|
Guy II, Marquis Of Namur
Guy II (1312 – 12 March 1336) was Count of Namur from 1335 to 1336. He was the second son of John I, Marquis of Namur, and Mary of Artois. He participated in 1332 on the side of the Count of Flanders against the Duke of Brabant, in the war over Mechelen. He succeeded his brother John II as Count of Namur on 2 April 1335. Under influence of his younger brother Robert of Namur, he recognized King Edward III of England as his Lord, in exchange for a pension. He also participated in the War against Scotland with 300 men, but was surprised by a larger Scottish force under John Randolph, 3rd Earl of Moray in the Battle of Boroughmuir The Battle of Boroughmuir was fought on 30 July 1335 between Guy, Count of Namur, a cousin of Queen Philippa of England, and John Randolph, 3rd Earl of Moray and Guardian of Scotland. Namur was on his way to join Edward III on his invasion .... Guy was taken prisoner, but released for ransom. After his return to Namur, he participated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Dampierre
The House of Dampierre played an important role during the Middle Ages. Named after Dampierre, in the Champagne region, where members first became prominent, members of the family were later Count of Flanders, Count of Nevers, Counts and Dukes of Rethel, Count of Artois and Count of Franche-Comté. Guy II of Dampierre, with his wedding with Mathilde of Bourbon, became also lord of Bourbon and founded the House of Bourbon-Dampierre. The senior line of the House came to an end with the death of Margaret III in March 1405. She was succeeded in Flanders, Artois, Nevers and Franche-Comté by her eldest son John the Fearless and in Rethel by her younger son Anthony, which marked the start of the House of Valois-Burgundy. The junior line, springing from a younger son of Guy I reigning in Namur, ended in 1429. The earliest known member of the House of Dampierre is Guy I of Dampierre, great-grandson of Guy I of Montlhéry through his son Milo I of Montlhéry. The members of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I, Marquis Of Namur
John I (1267 – 31 January 1330) was the count of Namur from 1305 to 1330. He was a member of the House of Dampierre, the son of Guy of Dampierre, Count of Flanders and Marquis of Namur, and his second wife Isabelle of Luxembourg. John was the father of Blanche of Namur, Queen of Sweden and Norway. He was the elder brother of Guy of Namur, whom he sent to command the Flemish rebels against the French Kingdom in the 1302 Battle of the Golden Spurs. Life In September 1290, he was betrothed to Blanche of France, daughter of Philip III. Instead, John married Margaret of Clermont, daughter of Robert, Count of Clermont and Beatrix, Dame de Bourbon, in 1307. He was Margaret's second husband. She died after two years of marriage, in 1309. John's second wife was Marie of Artois (1291 – 22 January 1365, Wijnendaele), (later to become Lady of Merode), daughter of Philip of Artois and Blanche of Brittany. They were married by contract in Paris on 6 March 1310, confirmed Poiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
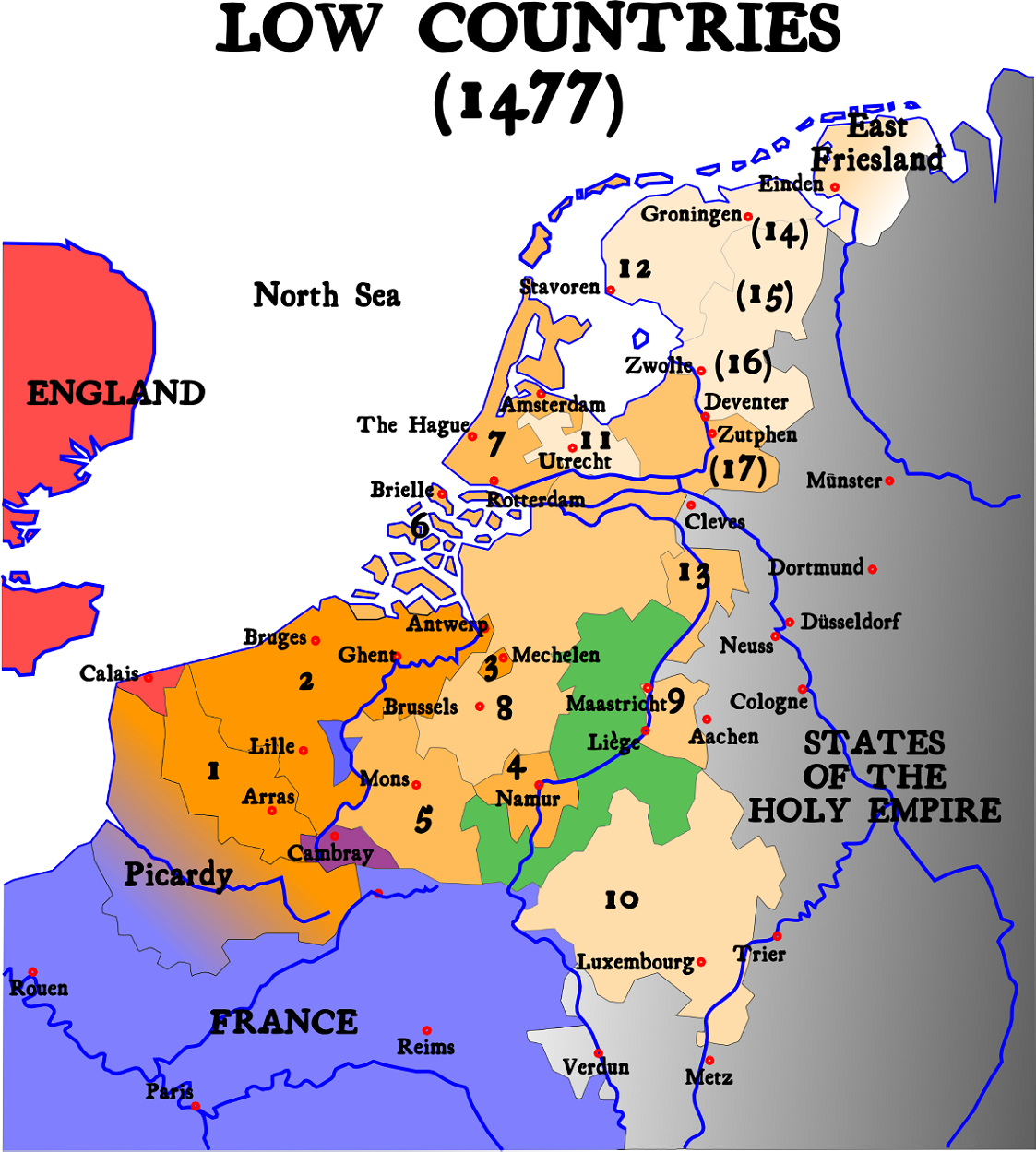
Counts Of Namur
The County of Namur was not often an independent state, rather under the dominion of other entities like the counties of Hainaut and Flanders or the Duchy of Burgundy. Succession is from father to son, unless otherwise noted. Counts House of Namur * Robert I (r. 946 – 981) * Albert I (r. 992 – 1010) * Robert II (r. 1010 – 1018?) * Albert II (r. 1018? – 1067) * Albert III (r. 1067 – 1102) * Godfrey I (r. 1102 – 1139) * Henry I ''the Blind'' (r. 1139 – 1189) ** Alice, sister of, married Baldwin IV, Count of Hainaut Marquises House of Flanders * Baldwin I (r. 1189 – 1195), nephew of * Philip I (r. 1195 – 1212) * Yolanda (r.1212 – 1217), sister of, also Empress of the Latin Empire as Yolanda I, married Peter II of Courtenay House of Courtenay * Philip II (r. 1217 – 1226) * Henry II (r. 1226 – 1229), brother of * Margaret (r. 1229 – 1237), sister of * Baldwin II (r. 1237 – 1256), brother of, also Emperor of the Latin Empire as Baldwin II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the county of Flanders was annexed to France and ceased to exist. In the 19th century, the title was appropriated by Belgium and granted twice to younger sons of Belgian kings. The most recent holder died in 1983. In 862 Baldwin I was appointed as the first Margrave of Flanders by King Charles II. It was a military appointment, responsible for repelling the Viking raids from the coast of Francia. The title of margrave (or marquis) evolved into that of count. Arnulf I was the first to name himself as count, by the Grace of God. The title of margrave largely fell out of use by the 12th century. Since then, the rulers of Flanders have only been referred to as counts. The counts of Flanders enlarged their estate through a series of diploma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Brabant
The Duke of Brabant (, ) was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven (who was duke of Lower Lorraine at that time). The Duchy of Brabant was a feudal elevation of the existing (since 1085/1086) title of landgrave of Brabant. This was an Imperial fief which was assigned to Count Henry III of Leuven shortly after the death of the preceding count of Brabant, Herman II of Lotharingia (born 20 September 1085). Although the corresponding county was quite small (limited to the territory between the rivers Senne and Dender) its name was applied to the entire country under control of the dukes from the 13th century on. In 1190, after the death of Godfrey III, Henry I also became duke of Lotharingia. Formerly Lower Lotharingia, this title was now practically without territorial authority, but was borne by the later dukes of Brabant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. The city's French name ' had also been used in English in the past (in the 19th and 20th century) however this has largely been abandoned. Meanwhile, the Dutch derived ' began to be used in English increasingly from late 20th century onwards, even while ''Mechlin'' remained still in use (for example a ''Mechlinian'' is an inhabitant of this city or someone seen as born-and-raised there; the term is also the name of the city dialect; as an adjective ''Mechlinian'' may refer to the city or to its dialect.) is a city and municipality in the province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Mechelen proper, some quarters at its outskirts, the hamlets of (adjacent) and (a few kilometers away), as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John II, Marquis Of Namur
John II (1311 – 2 April 1335) was Marquis of Namur from 1330 to 1335. He was the eldest son of John I, Marquis of Namur, and Mary of Artois. He succeeded his father on 26 January 1330. He joined an alliance against John III, Duke of Brabant, but by the intervention of King Philip VI of France, a conflict was averted. He died unmarried, but had an illegitimate son Philip, who was killed in 1380, while defending Dendermonde Dendermonde (; french: Termonde, ) is a city in the Flemish province of East Flanders in Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Dendermonde and the towns of Appels, Baasrode, Grembergen, Mespelare, Oudegem, Schoonaarde, and Sint-G .... He was succeeded by his brother Guy. {{DEFAULTSORT:John 02 of Namur 1311 births 1335 deaths House of Dampierre Counts of Namur John 02 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert De Namur
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III Of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. EdwardIII transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign was one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and the throne passed to his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover Roger Mortimer. At age seventeen he led a successful coup d'état against Mortimer, the ''de facto'' ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Randolph, 3rd Earl Of Moray
John Randolph, 3rd Earl of Moray (died 17 October 1346) was an important figure in the reign of David II of Scotland, and was for a time joint Regent of Scotland. Family He was son of the famous Thomas Randolph, 1st Earl of Moray, a companion-in-arms of Robert the Bruce. Upon the death of his elder brother Thomas, 2nd Earl at the Battle of Dupplin Moor in 1332, John succeeded to the earldom. He was brother to Agnes Randolph, Countess of Dunbar, sometimes referred to as "Black Agnes". His sister Isobel's daughter Agnes Dunbar, was the mistress of David II of Scotland. Military campaigns He at once took up arms on behalf of his sovereign and cousin King David II and surprised and defeated Edward Balliol at the Battle of Annan in December 1332. At the Battle of Halidon Hill on 19 July 1333, he commanded the first division of the Scots' Army, supported by Sir Andrew Fraser and his two brothers, Simon and James. Escaping from the carnage there he retired to France. Regency Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boroughmuir
The Battle of Boroughmuir was fought on 30 July 1335 between Guy, Count of Namur, a cousin of Queen Philippa of England, and John Randolph, 3rd Earl of Moray and Guardian of Scotland. Namur was on his way to join Edward III on his invasion of Scotland, when he was intercepted on the common grazing ground to the south of Edinburgh – the Borough Muir. The fighting continued into the city itself, and concluded in a desperate struggle in the ruins of the old castle. Randolph was victorious in a fight which forms a small part of the Second War of Scottish Independence. The Great Invasion Ever since 1332 a part of Anglo-Scots nobles, known collectively as the 'disinherited', had been trying to establish Edward Balliol, son and heir of John Balliol, on the throne of Scotland in place of David II. These men, who had fought against Robert Bruce during the First war of Independence, were given the active support of the English. Yet despite two remarkable victories at the Battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip III, Marquis Of Namur
Philip III (1319 – September 1337 in Famagusta) was Count of Namur from 1336 to 1337. He was the fourth son of John I, Marquis of Namur, and Mary of Artois. When his older brother Guy II, Marquis of Namur, Guy was killed in a tournament in Flanders in March 1336, Philip became his successor. At that time, Philip was in Sweden at the court of his sister Blanche of Namur, Queen consort of Sweden and Norway. From there he traveled to the Holy Land via Cyprus, with his brother-in-law Henry II of Vianden. It is recorded that "Philippus comes Namucensis" (as he was called) donated property to St Alban, in accordance with the testament of "frater noster dominus Guido quondam comes Namucensis", by charter dated 23 Jun 1336. On his stop-over in Famagusta, he and his companions misbehaved so badly that the citizens of Famagusta decided to kill them all. Philip and the Count of Vianden were buried in the Franciscan Order, Franciscan church of Famagusta.Émile de Borchgrave, "Philippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |