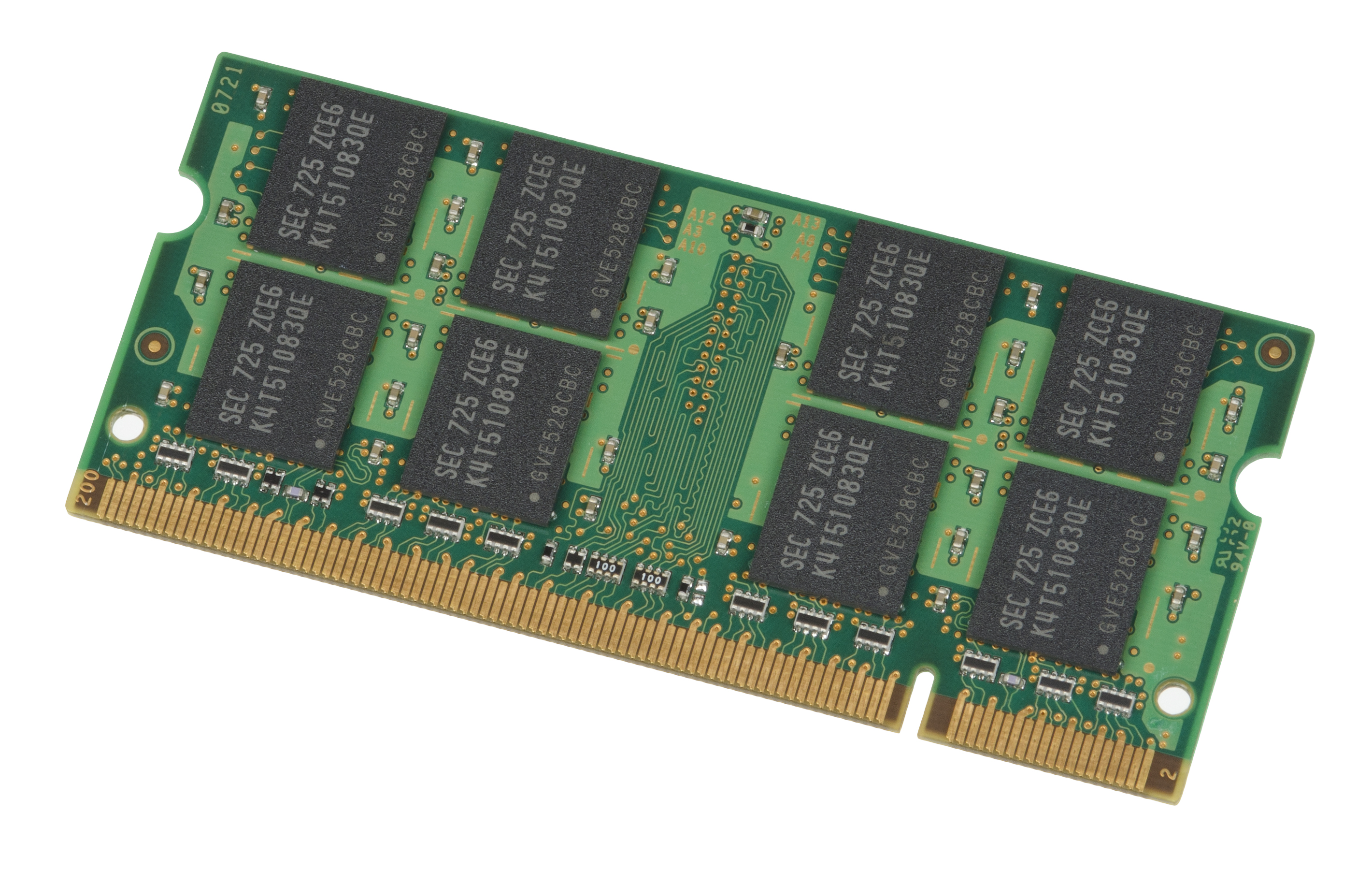
Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR4
GDDR4 SDRAM, an abbreviation for Graphics Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory, is a type of graphics card memory (SGRAM) specified by the JEDEC Semiconductor Memory Standard. It is a rival medium to Rambus's XDR DRAM. GDDR4 is based on DDR3 SDRAM technology and was intended to replace the DDR2-based GDDR3, but it ended up being replaced by GDDR5 within a year. History * On October 26, 2005, Samsung announced that it developed the first GDDR4 memory, a 256-Mbit chip running at 2.5 Gbit/s. Samsung also revealed plans to sample and mass-produce GDDR4 SDRAM rated at 2.8 Gbit/s per pin. * In 2005, Hynix developed the first 512-Mbit GDDR4 memory chip. * On February 14, 2006, Samsung announced the development of 32-bit 512-Mbit GDDR4 SDRAM capable of transferring 3.2 Gbit/s per pin, or 12.8 GB/s for the module. * On July 5, 2006, Samsung announced the mass-production of 32-bit 512-Mbit GDDR4 SDRAM rated at 2.4 Gbit/s per pin, or 9.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR3
GDDR3 SDRAM (Graphics Double Data Rate 3 SDRAM) is a type of DDR SDRAM specialized for graphics processing units (GPUs) offering less access latency and greater device bandwidths. Its specification was developed by ATI Technologies in collaboration with DRAM vendors including Elpida Memory, Hynix Semiconductor, Infineon (later Qimonda) and Micron. It was later adopted as a JEDEC standard. Overview It has much the same technological base as DDR2, but the power and heat dispersal requirements have been reduced somewhat, allowing for higher performance memory modules, and simplified cooling systems. GDDR3 is not related to the JEDEC DDR3 specification. This memory uses internal terminators, enabling it to better handle certain graphics demands. To improve throughput, GDDR3 memory transfers 4 bits of data per pin in 2 clock cycles. The GDDR3 interface transfers two 32 bit wide data words per clock cycle from the I/O pins. Corresponding to the 4n-prefetch a single write or re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR2
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |