|
Gällivare Dialects
Gällivare dialects are a dialect group of Meänkieli or Northern Finnish. They are spoken around Gällivare, but also in Killivaara and Nattavaara. Features of the dialects are absence of Vowel harmony: kyla 'village' (Meänkieli and Finnish: kylä), and the passive being used for the third person plural ending: ''äijät poltethin'' (Finnish: ukot polttivat). The dialect is also heavily influenced by Swedish and many loanwords have entered the Gällivare dialects. A Gällivare dialect dictionary was made in 1992 by Birger Winsa. Features * Passive being used for the third person plural ending * /o/ has changed to /u/ often: isu 'big', (Finnish: iso). * Triphthongs: syöi 'ate'. Example *Oliko tännet tietä ennen? * ei. * eei oles, tie on. jaa, kyllä se on kuuskymmentä vuotta aikaa tullu. * juust vasta tie tehty. * sit ei ol ollu tietä, se on ollu liki Jällivaarhaav viis peniŋkulmaa kantant. * ei se niiv niin ra hauska homma sekkää. * ei ole miellùtta olleŋkha. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gällivare Municipality In Norrbotten County
Gällivare (; fi, Jällivaara; se, Jiellevárri or ; smj, Jiellevárre or ; fit, Jellivaara) is a locality and the seat of Gällivare Municipality in Norrbotten County, province of Lapland, Sweden with 8,449 inhabitants in 2010. The town was founded in the 17th century. Together with nearby towns Malmberget and Koskullskulle it forms a conurbation with some 15,000 inhabitants. This conurbation is the second northernmost significant urban area of Sweden after Kiruna. Gällivare is situated at the northern end of the Inlandsbanan railway line, about 100 kilometres north of the Arctic Circle. Gällivare is located in a major iron ore mining region. Adjacent to Gällivare (about five kilometres) is Malmberget, known as a site for iron ore extraction from deep mines by LKAB. Outside Gällivare lies the ski resort Dundret, which is equipped with six ski lifts and ten groomed slopes along with a conference center and hotel. The ski season stretches from the end of October all the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
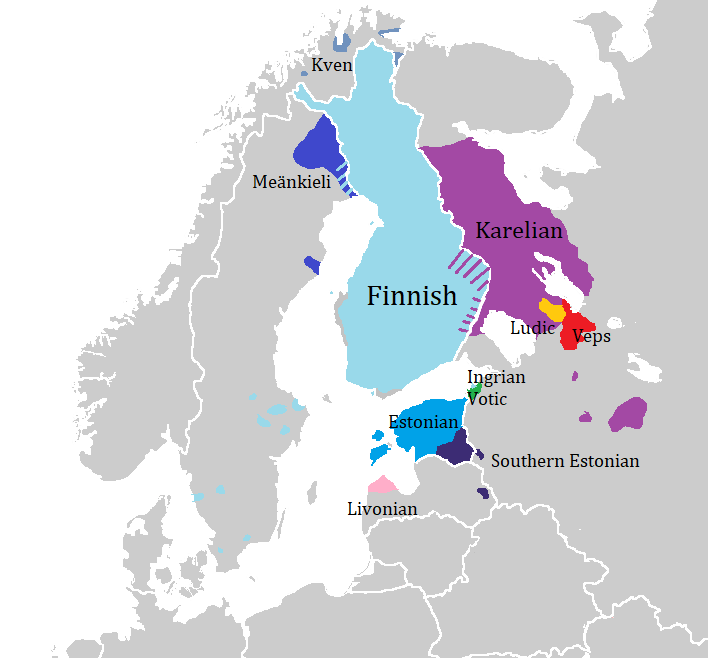
Meänkieli
(literally 'our language') is a group of distinct Finnish language, Finnish dialects or a Finnic languages, Finnic language spoken in the northernmost part of Sweden along the valley of the Torne River. Its status as an independent language is disputed, but in Sweden it is recognized as one of the Official minority languages of Sweden, country's five minority languages. Linguistically, Meänkieli consists of two dialect subgroups, the Torne Valley dialects (also spoken on the Finnish side of the Torne River) and the Gällivare dialects, which both belong to the larger Peräpohjola dialects, Peräpohjola dialect group. For historical and political reasons it has the status of a minority language in Sweden. In modern Swedish language, Swedish the language is normally referred to officially as , although colloquially an older name, ("Torne Valley Finnish"), is still commonly used. Sveriges Radio tends to use for the culture generally and ' specifically for the language. Meänkiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peräpohjola Dialects
The Peräpohjola dialects ( fi, Peräpohjalaiset murteet) are forms of Finnish spoken in Lapland in Finland, Sweden, and Norway. The dialect group belongs to the Western Finnish dialects and it is divided into five more specific dialect groups. Features Like the Northern Ostrobothnian (Oulu) dialects, Peräpohjola dialects are Western dialects that show features from Eastern dialects. For instance the reflex to standard ''-ts-'' in ''metsä'' is ''mettä'' according to a Western pattern, whereas the reflex of standard ''-d-'' is deletion, 'j', or 'v', as in Eastern dialects, e.g. ''vedän'' - ''vejän''. Epenthetic vowels (''tyhjä - tyhyjä'') are not common although found in southern Tornio dialects. There are no vowel or diphthong changes, a Western/standard feature, but there is a general gemination of consonants in short initial syllables (e.g. standard ''makaa'' is ), as in Oulu and Eastern dialects. Palatalization is absent, which is a very Western feature, since palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gällivare
Gällivare (; fi, Jällivaara; se, Jiellevárri or ; smj, Jiellevárre or ; fit, Jellivaara) is a locality and the seat of Gällivare Municipality in Norrbotten County, province of Lapland, Sweden with 8,449 inhabitants in 2010. The town was founded in the 17th century. Together with nearby towns Malmberget and Koskullskulle it forms a conurbation with some 15,000 inhabitants. This conurbation is the second northernmost significant urban area of Sweden after Kiruna. Gällivare is situated at the northern end of the Inlandsbanan railway line, about 100 kilometres north of the Arctic Circle. Gällivare is located in a major iron ore mining region. Adjacent to Gällivare (about five kilometres) is Malmberget, known as a site for iron ore extraction from deep mines by LKAB. Outside Gällivare lies the ski resort Dundret, which is equipped with six ski lifts and ten groomed slopes along with a conference center and hotel. The ski season stretches from the end of October all the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nattavaara
Nattavaara is a minor locality in Gällivare Municipality, Norrbotten County in the province of Lapland in Sweden. The settlement had a permanent population of 114 as of the year 2015. Nattavaara is located by road south of municipal seat Gällivare. That is also the nearest urban area, with Jokkmokk being slightly further away to the southwest. The only paved roads are to the north and the east, whereas the Jokkmokk road transitions into a gravel road just west of the village. The settlement has a station on the rail line between Stockholm and Narvik in Nordland, Norway. Adjacent to the small village is the even smaller settlement of Nattavaara by. Climate Nattavaara has a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') typical of central Lapland. Winters are long, dark and cold with an extensive snow cover, whereas the midnight sun The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is an Assimilation (linguistics), assimilatory process in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – have to be members of the same natural class (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, meaning that the affected vowels do not need to be immediately adjacent, and there can be intervening segments between the affected vowels. Generally one vowel will trigger a shift in other vowels, either progressively or regressively, within the domain, such that the affected vowels match the relevant feature of the trigger vowel. Common phonological features that define the natural classes of vowels involved in vowel harmony include vowel backness, vowel height, nasalization, roundedness, and advanced and retracted tongue root. Vowel harmony is found in many Agglutination, agglutinative languages. The given domain of vowel harmony taking effect often spans across morpheme boundaries, and suffixes and prefixes will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Finnish orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic language spoken predominantly in Sweden and in parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, the fourth most spoken Germanic language and the first among any other of its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is largely dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Written Norwegian and Danish are usually more easily understood by Swedish speakers than the spoken languages, due to the differences in tone, accent, and intonation. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional varieties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Dialects
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Finnish orthog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |