|
Gölpınar, Şanlıurfa
Gölpınar is a neighbourhood of the municipality and district of Karaköprü, Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Its population is 670 (2022). It is located about north of Urfa. It is located just south of the road to Kabahaydar, east of the road's intersection with the main Urfa-Siverek highway. It lies on a plain that stretches east toward Kabahaydar, between the Akziyaret Tepe hill to the north and the forested hills called Atatürk Ormanı (part of Germuş Dağ) to the south. There is a spring in the east of the village. Archaeology The village sits on top of a small archaeological mound about 250 m in diameter and 10 m in height. In some places, erosion from the spring has revealed basalt architectural fragments. Old relief fragments are also visible in the walls of some houses. Two ancient stone artifacts were found at Gölpınar: one is a broken stele, 116 cm tall and 42 cm wide, is now kept at the Şanlıurfa Museum; the other is an orthostat measuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
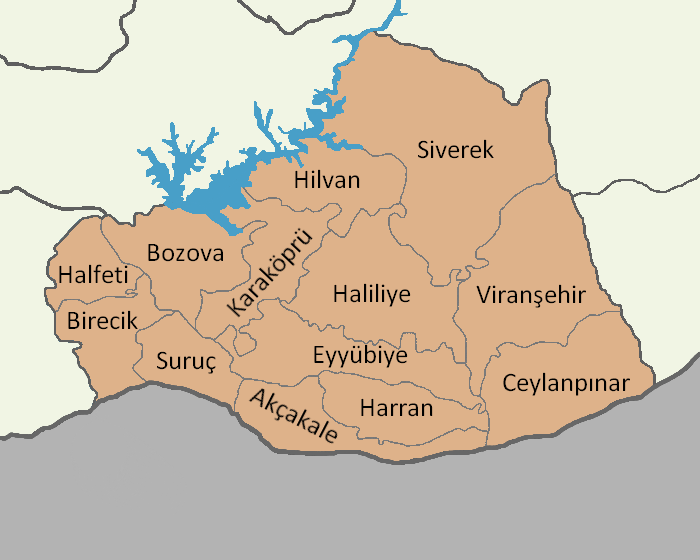
Karaköprü
Karaköprü ( ku, Pira Reş) is a district and second level municipality in Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Its eponymous city center is slightly north from central Urfa. In the local elections of March 2019, Metin Baydilli was elected Mayor of Karaköprü. The current Kaymakam is Ufuk Akıl. According to the 2012 Metropolitan Municipalities Law (Law No. 6360), all Turkish provinces with a population of more than 750,000, will become metropolitan municipalities and the districts within the metropolitan municipalities will be second level municipalities. The law also creates new districts within the provinces in addition to present districts. Therefore, in 2014, the Şanlıurfa Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features ... (Urfa) central district was split into three sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Şanlıurfa Province
Şanlıurfa Province ( tr, Şanlıurfa ili; ku, Parêzgeha Rihayê) or simply Urfa Province is a province in southeastern Turkey. The city of Şanlıurfa is the capital of the province which bears its name. The population is 1,845,667 (2014). The province is considered part of Turkish Kurdistan and has a Kurds, Kurdish majority with a significant Arabs, Arab and Turkish people, Turkish minority. Districts Şanlıurfa province is divided into 13 Districts of Turkey, districts (capital district in bold): * Urfa (Central district. In 2014 it was split into three districts: Eyyübiye, Haliliye and Karaköprü.) * Akçakale * Birecik * Bozova * Ceylanpınar * Halfeti * Harran * Hilvan * Siverek * Suruç * Viranşehir Geography Area 18,584 km2 (7,173 sq. miles), the largest province of Southeast Anatolia with: * Adıyaman to the north; * Syria to the south; * Mardin and Diyarbakır to the east; * Gaziantep to the west; Şanlıurfa includes several major components of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TÜİK
Turkish Statistical Institute (commonly known as TurkStat; tr, Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu or TÜİK) is the Turkish government agency commissioned with producing official statistics on Turkey, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It was founded in 1926 and has its headquarters in Ankara Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki .... Formerly named as the State Institute of Statistics (Devlet İstatistik Enstitüsü (DİE)), the Institute was renamed as the Turkish Statistical Institute on November 18, 2005. References External linksOfficial website of the institute National statistical services Statistical Organizations established in 1926 Organizations based in Ankara {{Sci-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urfa
Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features extremely hot, dry summers and cool, moist winters. About northeast of the city is the famous Neolithic site of Göbekli Tepe, the world's oldest known temple, which was founded in the 10th millennium BC. The area was part of a network of the first human settlements where the agricultural revolution took place. Because of its association with Jewish, Christian, and Islamic history, and a legend according to which it was the hometown of Abraham, Urfa is nicknamed the "City of Prophets." Religion is important in Urfa. The city "has become a center of fundamentalist Islamic beliefs" and "is considered one of the most devoutly religious cities in Turkey". The city is located 30 miles from the Atatürk Dam, at the heart of the Southeast Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siverek
Siverek (from hy, Սեւավերակ, lit=black ruins, translit=Sevaverag, ku, Sêwreg) is a city and district in the south-east of Turkey, in Şanlıurfa Province. Population 107,634 (city); 247,000 (district) (2000 census). Siverek is in Şanlıurfa province but closer geographically to the large city of Diyarbakır (approx 83 km). History Siverek was historically known in medieval Arabic as Hisn ar-Ran, which was corrupted into Greek Chasanara ( gr, Χασαναρᾶ) as found in the Escorial Taktikon. The town came under Byzantine control sometime after 956 and by the early 970s had become the seat of a strategos. In the Ottoman Empire period Siverek was within the Diyarbekir vilayet, and it had several Christian settlements. Climate Siverek has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: ''Csa''). Politics In common with other districts of Şanlıurfa, business and politics in Siverek are strongly influenced, even controlled, by a powerful c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthostat
This article describes several characteristic architectural elements typical of European megalithic (Stone Age) structures. Forecourt In archaeology, a forecourt is the name given to the area in front of certain types of chamber tomb. Forecourts were probably the venue for ritual practices connected with the burial and commemoration of the dead in the past societies that built these types of tombs. In European megalithic architecture, forecourts are curved in plan with the entrance to the tomb at the apex of the open semicircle enclosure that the forecourt creates. The sides were built up by either large upright stones or walls of smaller stones laid atop one another. Some also had paved floors and some had blocking stones erected in front of them to seal the tomb such as at West Kennet Long Barrow. Their shape, which suggests an attempt to focus attention on the tomb itself may mean that they were used ceremonially as a kind of open air auditorium during ceremonies. Excavation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |