|
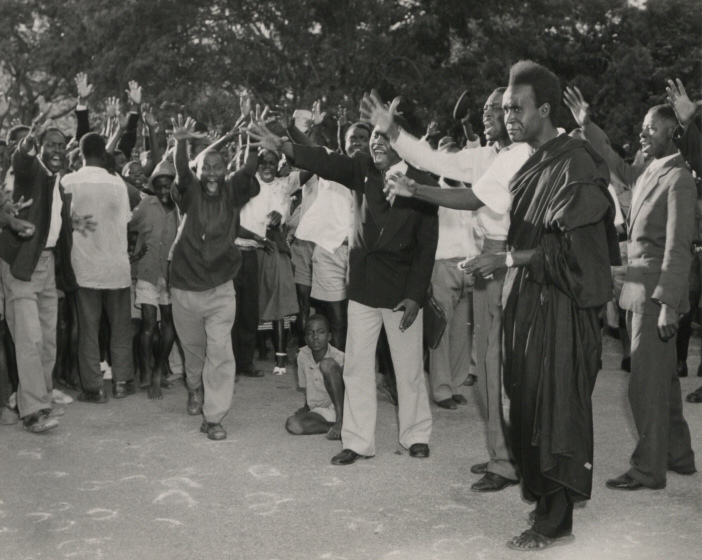
Guy Clutton-Brock
Arthur Guy Clutton-Brock (5 April 1906 – 29 January 1995) was an English social worker who became a Zimbabwean nationalist and co-founder of Cold Comfort Farm in what was then Rhodesia. Biography Clutton-Brock was born at Lake View, Green Lane, Ruislip, Middlesex to a stockbroker, Henry Alan Clutton-Brock, and his wife, Rosa Gertrude Eleanor ( Bowles) Clutton-Brock. His uncle was the writer Arthur Clutton-Brock. He was educated at Rugby School, and graduated from Magdalene College, Cambridge. He had a career in the prison and probation services, youth and community work in the East End of London and in post-war Germany. He met his wife and partner Frances "Molly" Allen in 1934 and they were known as "the CBs". During the Second World War he ran Oxford House, Bethnal Green, 1940–44, with the assistance of John Raven, Peter Kuenstler and later Merfyn Turner, all four being conscientious objectors. Personal life He and Molly had a daughter named Sarah-Anne in 1942. The couple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was published on Saturday 26 March 2016, leaving only the online edition. The newspaper was controlled by Tony O'Reilly's Irish Independent News & Media from 1997 until it was sold to the Russian oligarch and former KGB Officer Alexander Lebedev in 2010. In 2017, Sultan Muhammad Abuljadayel bought a 30% stake in it. The daily edition was named National Newspaper of the Year at the 2004 British Press Awards. The website and mobile app had a combined monthly reach of 19,826,000 in 2021. History 1986 to 1990 Launched in 1986, the first issue of ''The Independent'' was published on 7 October in broadsheet format.Dennis Griffiths (ed.) ''The Encyclopedia of the British Press, 1422–1992'', London & Basingstoke: Macmillan, 1992, p. 330 It was produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a landlocked self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally known as south Zambesia until annexed by Britain at the behest of Cecil Rhodes's British South Africa Company, for whom the colony was named. The bounding territories were Bechuanaland (Botswana), Northern Rhodesia (Zambia), Moçambique (Mozambique), and the Transvaal Republic (for two brief periods instead the British Transvaal Colony, from 1910 the Union of South Africa, and then from 1961 the Republic of South Africa). This southern region, known for its extensive gold reserves, was first purchased by the BSAC's Pioneer Column on the strength of a Mineral Concession extracted from its Matabele overlord, Lobengula, and various majority Mashona vassal chiefs in 1890. Though parts of the territory were laid claim to by the Bechuana and Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Nyerere
Julius Kambarage Nyerere (; 13 April 1922 – 14 October 1999) was a Tanzanian anti-colonial activist, politician, and political theorist. He governed Tanganyika as prime minister from 1961 to 1962 and then as president from 1962 to 1964, after which he led its successor state, Tanzania, as president from 1964 to 1985. He was a founding member and chair of the Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) party, and of its successor Chama Cha Mapinduzi, from 1954 to 1990. Ideologically an African nationalist and African socialist, he promoted a political philosophy known as Ujamaa. Born in Butiama, Mara, then in the British colony of Tanganyika, Nyerere was the son of a Zanaki chief. After completing his schooling, he studied at Makerere College in Uganda and then Edinburgh University in Scotland. In 1952 he returned to Tanganyika, married, and worked as a school teacher. In 1954, he helped form TANU, through which he campaigned for Tanganyikan independence from the British Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the northeast, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The nation's population of around 19.5 million is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country. Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. Following the arrival of European exploration of Africa, European explorers in the eighteenth century, the British colonised the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Kaunda
Kenneth David Kaunda (28 April 1924 – 17 June 2021), also known as KK, was a Zambian politician who served as the first President of Zambia from 1964 to 1991. He was at the forefront of the struggle for independence from British rule. Dissatisfied with Harry Nkumbula's leadership of the Northern Rhodesian African National Congress, he broke away and founded the Zambian African National Congress, later becoming the head of the socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP). Kaunda was the first president of independent Zambia. In 1973, following tribal and inter-party violence, all political parties except UNIP were banned through an amendment of the constitution after the signing of the Choma Declaration. At the same time, Kaunda oversaw the acquisition of majority stakes in key foreign-owned companies. The 1973 oil crisis and a slump in export revenues put Zambia in a state of economic crisis. International pressure forced Kaunda to change the rules that had kept him i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Smith
Ian Douglas Smith (8 April 1919 – 20 November 2007) was a Rhodesian politician, farmer, and fighter pilot who served as Prime Minister of Rhodesia (known as Southern Rhodesia until October 1964 and now known as Zimbabwe) from 1964 to 1979. He was the country's first premier not born abroad, and led the predominantly white government that unilaterally declared independence from the United Kingdom in November 1965 following prolonged dispute over the terms, particularly British demands for black majority rule. He remained Prime Minister for almost all of the 14 years of international isolation that followed, and oversaw Rhodesia's security forces during most of the Bush War, which pitted the unrecognised administration against communist-backed black nationalist guerrilla groups. Smith, who has been described as personifying white Rhodesia, remains a highly controversial figure. Smith was born to British immigrants in Selukwe, a small town in the Southern Rhodesian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Nyandoro
George Bodzo Nyandoro (8 July 1926 – 24 June 1994) was a Zimbabwean politician and activist in the struggle to end white minority rule in Rhodesia. Nyandoro was one of the founders of the Southern Rhodesia African National Congress (SRANC) and served as the General Secretary of the Zimbabwe African People's Union.Red Africa: Communist support and assistance to nationalist political groups in Rhodesia Embassy of Rhodesia in Iceland As a founder member of the earliest nationalist parties, his struggle against colonial domination dates back to the 1950s. An ethnic , Nyandoro was born in 1926 in the Chihota Reserve and ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didymus Mutasa
Didymus Noel Edwin Mutasa (born 27 July 1935) is a Zimbabwean politician who served as Zimbabwe's Speaker of Parliament from 1980 to 1990. Subsequently, he held various ministerial posts working under President Robert Mugabe in the President's Office. He was Minister of State for Presidential Affairs from 2009 to 2014 and also served as ZANU-PF's Secretary for Administration.Cris Chinaka"Zanu-PF decides plan of action" Reuters, 4 April 2008. Family background and education Didymus Mutasa was born in 1935 in Rusape, a town close to the Zimbabwe/Mozambique border in Africa. He was the sixth child of a devout Christian couple. Mutasa was a student of Fircroft College of Adult Education in Birmingham, UK, where he attended the Access to Higher Education Course. He studied at Birmingham University on a British Council scholarship. Mutasa was awarded the honorary degree of Doctor of Social Science (DSocSc) by the University of Birmingham in 1990. Political career Before Zimbabwean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Benson (campaigner)
Dorothy Mary Benson (8 December 1919 – 19 June 2000) was a South African civil rights campaigner and author. Early life Born in 1919 in Pretoria, Benson served in the South African Women's Army during World War II. After the war, she was secretary to film director David Lean. Activism and writing Benson became acquainted with the author Alan Paton, and read his novel ''Cry, the Beloved Country'' (1948), whose main theme was racial discrimination in South Africa. This affected her greatly, and she became a campaigner for the rights of black South Africans. She worked with Michael Scott (who, in 1946, was the first white man to be jailed for resisting South Africa's racial laws), becoming his secretary in 1950. With Scott, Benson helped to found the African Bureau. In 1957, Benson was appointed secretary to the Treason Trial Defence Fund. In 1961, Benson took on another secretarial role, moving to Natal to assist Chief Albert Lutuli when he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenner Brockway
Archibald Fenner Brockway, Baron Brockway (1 November 1888 – 28 April 1988) was a British socialist politician, humanist campaigner and anti-war activist. Early life and career Brockway was born to W. G. Brockway and Frances Elizabeth Abbey in Calcutta, British India. While attending the School for the Sons of Missionaries, then in Blackheath, London (now Eltham College), from 1897 to 1905, he developed an interest in politics. In 1908, Brockway became a vegetarian. Several decades later, during a debate in a House of Lords on animal cruelty, he said: "I am a vegetarian and I have been so for 70 years. On the whole, I think, physically I am a pretty good advertisement for that practice." After leaving school, he worked as a journalist for newspapers and journals including ''The Quiver'', the ''Daily News'' and the ''Christian Commonwealth''. In 1907, Brockway joined the Independent Labour Party (ILP) and was a regular visitor to the Fabian Society. He was appointed editor of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Huddleston
Ernest Urban Trevor Huddleston (15 June 191320 April 1998) was an English Anglican bishop. He was the Bishop of Stepney in London before becoming the second Archbishop of the Church of the Province of the Indian Ocean. He was best known for his anti-apartheid activism and his book ''Naught for Your Comfort''. Early life Huddleston was the son of Ernest Huddleston and was born in Bedford, Bedfordshire, and educated at Lancing College (1927–1931), Christ Church, Oxford, and at Wells Theological College. He joined an Anglican religious order, the Community of the Resurrection (CR), in 1939, taking vows in 1941, having already served for three years as a curate at St Mark's Swindon. He had been made a deacon at Michaelmas 1936 (27 September) and ordained a priest the following Michaelmas (26 September 1937) — both times by Clifford Woodward, Bishop of Bristol, at Bristol Cathedral. South Africa In September 1940 Huddleston sailed to Cape Town, and in 1943 he went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of Southern Rhodesia, which had been self-governing since achieving responsible government in 1923. A landlocked nation, Rhodesia was bordered by South Africa to the south, Bechuanaland (later Botswana) to the southwest, Zambia (formerly Northern Rhodesia) to the northwest, and Mozambique ( a Portuguese province until 1975) to the east. From 1965 to 1979, Rhodesia was one of two independent states on the African continent governed by a white minority of European descent and culture, the other being South Africa. In the late 19th century, the territory north of the Transvaal was chartered to the British South Africa Company, led by Cecil Rhodes. Rhodes and his Pioneer Column marched north in 1890, acquiring a huge block of territory that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



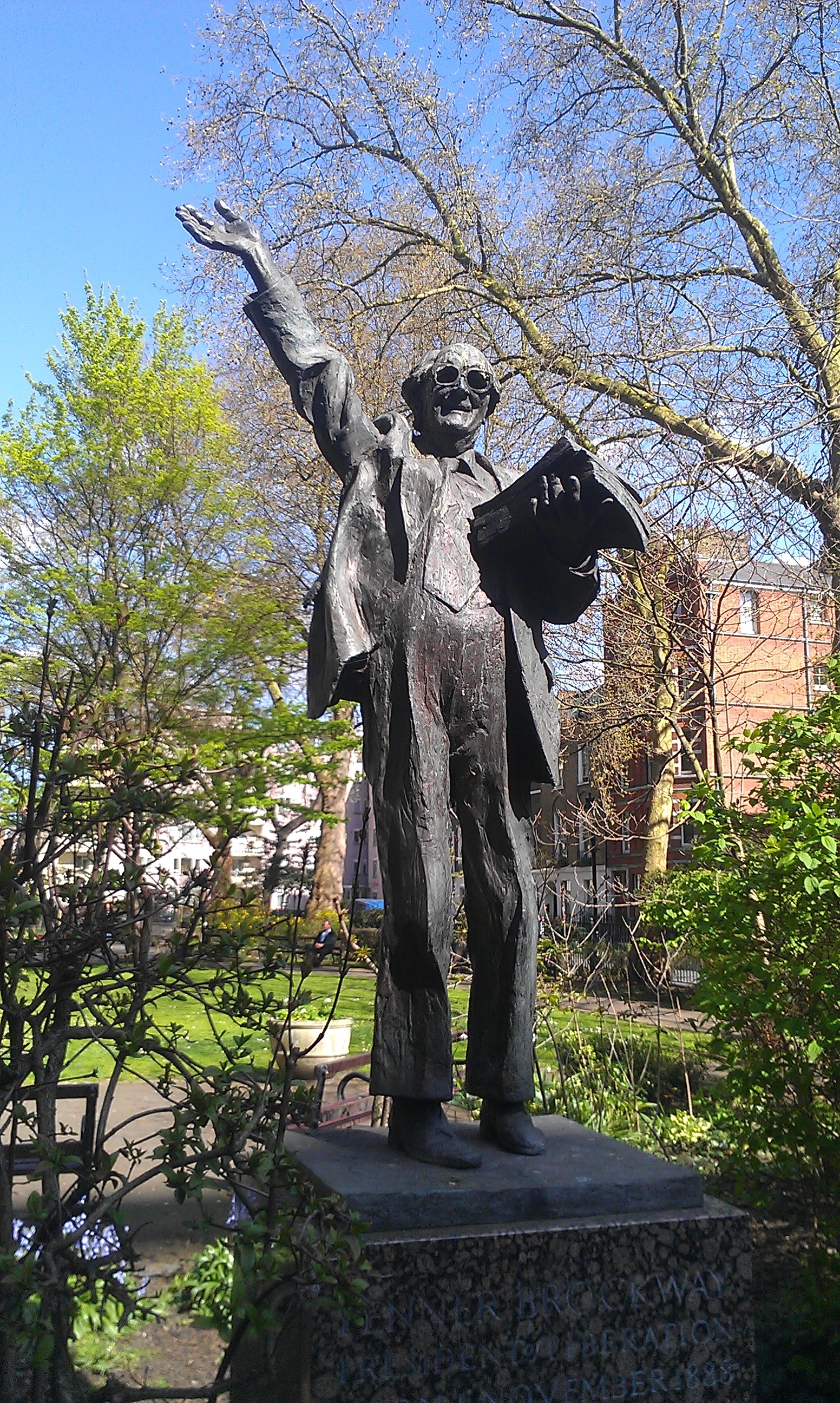
.jpg)