|
György Lépes
György Lépes (1375 – 18 March 1442, Sântimbru, Alba, Marosszentimre) was a Transylvanian Catholic Bishop. Life Lépes was born in what is now Arad County (former), Arad County to a noble family. He was the provost of Transylvania between 1403 and 1417, and was bishop from 1427 to 1442. In 1436, he invited James of the Marches as an inquisitor against the spread of the Hussite movement. In 1437, the Peasant Revolt of Babolna, Budai Nagy Antal revolt broke out because of Lépes' regulations that ordered the serfs to pay the tithe in the new currency of golden coins 3 years after the peasants had silver coins (worth four times more), and also wanted to order the Orthodox Romanians to pay it. The 1438 uprising was brutally crushed by the nobles, and the three estate nations (Hungarian, Székelys, Székely, and Transylvanian Saxons, Saxon) concluded with the Unio Trium Nationum#Brotherly Union (Union of Kápolna), Union of Kápolna. In 1442, Lépes, while leading the fighting again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sântimbru, Alba
Sântimbru ( hu, Marosszentimre; german: Sankt Emmerich) is a Commune in Romania, commune located in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania. It has a population of 2,740, and is composed of five villages: Coșlariu (''Koslárd''), Dumitra (''Demeterpataka''), Galtiu (''Gáldtő''), Sântimbru and Totoi (''Táté''). Following the Mongol invasion of Europe, Transylvanian Saxons settled in Sântimbru in the 13th century. Driven out by Ottomans in the 16th century, they were replaced by Hungarians, who practised woodcutting. Ethnic Romanians have been in the majority since the 19th century, and today, the inhabitants mainly build bricks and raise poultry. The village of Totoi has developed a speech form known as Totoiana which consists in the inversion of Romanian words so that other speakers of normal Romanian cannot understand it. It is unique to the village, and it is not spoken in other parts of Sântimbru. Points of interest The commune has a Hungarian Reformed church founded by J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arad County (former)
Arad County was an administrative unit in the Kingdom of Hungary, the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and the Principality of Transylvania. The county was established along the Maros (Mureș) river in the 11th or the , but its first head, or ''ispán'', was only mentioned in 1214. Its territory is now part of Romania, except a small area (the town of Elek and the surrounding villages) which is part of Hungary. The capital of the county was Arad. Geography The medieval Arad County was situated in the lands along both banks of the Maros (Mureș) River. The existence of arable lands, pastures, vineyards and orchards in the western lowlands in the Middle Ages is well-documented. The hilly eastern regions were sparsely populated. The total territory of the medieval county was around . In 1744, Arad County absorbed a large part of Zaránd County, including its capital Zaránd/Zărand (the remainder of Zarand County was then reorganized, with Körösbánya/Baia de Criș as the new ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Of The Marches
Jacob de Marchia ( la, Jacobus de Marchia, it, Giacomo della Marca; c. 1391 – 28 November 1476), commonly known in English as Saint James of the Marches, was an Italian Friar Minor, preacher and writer. He was a Papal legate and Inquisitor. Early life He was born Dominic Gangala ( it, Domenico Gangala) in the early 1390s to a poor family in Monteprandone, then in the March of Ancona (now in Ascoli Piceno) in central Italy along the Adriatic Sea. As a child, he began his studies at Offida under the guidance of his uncle, a priest, who soon afterwards sent him to school in the nearby city of Ascoli Piceno. He later studied at the University of Perugia where he took the degree of Doctor in Canon and Civil Law. After a short stay at Florence as tutor for a noble family, and as judge of sorcerers, he was received into the Order of Friars Minor, in the chapel of the Portiuncula, in Assisi, on 26 July 1416. At that time, he took the monastic name Jacobus (Jacob, Jacopo; rendered Jam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussite Movement
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation. The Hussite movement began in the Kingdom of Bohemia and quickly spread throughout the remaining Lands of the Bohemian Crown, including Moravia and Silesia. It also made inroads into the northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary (now Slovakia), but was rejected and gained infamy for the plundering behaviour of the Hussite soldiers.Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 52.Kirschbaum 2005, p. 48. There were also very small temporary communities in Poland-Lithuania and Transylvania which moved to Bohemia after being confronted with religious intolerance. It was a regional movement that failed to expand anywhere farther. Hussites emerged as a majority Utraquist movement with a significant Taborite faction, and smaller regional ones that included Adamites, Orebites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasant Revolt Of Babolna
The Transylvanian peasant revolt ( hu, erdélyi parasztfelkelés), also known as the peasant revolt of Bábolna or Bobâlna revolt ( ro, Răscoala de la Bobâlna), was a popular revolt in the eastern territories of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1437. The revolt broke out after George Lépes, bishop of Transylvania, had failed to collect the tithe for years because of a temporary debasement of the coinage, but then demanded the arrears in one sum when coins of higher value were again issued. Most commoners were unable to pay the demanded sum, but the bishop did not renounce his claim and applied interdict and other ecclesiastic penalties to enforce the payment. The Transylvanian peasants had already been outraged because of the increase of existing seigneurial duties and taxes and the introduction of new taxes during the first decades of the century. The bishop also tried to collect the tithe from the petty noblemen and from Orthodox Vlachs who had settled in parcels abandoned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
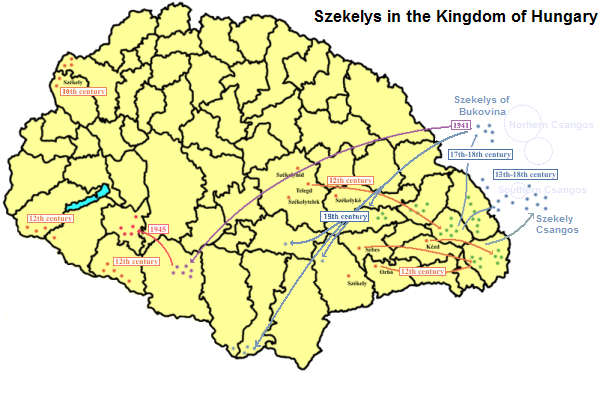
Székelys
The Székelys (, Székely runes: 𐳥𐳋𐳓𐳉𐳗), also referred to as Szeklers,; ro, secui; german: Szekler; la, Siculi; sr, Секељи, Sekelji; sk, Sikuli are a Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. A significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina lives in Tolna and Baranya counties in Hungary and certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In the Middle Ages, the Székelys played a role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottomans in their posture as guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the Székely Land) became part of Romania, and the Székely population was a target of Romanianization efforts. In 1952, during the communist rule of Romania, the former counties with the highest concentration of Székely population – Mureș, Odorhei, Ciuc, and Trei Scaune – were legally designated as the Magyar Autonomous Region. It was superseded in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania (german: Siebenbürgen) in waves starting from the mid- 12th century until the mid 19th century. The legal foundation of the settlement was laid down in the Diploma Andreanum issued by King Andrew II of Hungary that is known for providing the first territorial autonomy hitherto in the history. The Transylvanian "Saxons" originally came from Flanders, Hainaut, Brabant, Liège, Zeeland, Moselle, Lorraine, and Luxembourg, then situated in the north-western territories of the Holy Roman Empire around the 1140s. After 1918 and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, in the wake of the Treaty of Trianon, Transylvania united with the Kingdom of Romania. Consequently, the Transylvanian Saxons, together with other ethnic German sub-groups in newly e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unio Trium Nationum
Unio Trium Nationum (Latin for "Union of the Three Nations") was a pact of mutual aid codified in 1438 by three Estates of Transylvania: the (largely Hungarian) nobility, the Saxon (German) patrician class, and the free military Székelys. The union was directed against the whole of the peasantry, regardless of ethnicity, in response to the Transylvanian peasant revolt. László Fosztó: ''Ritual Revitalisation After Socialism: Community, Personhood, and Conversion among Roma in a Transylvanian Village'', Halle-Wittenberg, 200 In this typical feudal estate parliament, the peasants (whether Hungarian, Saxon, Székely or Romanian in origin) were not represented, and they did not benefit from its acts, as the commoners were not considered to be members of these feudal "nations". Background Medieval administrative structure in Transylvania In medieval times, Transylvania was organised into two separate types of territorial units: the Noble Counties ( Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hermannstadt
The Battle of Hermannstadt, also known as the Battle of Sibiu or the Battle of Szeben, was fought between the army of the Hungarian Kingdom and the Ottoman Empire on March 18 and March 22, 1442, near Marosszentimre and Hermannstadt (Szeben), (today Sântimbru and Sibiu, Romania). The Hungarian forces were commanded by John Hunyadi. Hermannstadt was Hunyadi's third victory over the Ottomans after the relief of Smederevo in 1437 and the defeat of Ishak Beg midway between Semendria and Belgrade in 1441. Background In 1438 Ottoman marauders attacked Transylvania, where in 1437 the Ottomans had been beaten by an uprising under Antal Nagy de Buda. For up to 45 days the Ottomans without let or hindrance attacked the Transylvanian Saxon lands and Hungarian villages and market towns. In 1441 John Hunyadi came to power. Hunyadi attacked the Ottomans in Serbia and at the Battle of Smederevo got the best of Ishak bey. The Ottoman Sultan, Murad II, proclaimed in the autumn of 1441 that a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Pallas Nagy Lexikona
''A Pallas nagy lexikona'' (''Pallas's Great Encyclopedia'') was the first Hungarian encyclopedia which was not a translation from other languages. It was published by the Pallas Literary and Press Corporation between 1893 and 1897. The encyclopedia comprised 16 volumes, 150 000 articles, and it was the work of 300 authors. History ''A Pallas nagy lexikona'' (literally Pallas's large encyclopedia) is a great universal encyclopedia in Hungarian. It gradually developed in the years 1893 to 1897 in Budapest Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population .... In 1900 it was issued as two parts, but the Encyclopedia eventually reached a total of 18 volumes containing more than 150,000 entries. Chief editor was József Bokor. The authors were renowned Hungarian scientists, most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1375 Births
Year 1375 (Roman numerals, MCCCLXXV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * April 14 – The Mamluks from Egypt complete their conquest of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia. Levon V Lusignan of Armenia is imprisoned for several years in Cairo, until a ransom is paid by King John I of Castile. * April 21 – Mujahid Shah succeeds his father, Mohammed Shah I, as ruler of the Bahmani Sultanate in the Deccan Plateau of southern India. * June 18 – The future King John I of Castile marries Eleanor of Aragon, Queen of Castile, Eleanor of Aragon. * June 27 – Hundred Years' War: The England, English, weakened by the plague, lose so much ground to the France, French that they agree to sign the Treaty of Bruges (1375), Treaty of Bruges, leaving them with only the coastal towns of Calais, Bordeaux and Bayonne. * October 24 – Margaret I of Denmark becomes Regent of Denmark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1442 Deaths
144 may refer to: * 144 (number), the natural number following 143 and preceding 145 * AD 144, a year of the Julian calendar, in the second century AD * 144 BC, a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar * ''144'' (film), a 2015 Indian comedy * ''144'' (video game), working title of ''The Path'', a psychological horror art game * 144 (New Jersey bus), a bus route in New Jersey, USA * Volvo 144, the main 4-door sedan model of the Volvo 140 Series * Worcestershire bus route 144 Worcestershire bus route 144 is a bus service connecting the Worcestershire areas of Catshill, Bromsgrove. Droitwich and Worcester, operated by First Worcestershire. The service dates back to 1914 and was one of the longest-running double-deck ... See also * List of highways numbered 144 * {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |