|
Gustave Roussy
Gustave Roussy (24 November 1874 – 30 September 1948) was a Swiss-French neuropathologist born in Vevey, Switzerland. Career As a hospital interne in Paris, Roussy worked under neurologists Pierre Marie and Joseph Jules Dejerine. In 1907 he earned his doctorate from the University of Paris, and in 1925 was appointed professor of pathological anatomy at the '' Faculté de Médecine''. Later on, he was named dean (1933) and rector (1937) to the faculty of medicine at the university. Roussy made several contributions in the field of neurology, in particular, his investigations on the role of the thalamus and the autonomic nervous system. During World War I he was chief of neurology of the 7th Military Region Besançon, publishing extensively on his experiences with battle-related wounds. He was the author or co-author of a number of works on psychological and neuropsychological issues as a consequence of war. In 1926, in collaboration with his colleague Gabrielle Charlotte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropsychological
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brain affect cognitive and behavioral functions. It is both an experimental and clinical field of psychology, thus aiming to understand how behavior and cognition are influenced by brain function and concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of behavioral and cognitive effects of neurological disorders. Whereas classical neurology focuses on the pathology of the nervous system and classical psychology is largely divorced from it, neuropsychology seeks to discover how the brain correlates with the mind through the study of neurological patients. It thus shares concepts and concerns with neuropsychiatry and with behavioral neurology in general. The term ''neuropsychology'' has been applied to lesion studies in humans and animals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue, and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
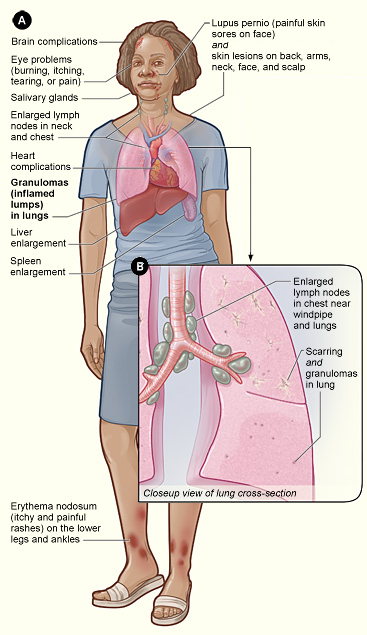
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and brain. Any organ can be affected though. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no, or only mild, symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, large lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by biopsy. Findings that make it likely include large lymph n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Gustave Roussy
Gustave Roussy is the first leader cancer-research hospital in Europe and ranked among the top 3 best specialized hospitals in the world . It is a centre for high quality patient care, research and teaching. It is highly-known for the treatment of (among others): skin cancers like melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer. It provides access to care with many expert doctors who have historically revolutionized the treatment of cancer and contributed to the surge of new molecules in the treatment of cancers and tumors. It is located in the Parisian area. It is named after Gustave Roussy, a Swiss-French neuropathologist. In April 2019, three new interventional radiology rooms were inaugurated, making it the largest platform of this type in Europe, entirely dedicated to oncology. Interventional radiology is a so-called "minimally invasive" diagnostic and treatment technique, which uses images to guide access to deep-lying organs, without having to "open up" patients. Gustave Roussy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villejuif
Villejuif () is a commune in the southern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris. Name The earliest reference to Villejuif appears in a bill signed by the Pope Callixtus II on 27 November 1119. It refers to Villa Judea, the Latinized version of the Old French expression meaning 'Jewish settlement'. During the following centuries, the toponym appears as Villejuifve, that is, following the archaic French spelling of the expression with the same meaning, cognate to modern French Villejuive. The French author from the 17th century Louis Moréri indicates that the settlement was founded by Jews expelled from Paris. This idea, however, remains speculative as available medieval Christian and Jewish sources do not mention the existence of the Jewish community in this place. Geography Climate Villejuif has a oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfb''). The average annual temperature in Villejuif is . The average annual rainfall is with October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrinology
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine systems often act together in a process called neuroendocrine integration, to regulate the physiological processes of the human body. Neuroendocrinology arose from the recognition that the brain, especially the hypothalamus, controls secretion of pituitary gland hormones, and has subsequently expanded to investigate numerous interconnections of the endocrine and nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands throughout the body that produce and secrete hormones of diverse chemical structure, including peptides, steroids, and neuroamines. Collectively, hormones regulate many physiological processes. The neuroendocrine system is the mechanism by which the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, regulating reproduction, metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject. In library cataloging, ''monograph'' has a broader meaning—that of a nonserial publication complete in one volume (book) or a definite number of volumes. Thus it differs from a serial or periodical publication such as a magazine, academic journal, or newspaper. In this context only, books such as novels are considered monographs.__FORCETOC__ Academia The English term "monograph" is derived from modern Latin "monographia", which has its root in Greek. In the English word, "mono-" means "single" and "-graph" means "something written". Unlike a textbook, which surveys the state of knowledge in a field, the main purpose of a monograph is to present primary research and original scholarship ascertaining reliable credibility to the required recipient. This research is prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from senso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)