|
Gusuku Period
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the ''Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeological epoch of the Okinawa Islands that follows the shell-mound period and precedes the Sanzan period, when most ''gusuku'' are thought to have been built. Many ''gusuku'' and related cultural remains on Okinawa Island have been listed by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites under the title ''Gusuku Sites and Related Properties of the Kingdom of Ryukyu''. Philological analysis The '' Yarazamori Gusuku Inscription'' (1554) contains phrases, "pile ''gusuku''" (くすくつませ) and "pile up ''gusuku'' and ..." (くすくつみつけて); apparently, ''gusuku'' in these phrases refers to stone walls. In the ''Omoro Sōshi'' (16th–17th centuries), the term ''gusuku'' is written as "くすく," or "ぐすく" in hiragana. Occasionally, the Chinese char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naha Shuri Castle08s5s3200
is the capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 persons per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). The total area is Naha is located on the East China Sea coast of the southern part of Okinawa Island, the largest of Okinawa Prefecture. The modern city was officially founded on May 20, 1921. Before that, Naha had been for centuries one of the most important and populous sites in Okinawa. Naha is the political, economic and education center of Okinawa Prefecture. In the medieval and early modern periods, it was the commercial center of the Ryukyu Kingdom. Geography City center Central Naha consists of the Palette Kumoji shopping mall, the Okinawa Prefecture Office, Naha City Hall, and many banks and corporations, located at the west end of Kokusai-dōri, the city's main street. boasts a 1.6 kilometer (1 mile) long stretch of stores, restaurants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakijin Castle
is a Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' located in Nakijin, Okinawa. It is currently in ruins. In the late 14th century, the island of Okinawa consisted of three principalities: Nanzan to the south, Chūzan in the central area, and Hokuzan in the north. Nakijin was the capital of Hokuzan. The fortress includes several sacred Utaki groves, reflecting the castle's role as a center of religious activity. It is today known for the Hikan cherries which bloom in northern Okinawa between mid-January and early February, providing the first cherry blossoms each year in Japan. In 2000, Nakijin Castle was designated as a World Heritage Site, as a part of the Gusuku Sites and Related Properties of the Kingdom of Ryukyu. History Though there had been Lords of Nakijin prior to the creation of the Hokuzan kingdom, and thus some form of chiefly residence can be presumed to have been on or near the site before, it is believed that the ''gusuku'' form of Nakijin castle only emerged at the founding of the kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakagusuku Castle
is a ''gusuku'' in the village of Kitanakagusuku, Okinawa, Japan. It is one of a number of castles built on the island of Okinawa by the Ryukyu Kingdom now in ruins. The legendary Ryukyuan commander, Gosamaru, built the fortress in the early 15th century to defend against attacks from the east by Lord Amawari of Katsuren Castle. Amawari attacked the castle in 1458 and defeated Gosamaru shortly before his own castle was attacked by Uni-Ufugusuku. The castle was visited by Commodore Matthew C. Perry in 1853, who noted that the walls seemed to be designed to absorb cannon fire. The six courtyards of this fortress with stacked stone walls make it a prime example of a gusuku. It was added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 2000. It is regarded as one of the 100 most famous castles in Japan. Less than away from the castle is the Nakagusuku Hotel ruins The , also known as the Royal Hotel or , is an abandoned, unfinished hotel in Kitanakagusuku, Okinawa. It sits no more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtain Wall (fortification)
A curtain wall is a defensive wall between two fortified towers or bastions of a castle, fortress, or town. Ancient fortifications Evidence for curtain walls or a series of walls surrounding a town or fortress can be found in the historical sources from Assyria and Egypt. Some notable examples are ancient Tel Lachish in Israel and Buhen in Egypt. Curtain walls were built across Europe during the Roman Empire; the early 5th century Theodosian Walls of Constantinople influenced the builders of medieval castles many centuries later. Curtain wall castles In medieval castles, the area surrounded by a curtain wall, with or without towers, is known as the bailey. The outermost walls with their integrated bastions and wall towers together make up the enceinte or main defensive line enclosing the site. In medieval designs of castle and town, the curtain walls were often built to a considerable height and were fronted by a ditch or moat to make assault difficult. Walls were toppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burg Shuri Plan
The German word Burg means castle. Burg or Bürg may refer to: Places Placename element * ''-burg'', a combining form in Dutch, German and English placenames * Burg, a variant of burh, the fortified towns of Saxon England Settlements * Burg, Aargau, Switzerland * Burg, Bernkastel-Wittlich, Germany * Burg, Bitburg-Prüm, Germany * Burg, Brandenburg, Germany * Burg, Dithmarschen, Germany * Burg auf Fehmarn, Germany * Burg bei Magdeburg, Germany * Burg im Leimental, Switzerland * Den Burg, Netherlands * The Burg, Illinois, United States * Burg, Hautes-Pyrénées, France * Burg, Kilninian and Kilmore, a place on the Isle of Mull, Argyll and Bute, Scotland * Melber, Kentucky, United States, also known as Burg Other uses * Burg (surname) or Bürg * Bürg (crater) * Burg (ship, 2003), a car ferry operating on Switzerland's Lake Zurich * Burgs (fast-food chain) See also * * Burgh (other) * Borg (other) * Bourg (other) * Borough and -bury, common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakahara Zenchū
Nakahara (written: 中原 or 仲原) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *, Japanese manga artist *Andrews Nakahara (born 1983), Japanese-Brazilian mixed martial artist *, Japanese manga artist *, Japanese poet *, Japanese graphic artist and fashion designer *Kellye Nakahara (born 1950), American actor *, Japanese voice actress and singer *, Japanese shogi player *, Japanese musician, writer and actor *, Japanese singer * Morihiko Nakahara (born 1975), Japanese conductor *, Japanese Zen Buddhist *, Japanese architect *, Japanese composer *, Japanese voice actor *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese film director *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese actor *, Japanese electrical engineer *, Japanese footballer *, Japanese ethnologist See also *Nakahara-ku, Kawasaki, a ward of Kawasaki, Japan *Nakahara Prize The Nakahara Prize (中原賞) is an annual award given by the Japanese Economic Association to Japanese economists under the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higashionna Kanjun
also Higaonna Kanjun (14 October 1882–24 January 1963) was a Japanese scholar who specialized in the history of Okinawa. Alongside Iha Fuyū and Majikina Ankō, he is considered one of the pioneers of modern Okinawan studies. After reading Japanese history at Tokyo Imperial University, where he wrote his dissertation on the approach of the Shimazu clan towards the Ryūkyū Kingdom, his subsequent career included posts at Hosei University and Takushoku University and travels in Southeast Asia and India. His extensive body of writings, collected as in ten volumes, centre around Ryukyuan history and culture, personal and place names, and classics such as the ''Omoro Sōshi''. His private collection of documents and historical materials, numbering some 3,384 items, is preserved as the Higashionna Kanjun Collection at Okinawa Prefectural Library. See also * List of Cultural Properties of Japan - writings (Okinawa) * List of Cultural Properties of Japan - historical materials (Oki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirata Tsugumasa
Hirata may refer to: Places *Hirata, Fukushima, former village in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan * Hirata, Gifu, former town in Gifu Prefecture, Japan * Hirata, Shimane, former city in Shimane Prefecture, Japan *Hirata, Yamagata was a town located in Akumi District, Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. As of 2003, the town had an estimated population of 7,065 and a population density of 39.42 persons per km2. The total area was 179.22 km2. On November 1, 2005, Hirata, along ..., former town in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan Other uses * Hirata (surname) * Hirata Station (other), multiple train stations in Japan {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iha Fuyū
was the father of Okinawaology and a Japanese scholar who studied various aspects of Japanese and Okinawan culture, customs, linguistics, and lore. His signature was Ifa Fuyu in English, because of the Okinawan pronunciation. Iha studied linguistics in the University of Tokyo and was devoted to the study of Okinawan linguistics, folklore, and history. His most famous book on the subject, ''Ko Ryūkyū'' (''Old Ryūkyū''), was published in 1911 and remains one of the best works on Okinawan studies. He devoted much time to the discovery of the origins of Okinawan people to establish their history. He had considerable influence not only on the study of Okinawan folklore but also of Japanese folklore. Life *In 1876, he was born in Naha as an eldest son of a lower-class pechin. *In 1891, he entered Okinawa Middle School, now corresponding to Shuri High School. *In 1895, he was dismissed from school, because he was a leader of a student strike; they requested the resignation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
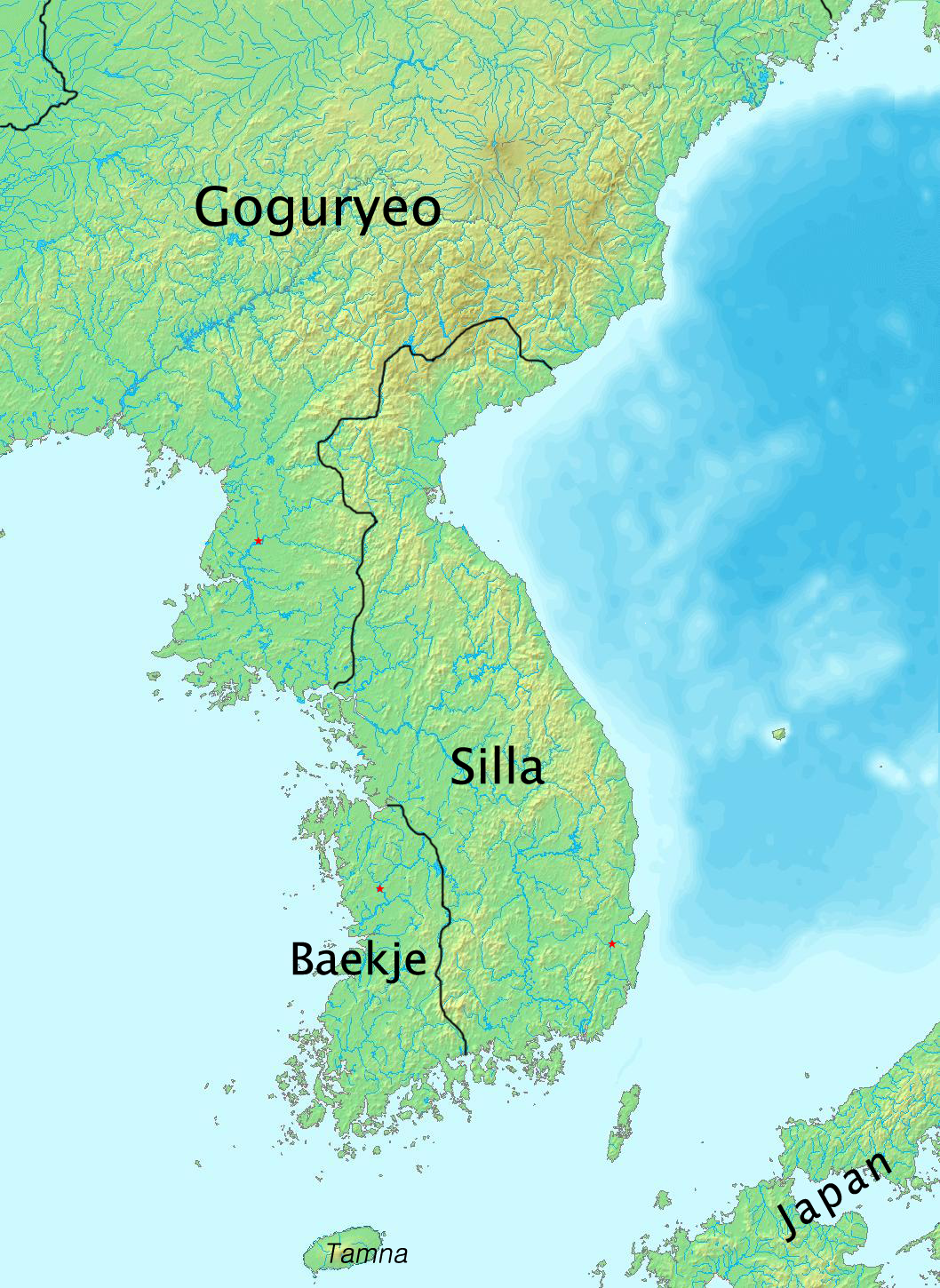
Old Korean Language
Old Korean () is the first historically documented stage of the Korean language, typified by the language of the Unified Silla period (668–935). The boundaries of Old Korean periodization remain in dispute. Some linguists classify the sparsely attested languages of the Three Kingdoms of Korea as variants of Old Korean, while others reserve the term for the language of Silla alone. Old Korean traditionally ends with the fall of Silla in 935. This too has recently been challenged by South Korean linguists who argue for extending the Old Korean period to the mid-thirteenth century, although this new periodization is not yet fully accepted. This article focuses on the language of Silla before the tenth century. Old Korean is poorly attested. The only surviving literary works are a little more than a dozen vernacular poems called ''hyangga''. Hyangga use hyangchal writing. Other sources include inscriptions on steles and wooden tablets, glosses to Buddhist sutras, and the transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Japanese
is the oldest attested stage of the Japanese language, recorded in documents from the Nara period (8th century). It became Early Middle Japanese in the succeeding Heian period, but the precise delimitation of the stages is controversial. Old Japanese was an early member of the Japonic language family. No genetic links to other language families have been proven. Old Japanese was written using man'yōgana, using Chinese characters as syllabograms or (occasionally) logograms. It featured a few phonemic differences from later forms, such as a simpler syllable structure and distinctions between several pairs of syllables that have been pronounced identically since Early Middle Japanese. The phonetic realization of these distinctions is uncertain. Internal reconstruction points to a pre-Old Japanese phase with fewer consonants and vowels. As is typical of Japonic languages, Old Japanese was primarily an agglutinative language with a subject–object–verb word order, adjectives and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |