|
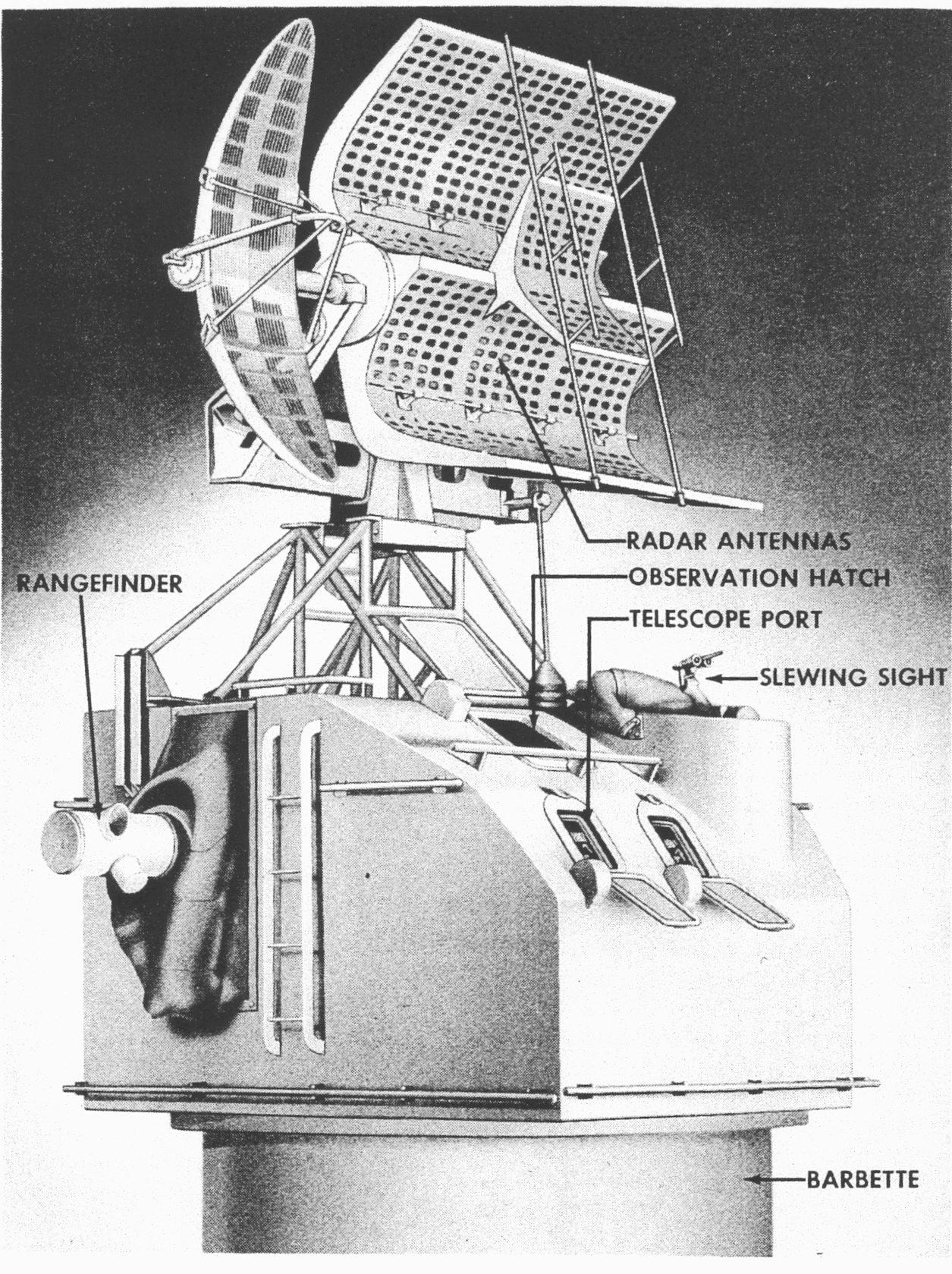
Gun Fire Control Systems
Ship gun fire-control systems (GFCS) are analogue fire-control systems that were used aboard naval warships prior to modern electronic computerized systems, to control targeting of guns against surface ships, aircraft, and shore targets, with either optical or radar sighting. Most US ships that are destroyers or larger (but not destroyer escorts except Brooke class DEG's later designated FFG's or escort carriers) employed gun fire-control systems for and larger guns, up to battleships, such as . Beginning with ships built in the 1960s, warship guns were largely operated by computerized systems, i.e. systems that were controlled by electronic computers, which were integrated with the ship's missile fire-control systems and other ship sensors. As technology advanced, many of these functions were eventually handled fully by central electronic computers. The major components of a gun fire-control system are a human-controlled director, along with or later replaced by radar or tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander-in-Chief, China (Royal Navy)
The Commander-in-Chief, China was the admiral in command of what was usually known as the China Station, at once both a British Royal Navy naval formation and its admiral in command. It was created in 1865 and deactivated in 1941. From 1831 to 1865, the East Indies Station and the China Station were a single command known as the East Indies and China Station. The China Station, established in 1865, had as its area of responsibility the coasts of China and its navigable rivers, the western part of the Pacific Ocean, and the waters around the Dutch East Indies. The navy often co-operated with British commercial interests in this area. The formation had bases at Singapore (Singapore Naval Base), HMS ''Tamar'' (1865–1941 and 1945–1997) in Hong Kong and Wei Hai (at Liugong Island) (1898–1940). The China Station complement usually consisted of several older light cruisers and destroyers, and the Chinese rivers were patrolled by a flotilla of suitable, shallow-draught gunboats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Mikasa
is a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the late 1890s. Named after Mount Mikasa in Nara, Japan, the ship served as the flagship of Vice Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō throughout the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, including the Battle of Port Arthur on the second day of the war and the Battles of the Yellow Sea and Tsushima. Days after the end of the war, ''Mikasa''s magazine accidentally exploded and sank the ship. She was salvaged and her repairs took over two years to complete. Afterwards, the ship served as a coast-defence ship during World War I and supported Japanese forces during the Siberian Intervention in the Russian Civil War. After 1922, ''Mikasa'' was decommissioned in accordance with the Washington Naval Treaty and preserved as a museum ship at Yokosuka. She was badly neglected during the post-World War II Occupation of Japan and required extensive refurbishing in the late 1950s. She has been partially restored, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Asahi
was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the late 1890s. As Japan lacked the industrial capacity to build such warships itself, the ship was designed and built in the United Kingdom. Shortly after her arrival in Japan, she became flagship of the Standing Fleet, the IJN's primary combat fleet. She participated in every major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905 and was lightly damaged during the Battle of the Yellow Sea and the Battle of Tsushima. ''Asahi'' saw no combat during World War I, although the ship participated in the Siberian Intervention in 1918. Reclassified as a coastal defence ship in 1921, ''Asahi'' was disarmed two years later to meet the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty, after which she served as a training and submarine depot ship. She was modified into a submarine salvage and rescue ship before being placed in reserve in 1928. ''Asahi'' was recommissioned in late 1937, after the start of the Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Pacific Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Pacific Fleet.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Russian Pacific Fleet Great emblem , dates = 1731–present , country = , allegiance = (1703–1917) (1922–1991) (1991–present) , branch = Russian Navy , type = , role = At sea nuclear deterrence;Naval warfare; Amphibious military operations;Combat patrols in the Pacific/Arctic;Naval presence/diplomacy missions in the Pacific and elsewhere , size = c. 46 Surface Warships (major surface units, light corvettes, mine warfare, amphibious) plus support ships/auxiliaries c. 23-24 Submarines (of which about 2/3 active as of 2022) , command_structure = Russian Armed Forces , garrison = Fokino (HQ)Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Vilyuchins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea ( ja, 黄海海戦, Kōkai kaisen; russian: Бой в Жёлтом море) was a major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 August. The battle foiled an attempt by the Russian fleet at Port Arthur to break out and form up with the Vladivostok squadron, forcing them to return to port. Four days later, the Battle off Ulsan similarly ended the Vladivostok group's sortie, forcing both fleets to remain at anchor. Background The Imperial Russian Navy's First Pacific Squadron, commanded by Admiral Wilgelm Vitgeft, had been trapped in Port Arthur since the Imperial Japanese Navy's blockade began on 8 February 1904 with the Battle of Port Arthur. Throughout late July and early August, as the Imperial Japanese Army laid siege to Port Arthur, relations between Admiral Vitgeft and Russian Viceroy Yevgeni Alekseyev increasingly soured. Viceroy Alekseyev, a former admir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender in World War II. The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) was formed between 1952–1954 after the dissolution of the IJN. The Imperial Japanese Navy was the third largest navy in the world by 1920, behind the Royal Navy and the United States Navy (USN). It was supported by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service for aircraft and airstrike operation from the fleet. It was the primary opponent of the Western Allies in the Pacific War. The origins of the Imperial Japanese Navy go back to early interactions with nations on the Asian continent, beginning in the early medieval period and reaching a peak of activity during the 16th and 17th centuries at a time of cultural exchange with European powers during the Age of Discovery. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperialism, imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a Port#Warm-water port, warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; Lüshunkou, Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
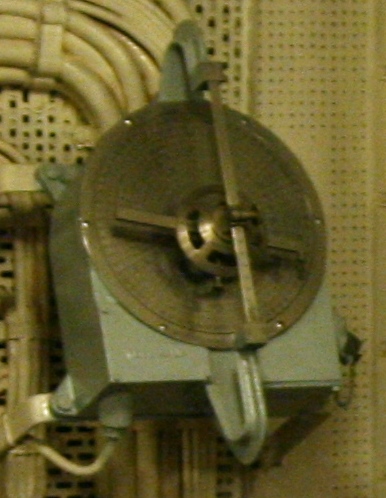
Dumaresq
The Dumaresq is a mechanical calculating device invented around 1902 by Lieutenant John Dumaresq of the Royal Navy. It is an analogue computer that relates vital variables of the fire control problem to the movement of one's own ship and that of a target ship. It was often used with other devices, such as a Vickers range clock, to generate range and deflection data so the gun sights of the ship could be continuously set. A number of versions of the Dumaresq were produced of increasing complexity as development proceeded. Geometric principle The dumaresq relies on sliding and rotating bars and dials to represent the motion of the two ships. Normally the motion of the ship carrying the dumaresq is represented by a metal bar running above the instrument. Below the bar is a round metal plate inscribed with a coordinate plot, and an angle scale around its outer rim. The fixed bar is mounted on a bearing that allows it to be turned to represent the direction of motion of the ship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Dictionary Of Biography
The ''Australian Dictionary of Biography'' (ADB or AuDB) is a national co-operative enterprise founded and maintained by the Australian National University (ANU) to produce authoritative biographical articles on eminent people in Australia's history. Initially published in a series of twelve hard-copy volumes between 1966 and 2005, the dictionary has been published online since 2006 by the National Centre of Biography at ANU, which has also published ''Obituaries Australia'' (OA) since 2010. History The ADB project has been operating since 1957. Staff are located at the National Centre of Biography in the History Department of the Research School of Social Sciences at the Australian National University. Since its inception, 4,000 authors have contributed to the ADB and its published volumes contain 9,800 scholarly articles on 12,000 individuals. 210 of these are of Indigenous Australians, which has been explained by Bill Stanner's "cult of forgetfulness" theory around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Hugh Thring
Walter may refer to: People * Walter (name), both a surname and a given name * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–1968) * Gunther (wrestler), Austrian professional wrestler and trainer Walter Hahn (born 1987), who previously wrestled as "Walter" * Walter, standard author abbreviation for Thomas Walter (botanist) ( – 1789) Companies * American Chocolate, later called Walter, an American automobile manufactured from 1902 to 1906 * Walter Energy, a metallurgical coal producer for the global steel industry * Walter Aircraft Engines, Czech manufacturer of aero-engines Films and television * ''Walter'' (1982 film), a British television drama film * Walter Vetrivel, a 1993 Tamil crime drama film * ''Walter'' (2014 film), a British television crime drama * ''Walter'' (2015 film), an American comedy-drama film * ''Walter'' (2020 film), an Indian crime drama film * '' W*A*L*T*E*R'', a 1984 pilot for a spin-off of the TV series ''M*A*S*H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |