|
Guy De Penthièvre
Guy de Bretagne de Penthièvre or Guy VII de Limoges (1287 – March 27, 1331), was Viscount of Limoges from 1314 to 1317 and Count of Penthièvre from 1317 to 1331. Life Guy was born in Chaillot, the second son of the Duke of Brittany Arthur II and Marie, Viscountess of Limoges. Dispute with the Breton Duke Guy's brother Duke John III of Brittany married Isabella of Castile, and as a marriage gift, gave her the viscounty of Limoges. Guy refused to ratify the gift of this property, inherited from their mother, to which he himself had rights. After several years of marriage, while Isabelle remained childless, Duke John III invested his brother in March 1314 with the contested viscounty. Isabelle protested to the Pope, who by a bull on 1 September 1314 invited the Duke to restore her domain. She recovered the viscounty in 1317. John III in turn compensated his brother with the county of Penthièvre. First marriage In 1318, Guy married Jeanne d'Avaugour (1300–1327), la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breton People
The Bretons (; or , ) are an ethnic group native to Brittany, north-western France. Originally, the demonym designated groups of Brittonic speakers who emigrated from southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwall and Devon, mostly during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. They migrated in waves from the 3rd to 9th century (most heavily from 450 to 600) to Armorica. The region was subsequently named after them, as were the inhabitants of Armorica as a whole. The main traditional language of Brittany is Breton (''Brezhoneg''), spoken in Lower Brittany (i.e., the western part of the peninsula). Breton is spoken by around 206,000 people as of 2013. The other principal minority language of Brittany is Gallo; Gallo is spoken only in Upper Brittany, where Breton used to be spoken as well but it has seen a decline and has been less dominant in Upper Brittany since around the year 900. Currently, most Bretons' native language is standard French. Historically, Brittany a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles, Duke Of Brittany
Charles of Blois-Châtillon (131929 September 1364), nicknamed "the Saint", was the legalist Duke of Brittany from 1341 until his death, via his marriage to Joan of Penthièvre, Joan, Duchess of Brittany and Countess of Penthièvre, holding the title against the claims of John of Montfort. The cause of his possible canonization was the subject of a good deal of political maneuvering on the part of his cousin, Charles V of France, who endorsed it, and his rival, John IV, Duke of Brittany, John of Montfort, who opposed it. The cause fell dormant after Pope Gregory XI left Avignon in 1376, but was revived in 1894. Charles of Blois was beatified in 1904. Biography Charles was born in Blois, the son of Guy I of Blois-Châtillon, Guy de Châtillon, count of Blois, by Margaret of Valois, Countess of Blois, Margaret of Valois, a sister of King Philip VI of France. A devout Asceticism, ascetic from an early age, he showed interest in religious books but was forbidden from reading them b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Breton People
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1331 Deaths
Year 1331 ( MCCCXXXI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events September–December * September 8 – Stefan DuÅ¡an declares himself king of Serbia. * September 27 – Battle of PÅowce: The German Teutonic Knights and the Poles battle to a draw. Date unknown * The Sieges of Cividale del Friuli and Alicante begin. * The GenkÅ War begins in Japan. * Ibn Battuta visits Kilwa. * The first recorded outbreak of the Black Death occurs, in the Chinese province of Hubei. Births * February 16 – Coluccio Salutati, Florentine political leader (d. 1406) * April 14 – Jeanne-Marie de Maille, French Roman Catholic saint (b. 1414) * April 30 – Gaston III, Count of Foix (d. 1391) * October 4 – James Butler, 2nd Earl of Ormonde (d. 1382) * ''date unknown'' ** Hamidüddin Aksarayî, Ottoman teacher of Islam (d. 1412) ** Blanche d'Ãvreux, queen consort of France (d. 1398) ** Michael Palaiologos, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1287 Births
Year 1287 ( MCCLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * January 17 – Aragonese forces led by King Alfonso III (the Liberal) conquer the island of Menorca. He signs the "Treaty of San Agayz" with Sultan Abû 'Umar ibn Sa'îd on January 21. Alfonso accepts a policy of free trade for merchants and their property. He also concludes an alliance against the Marinids with Abu Said Uthman I, ruler of the Zayyanid Kingdom of Tlemcen (modern Algeria). He proposes to supply him with five to ten galleys (with food and other goods) in exchange for 500 elite Zayyanid horsemen. * Alfonso III (the Liberal) is forced to make concessions to the nobility after an aristocratic uprising (called the Union of Aragon). In particular, he grants his barons a "Bill of Rights", known as the ''Privilegium Generale''. This leaves a heritage of disunity and further dissent among the nobility, who increasingly see little reason to respe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guingamp
Guingamp (; ) is a commune in the Côtes-d'Armor department in Brittany in northwestern France. With a population of 7,115 as of 2020, Guingamp is one of the smallest towns in Europe to have a top-tier professional football team: En Avant Guingamp, which played in Ligue 1 from 2013 until 2019. Guingamp station is served by high speed trains to Brest, Rennes and Paris, and regional trains to Brest, Lannion, Carhaix, Paimpol and Rennes. History The town has the remains of three successive castles, the last of which was razed to the ground by the order of Cardinal Richelieu in the early 17th century. They were reduced to three towers. Vincent de Bourbon, great-grandson of Louis XIV, was Count of Guingamp from 1750 to his death in 1752. Urbanism Guingamp is an urban commune part of the urban unit of Guingamp with 5 others cities of the department representing 22,049 inhabitants. The commune is also part of the Guingamp functional area. This area, which includes 15 communes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
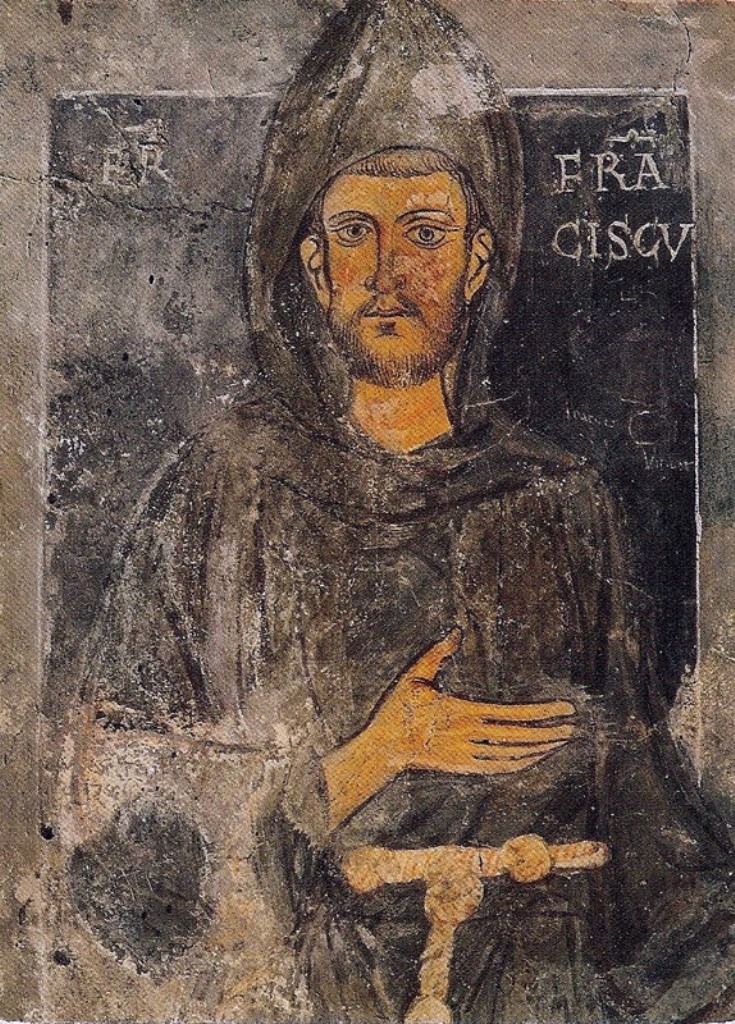
Order Of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (commonly called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; Post-nominal letters, postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a Mendicant orders, mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary, among many others. The Order of Friars Minor is the largest of the contemporary Religious institute#Categorization, First Orders within the Franciscan movement. Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval of his order from Pope Innocent III in 1209. The original Rule of Saint Francis approved by the pope disallowed ownership of property, requiring members of the order to beg for food while preaching. The austerity was meant to emulate the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Franciscans traveled and preached in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip VI Of France
Philip VI (; 1293 â 22 August 1350), called the Fortunate (), the Catholic (''le Catholique'') and of Valois (''de Valois''), was the first king of France from the House of Valois, reigning from 1328 until his death in 1350. Philip's reign was dominated by the consequences of a succession dispute. When King Charles IV of France died in 1328, his nearest male relative was his sororal nephew, Edward III of England, but the French nobility preferred Charles's paternal cousin, Philip of Valois. At first, Edward seemed to accept Philip's succession, but he pressed his claim to the throne of France after a series of disagreements with Philip. The result was the beginning of the Hundred Years' War in 1337. After initial successes at sea, Philip's navy was annihilated at the Battle of Sluys in 1340, ensuring that the war would occur on the continent. The English took another decisive advantage at the Battle of Crécy (1346), while the Black Death struck France, further destabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope John XXII
Pope John XXII (, , ; 1244 â 4 December 1334), born Jacques Duèze (or d'Euse), was head of the Catholic Church from 7 August 1316 to his death, in December 1334. He was the second and longest-reigning Avignon Papacy, Avignon Pope, elected by the Papal conclave, Conclave of Cardinal (Catholic Church), Cardinals, which was assembled in Lyon. Like his predecessor, Pope Clement V, Clement V, Pope John centralized power and income in the Papacy and lived a princely life in Avignon. John opposed the policies of Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis IV the Bavarian as Holy Roman Emperor, which prompted Louis to invade Italy and set up an antipope, antipope Nicholas V, Nicholas V. John also opposed the Franciscans, Franciscan understanding of the poverty of Christ and his apostles, promulgating multiple papal bulls to enforce his views. This led William of Ockham to write against unlimited papal power. Following a three-year process, John Canonization of Thomas Aquinas, canonized Thoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Rennes
The Archdiocese of Rennes, Dol, and Saint-Malo (Latin: ''Archidioecesis Rhedonensis, Dolensis et Sancti Maclovii''; French: ''Archidiocèse de Rennes, Dol et Saint-Malo''; ) is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in France. The diocese is coextensive with the department of Ille et Vilaine. The Archdiocese has 8 suffragans: the Diocese of Angers, the Diocese of Laval, the Diocese of Le Mans, the Diocese of Luçon, the Diocese of Nantes, the Diocese of Quimper and Léon, the Diocese of Saint-Brieuc and Tréguier, and the Diocese of Vannes. The Concordat of 1802 re-established the Diocese of Rennes which since then has included: the ancient Diocese of Rennes with the exception of three parishes given to the Diocese of Nantes"> ... re-established the Diocese of Rennes which since then has included: the ancient Diocese of Rennes with the exception of three parishes given to the Diocese of Nantes; the greater part of the ancient Diocese of Dol; the greater part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Vannes
The Diocese of Vannes (Latin: ''Dioecesis Venetensis''; French language, French: ''Diocèse de Vannes'') is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in France. It was established in the 5th century. The seat of the bishop is Vannes Cathedral, in the city of Vannes, on the southern shore of the peninsula of Brittany (Bretagne). The diocese corresponds to the French civil department of Morbihan, and has been a suffragan to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rennes, Archdiocese of Rennes, Dol, and Saint-Malo since 3 January 1859. Raymond Michel René Centène is the current bishop since his appointment in 2005. In 2022, in the Diocese of Vannes there was one priest for every 1,884 Catholics. History The ancient Gallo-Roman name for the city of Vannes (city of the Veneti) was Darioritum. ''Sede vacante'' Bishop Guido Conley died on 21 (or 31) October 1270. On the appointed day, seventeen dignities and canons assembled to elect his successor. Four scrutators were selected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duchy of Brittany, duchy before being Union of Brittany and France, united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a provinces of France, province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany is the traditional homeland of the Breton people and is one of the six Celtic nations, retaining Culture of Brittany, a distinct cultural identity that reflects History of Brittany, its history. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |