|
Guy Newland
Guy Martin Newland (born 1955) is a scholar of Tibetan Buddhism who has been a professor at Central Michigan University in Mount Pleasant, Michigan since 1988. He served as Chairperson of Central Michigan University's Department of Philosophy and Religion during the periods 2000–2003, 2006–2009, and 2016-. He was elected to the Mount Pleasant Board of Education in July 2003 and served until December 2007, including six months as President of the Board and one year as Secretary. Newland received his PhD from the University of Virginia, where he was a student of Jeffrey Hopkins. Publications In 2016, Newland published a personal memoir: ''A Buddhist Grief Observed'' (Wisdom Publications, 2016). Newland has authored, translated, and edited a number of publications on Tibetan Buddhism, including: *''Moonpaths: Ethics and Emptiness'' by the Cowherds (a scholarly collective producing work collaboratively, including Guy Newland, Jay Garfield, Tom Tillemans, Jan Westerhoff, and sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majority regions surrounding the Himalayan areas of India (such as Ladakh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and a minority in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), in much of Central Asia, in the southern Siberian regions such as Tuva, and in Mongolia. Tibetan Buddhism evolved as a form of Mahāyāna Buddhism stemming from the latest stages of Indian Buddhism (which also included many Vajrayāna elements). It thus preserves many Indian Buddhist tantric practices of the post-Gupta early medieval period (500 to 1200 CE), along with numerous native Tibetan developments. In the pre-modern era, Tibetan Buddhism spread outside of Tibet primarily due to the influence of the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), founded by Kublai Khan, which had ruled China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Michigan University
Central Michigan University (CMU) is a public research university in Mount Pleasant, Michigan. Established in 1892 as the Central Michigan Normal School and Business Institute, the private normal school became a state institution and renamed Central State Normal School in 1895 after the Michigan State Board of Education took over governance of the school. The institution came into its own as a university and gained its current name Central Michigan University in 1959 under the university's 6th president Judson W. Foust. CMU is one of the eight research universities in Michigan and is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". It has more than 15,000 students on its Mount Pleasant campus. CMU offers 200 academic programs at the undergraduate, master's, specialist, and doctoral levels, including programs in entrepreneurship, journalism, music, audiology, teacher education, psychology, and physician assistant. The School of Engineering and Technology h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
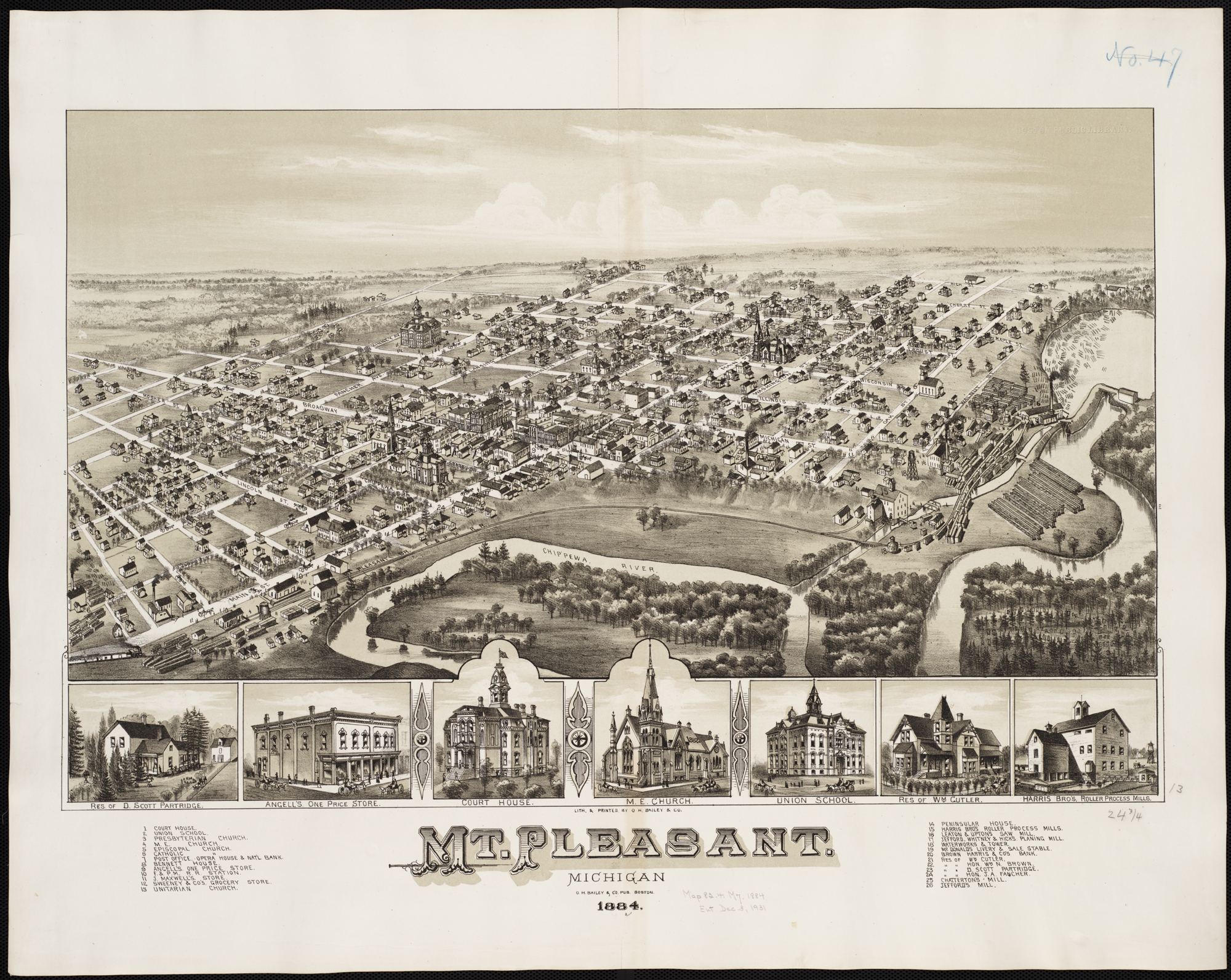
Mount Pleasant, Michigan
Mount Pleasant is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. Located in Central Michigan, the city is the county seat of Isabella County. The population was 21,688 as of the 2020 United States census. It is surrounded by Union Township but is politically independent. Part of the city (with a population of 8,741) is located within the Isabella Indian Reservation, the base of the federally recognized Saginaw Chippewa Tribal Nation. The tribe's Soaring Eagle Casino & Resort in nearby Chippewa Township is also within the reservation boundaries. The city is home to the main campuses of Central Michigan University, one of the largest universities in the state with 20,000 students at Mount Pleasant, and Mid Michigan Community College. The student population nearly doubles the population of the city during the academic year, making it a college town. Despite its name, the surrounding area is mostly flat and does not feature any mountains or hills. History Until the mid-19th century, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Religion
Philosophy of religion is "the philosophical examination of the central themes and concepts involved in religious traditions". Philosophical discussions on such topics date from ancient times, and appear in the earliest known texts concerning philosophy. The field is related to many other branches of philosophy, including metaphysics, epistemology, and ethics.Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy"Philosophy of Religion."/ref> The philosophy of religion differs from religious philosophy in that it seeks to discuss questions regarding the nature of religion as a whole, rather than examining the problems brought forth by a particular belief-system. It can be carried out dispassionately by those who identify as believers or non-believers. Overview Philosopher William L. Rowe characterized the philosophy of religion as: "the critical examination of basic religious beliefs and concepts." Philosophy of religion covers alternative beliefs about God or gods or both, the varieties of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Education
A board of education, school committee or school board is the board of directors or board of trustees of a school, local school district or an equivalent institution. The elected council determines the educational policy in a small regional area, such as a city, county, state, or province. Frequently, a board of directors power with a larger institution, such as a higher government's department of education. The name of such board is also often used to refer to the school system under such board's control. The government department that administered education in the United Kingdom before the foundation of the Ministry of Education An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ... was formerly called the Board of Education. See also * National Association of State Boards of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with College admissions in the United States, highly selective admission. Set within the The Lawn, Academical Village, a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site, the university is referred to as a "Public Ivy" for offering an academic experience similar to that of an Ivy League university. It is known in part for certain rare characteristics among public universities such as #1800s, its historic foundations, #Honor system, student-run academic honor code, honor code, and Secret societies at the University of Virginia, secret societies. The original governing Board of Visitors included three List of presidents of the United States, U.S. presidents: Thomas Jefferson, Jefferson, James Madison, and James Monroe. The latter as si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Hopkins
Jeffrey Hopkins (born 1940) is an American Tibetologist. He is Emeritus professor of Tibetan and Buddhist Studies at the University of Virginia, where he taught for more than three decades since 1973. He has authored more than twenty-five books about Tibetan Buddhism, among them the highly influential ''Meditation on Emptiness'', which appeared in 1983, offering a pioneering exposition of Prasangika-Madyamika thought in the Geluk tradition. From 1979 to 1989 he was the Dalai Lama's chief interpreter into English and he played a significant role in the development of the Free Tibet Movement. In 2006 he published his English translation of a major work by the Jonangpa lama, Dolpopa, on the Buddha Nature and Emptiness called ''Mountain Doctrine''.Jeffrey Hopkins, ''Mountain Doctrine: Tibet's Fundamental Treatise on Other-Emptiness and the Buddha Matrix'', Snow Lion, 2006 Works * *''Maps of the Profound: Jam-Yang-Shay-Ba's Great Exposition of Buddhist and Non-Buddhist Views on the Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Je Tsongkhapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism.Tsong khapa (2006), pp. ix-x. He is also known by his ordained name Losang Drakpa (, Skt. Sumatikīrti) or simply as "Je Rinpoche" (, "Precious Lord"). He is also known by Chinese as Zongkapa Lobsang Zhaba or just Zōngkàbā (宗喀巴). Tsongkhapa was born in Amdo, the son of a Tibetan Longben Tribal leader who also once served as an official of the Yuan Dynasty. As a monk, he studied under numerous teachers of the various Tibetan Buddhist traditions which flourished in central Tibet, including Sakya, Jonang, Kagyu and Kadam. Tsongkhapa was a prolific author with a broad knowledge of Buddhist philosophy, logic, hermeneutics and practice. He wrote numerous works on madhyamaka philosophy (such as ''Ocean of Reasoning,'' a comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Editing
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, organisation, and many other modifications performed with an intention of producing a correct, consistent, accurate and complete piece of work. The editing process often begins with the author's idea for the work itself, continuing as a collaboration between the author and the editor as the work is created. Editing can involve creative skills, human relations and a precise set of methods. There are various editorial positions in publishing. Typically, one finds editorial assistants reporting to the senior-level editorial staff and directors who report to senior executive editors. Senior executive editors are responsible for developing a product for its final release. The smaller the publication, the more these roles overlap. The top editor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama (, ; ) is a title given by the Tibetan people to the foremost spiritual leader of the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" school of Tibetan Buddhism, the newest and most dominant of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. The 14th and current Dalai Lama is Tenzin Gyatso, who lives as a refugee in India. The Dalai Lama is also considered to be the successor in a line of tulkus who are believed to be incarnations of Avalokiteśvara, the Bodhisattva of Compassion. Since the time of the 5th Dalai Lama in the 17th century, his personage has always been a symbol of unification of the state of Tibet, where he has represented Buddhist values and traditions. The Dalai Lama was an important figure of the Geluk tradition, which was politically and numerically dominant in Central Tibet, but his religious authority went beyond sectarian boundaries. While he had no formal or institutional role in any of the religious traditions, which were headed by their own high lamas, he was a unifying sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamrim
Lamrim (Tibetan: "stages of the path") is a Tibetan Buddhist textual form for presenting the stages in the complete path to enlightenment as taught by Buddha. In Tibetan Buddhist history there have been many different versions of ''lamrim'', presented by different teachers of the Nyingma, Kagyu and Gelug schools. However, all versions of the ''lamrim'' are elaborations of Atiśa's 11th-century root text '' A Lamp for the Path to Enlightenment'' (''Bodhipathapradīpa''). History When Atiśa, the originator of the ''lamrim'' came from India to Tibet, he was asked by king Jang Chub Ö to give a complete and easily accessible summary of the doctrine in order to clarify wrong views, especially those resulting from apparent contradictions across the sutras and their commentaries. Based upon this request he wrote the ''Bodhipathapradīpa'' ("A Lamp for the Path to Awakening"), teaching what came to be known as the ''lamrim'' for the Tibetans. Atiśa's presentation of the doctrine later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Mount Pleasant, Michigan
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg/1200px-Tibetan_Buddhism_(214837929).jpeg)


.jpg)

_1938.jpg)