|
Gymnocanthus Pistilliger
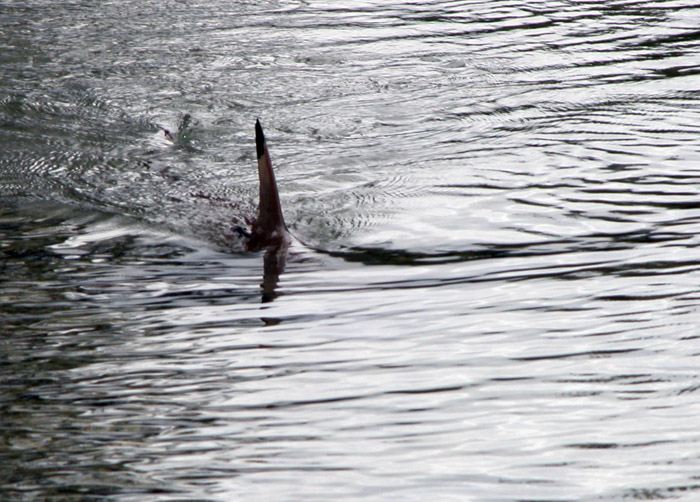
''Gymnocanthus pistilliger'', the threaded sculpin, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species occurs in the northern Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy ''Gymnocanthus pistilliger'' was first formally described as ''Cottus pistilliger'' in 1815 by the German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas with the type locality given as Unalaska Island and Port Avatsch. In 1829 the French zoologist Georges Cuvier described a new species, ''Cottus ventralis'', from Kamchatka and in 1839 the English zoologist William John Swainson classified this taxon within the monospecific genus ''Gymnocanthus''. Cuvier's ''C. ventralis'' has since been regarded as a synonym of Pallas's ''C. pistilliger''. The specific name ''pistilliger'' means "to bear pistils", a reference to the axillary papillae of the males. Description ''Gymnocanthus pistilliger'' has dorsal fins supported by between 9 and 11 spines and between 13 and 16 soft rays while the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Netherlands and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new system of animal classification was praised by Georges Cuvier. Pallas wrote ''Miscellanea Zoologica'' (1766), which included descriptions of several vertebrates new to science which he had discovered in the Dutch museum collections. A planned voyage to southern Africa and the East Indies fell through when his father reca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through convergent evolution they have independently evolved external superficial fish-like body plans adapted to their marine environments, including most numerously fish, but also mammals such as cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises), and even extinct ancient marine reptiles such as various known species of ichthyosaurs. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of large cetaceans to identify individuals in the field. The bony or cartilaginous bones that support the base of the dorsal fin in fish are called ''pterygiophores''. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is to stabilize the animal against rollin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spawning
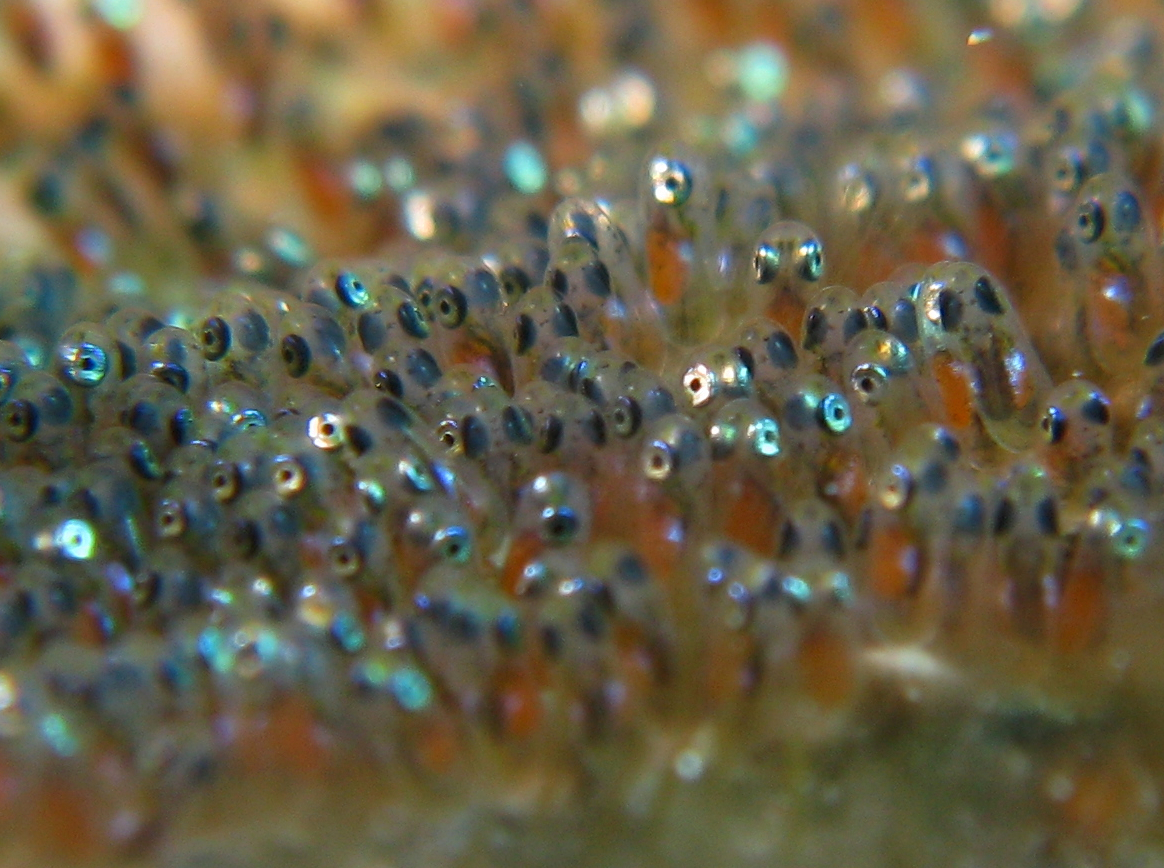
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquatic mammals and reptiles, reproduce through the process of spawning. Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of many aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs. Most fish reproduce by spawning, as do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mosquitoes and corals, which are actually small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an ''insular shelf''. The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores of a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crangonidae
Crangonidae is a family of shrimp, of the superfamily Crangonoidea, including the commercially important species ''Crangon crangon''. Its type genus is ''Crangon''. Twenty-four genera are included in the family: *'' Aegaeon'' Agassiz, 1846 *''Argis'' Krøyer, 1842 *''Crangon'' Fabricius, 1798 *'' Lissocrangon'' Kuris & Carlton, 1977 *'' Lissosabinea'' Christoffersen, 1988 *'' Mesocrangon'' Zarenkov, 1965 *''Metacrangon'' Zarenkov, 1965 *†'' Morscrangon'' Garassino & Jakobsen, 2005 *''Neocrangon ''Neocrangon'' is a genus of crustaceans belonging to the family Crangonidae. Its native range is Northern America and Japan. Species: *''Neocrangon abyssorum'' *''Neocrangon communis'' *''Neocrangon geniculata'' *''Neocrangon joloensis'' ...'' Zarenkov, 1965 *'' Notocrangon'' Coutière, 1900 *'' Paracrangon'' Dana, 1852a *'' Parapontocaris'' Alcock, 1901 *'' Parapontophilus'' Christoffersen, 1988 *'' Philocheras'' Stebbing, 1900 *'' Placopsicrangon'' Komai & Chan, 2009 *'' P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class (biology), class of generally marine invertebrate, marine annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gammaridae
Gammaridae is a family of amphipods. In North America they are included among the folk taxonomic category of " scuds", and otherwise gammarids is usually used as a common name. They have a wide distribution, centered on Eurasia, and are euryhaline as a lineage, inhabiting fresh to marine waters. Systematics The Gammaridae were for a long time used as a "wastebin taxon", which included numerous genera of gammaridean amphipods that since then have been removed to their own families, such as the Anisogammaridae, Melitidae, Niphargidae. The following genera are currently listed in the family: *'' Akerogammarus'' Derzhavin & Pjatakova, 1967 *'' Albanogammarus'' Ruffo, 1995 *'' Amathillina'' G. O. Sars, 1894 *'' Axelboeckia'' Stebbing, 1899 *''Baku'' Karaman & Barnard, 1979 *'' Cephalogammarus'' Karaman & Barnard, 1979 *'' Chaetogammarus'' Martynov, 1924 *'' Comatogammarus'' Stock, 1981 *'' Condiciogammarus'' G. Karaman, 1984 *'' Dershavinella'' Birstein, 1938 *'' Dikerogamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutians
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude ( Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude (Semisopochnoi Island). The westernmost U.S. island in real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiska
Kiska ( ale, Qisxa, russian: Кыска) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is required to visit it. The island has no permanent population. History European Discovery (1741) In 1741 while returning from his second voyage at sea during the Great Northern Expedition, Danish-born Russian explorer Vitus Bering made the first European discovery of most of the Aleutian Islands, including Kiska. Georg Wilhelm Steller, a naturalist-physician aboard Bering's ship, wrote: ''On 25 October 1741 we had very clear weather and sunshine, but even so it hailed at various times in the afternoon. We were surprised in the morning to discover a large tall island at 51° to the north of us.'' Prior to European contact, Kiska Island had been densely populated by native peoples for thousands of years. After Discovery (1741–1939) Kis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norton Sound
Norton Sound (russian: Нортон-Саунд) is an inlet of the Bering Sea on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, south of the Seward Peninsula. It is about 240 km (150 mi) long and 200 km (125 mi) wide. The Yukon River delta forms a portion of the south shore and water from the Yukon influences this body of water. It is ice-free from June to October. Norton Sound was explored by Captain James Cook in September 1778. He named the body of water after Sir Fletcher Norton, then Speaker of the British House of Commons. The Norton Sound area has been home to Yup'ik and Inupiat for many centuries. It is the boundary between the two peoples; the Inupiat live to the north and the Yup'ik to the south. The town of Nome is along the northern edge of Norton Sound. The villages of Elim, Golovin, Stebbins, White Mountain, Koyuk, Shaktoolik, St. Michael, and Unalakleet are on the shores or waterways flowing into Norton Sound. The Iditarod Trail Sled Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
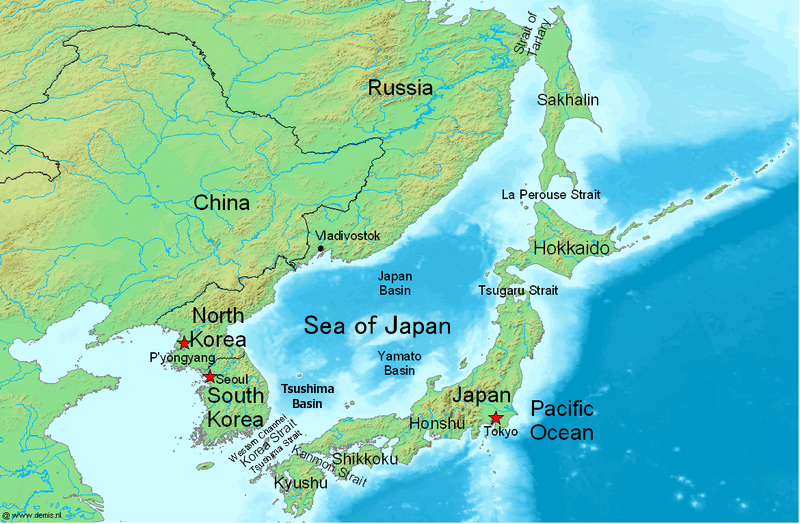
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies. These data are used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fisheries biology. Overall length * Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. Simply put, this measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. * Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys), and (usually) Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays), as well as some other fishes. Total length me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |