|
Güines Formation
The Güines Formation is a geologic formation in Cuba. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early to Middle Miocene period. Among others, fossils of the prehistoric dugong, ''Metaxytherium'' were found in the formation. at .org Fossil content * '' Aturia cubaensis'' * '' Metaxytherium riveroi''See also * |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was created in 1998 by John Alroy and housed at Macquarie University Macquarie University ( ) is a Public university, public research university in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the Sydney metropolitan area. .... It included many analysis and data visualization tools formerly included in the Paleobiology Database.{{cite web, title=Frequently asked questions, url=http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, publisher=Fossilworks, access-date=17 December 2021, archive-date=18 May 2022, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220518205516/http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?page=FAQ, url-status=dead Fossilworks was sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology In Cuba
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin who popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Cuba
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Formations Of Cuba
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In Cuba
The Paleobiology Database lists no known fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Dominica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The database also records no fossiliferous stratigraphic units within several regions of the Caribbean like the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Bonaire, Saba, Sint Eustatius, and Nueva Esparta. Antigua and Barbuda The Bahamas Barbados Cuba Dominican Republic Grenada Haiti Jamaica Trinidad and Tobago Dependencies of France The Paleobiology Database lists no known fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the French dependencies of St. Barthélemy or St. Martin. Dependencies of the Netherlands The Paleobiology Database lists no known fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the Dutch dependencies of Aruba, Bonaire, Saba, Sint Eustatius and Sint Maarten. Curaçao Dependencies of the United Kingdom The Paleobiology Data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
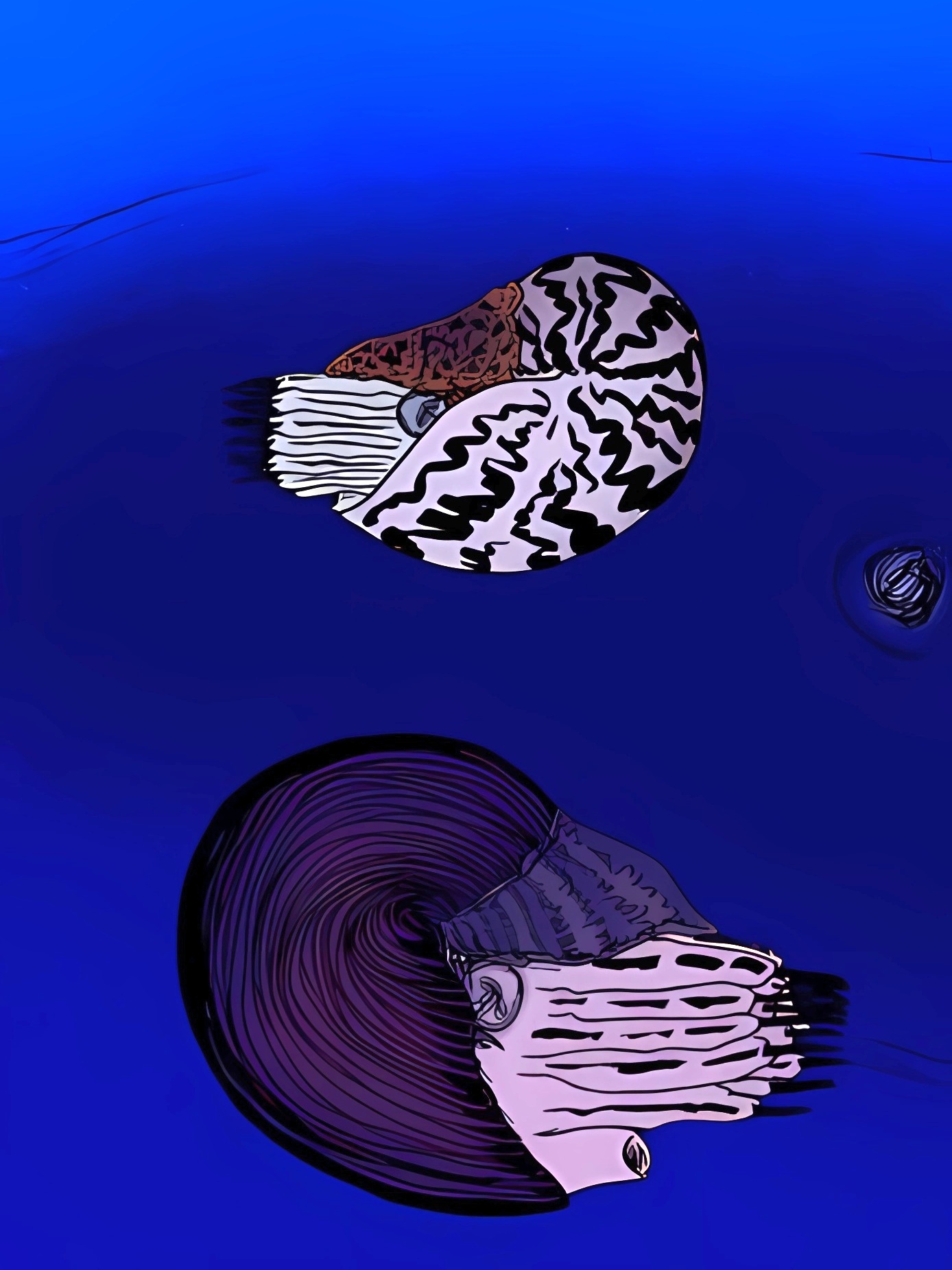
Aturia Cubaensis
''Aturia'' is an extinct genus of Paleocene to Miocene nautilids within Aturiidae, a monotypic family, established by Campman in 1857 for ''Aturia'' Bronn, 1838, and is included in the superfamily Nautilaceae in Kümmel 1964. ''Aturia'' is characterized by a smooth, highly involute, discoidal shell with a complex suture and subdorsal siphuncle. The shell of ''Aturia'' is rounded ventrally and flattened laterally; the dorsum is deeply impressed. The suture, one of the most complex in the Nautiloidea, has a broad flattened ventral saddle, narrow pointed lateral lobes, broad rounded lateral saddles, broad lobes on the dorso-umbilical slopes, and a broad dorsal saddle divided by a deep, narrow median lobe. The siphuncle is moderate in size and located subdorsally in the adapical dorsal flexture of the septum. Based on the feeding and hunting behaviors of living nautiluses, ''Aturia'' most likely preyed upon small fish and crustaceans. ''Aturia'' is likely derived from species of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaxytherium
''Metaxytherium'' is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of ''Metaxytherium'' are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's sea cow. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Metaxytherium'' were described in 1822 by Anselme-Gaëtan Demarest as a species of Hippopotamus, Hippo, ''H. medius'' before the genus name ''Metaxytherium'' was coined in 1840 by De Christol. Although the type species was initially designated to be ''M. cuvieri'', later publications argued that the two species are synonymous and ''M. medium'' thus holds precedence. The grammatical changes of the species name were made to match the rules of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (a scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardised international units of geological time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |