|
Gullane Church Window
Gullane ( or ) is a town on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth in East Lothian on the east coast of Scotland. There has been a church in the village since the ninth century. The ruins of the Old Church of St. Andrew built in the twelfth century can still be seen at the western entrance to the village; the church was abandoned after a series of sandstorms made it unusable, and Dirleton Parish Church took its place. Gullane Bents, the village's award-winning beach, is backed by large sand dunes that in recent years have become rather overgrown by invasive shrubs like sea-buckthorn. Gullane is part of the John Muir Way, a long-distance footpath along the coast between Musselburgh and Dunglass. The local population includes a higher than average percentage of elderly people, but also attracts young families and commuters for Edinburgh. Urbanisation has led to some recent housing developments being approved on greenbelt land around the village, and Gullane is gaining p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainmean-Àite Na H-Alba
Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba (; "Gaelic Place-Names of Scotland") is the national advisory partnership for Gaelic place names in Scotland. Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba are based at Sabhal Mòr Ostaig on Skye. History Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba began as the Gaelic Names Liaison Committee, established in 2000 by the Ordnance Survey to improve consistency in Gaelic names on their mapping products. The committee expanded to become the Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba partnership in 2006. Functions Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba research and agree on place names, using local knowledge, historical sources and the principles of the Gaelic Orthographic Conventions. These names are used by local councils, roads authorities and the Ordnance Survey for signs and maps. AÀA are also producing a National Place-Names Database. This database was launched in August 2010, and contains over 3000 entries. Partnerships The partners are Argyll and Bute Council, Bòrd na Gàidhlig, Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, Highlands and Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas. Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth. Urbanization refers to the ''proportion'' of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the ''absolute'' number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050 about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. That is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all globa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic language family, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). Historically, it has also been known in English as "British", "Cambrian", "Cambric" and "Cymric". The Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011 gave the Welsh language official status in Wales. Both the Welsh and English languages are ''de jure'' official languages of the Welsh Parliament, the Senedd. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 17.8% (538,300 people) and nearly three quarters of the population in Wales said they had no Welsh language skills. Other estimates suggest that 29.7% (899,500) of people aged three or older in Wales could speak Welsh in June 2022. Almost half of all Welsh speakers consider themselves fluent Welsh speakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
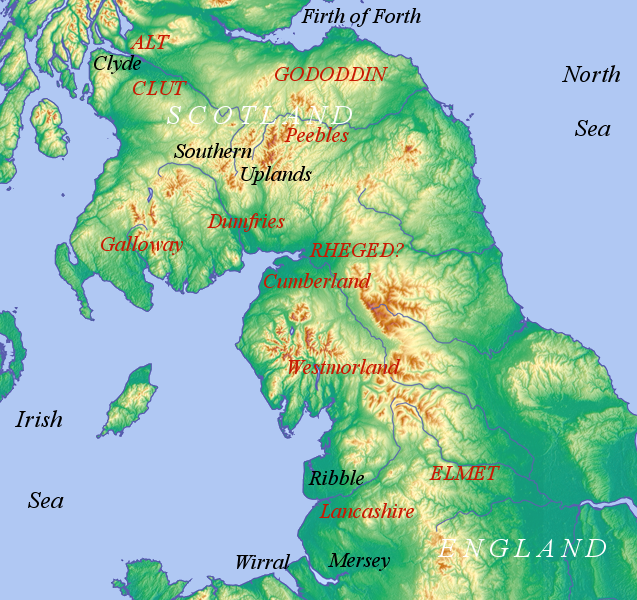
Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the semi-independent Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittonic Languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. The name ''Brythonic'' was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word , meaning Ancient Britons as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael. The Brittonic languages derive from the Common Brittonic language, spoken throughout Great Britain during the Iron Age and Roman period. In the 5th and 6th centuries emigrating Britons also took Brittonic speech to the continent, most significantly in Brittany and Britonia. During the next few centuries the language began to split into several dialects, eventually evolving into Welsh, Cornish, Breton, Cumbric, and probably Pictish. Welsh and Breton continue to be spoken as native languages, while a revival in Cornish has led to an increase in speakers of that language. Cumbric and Pictish are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Scots
Early Scots was the emerging literary language of the Northern Middle English speaking parts of Scotland in the period before 1450. The northern forms of Middle English descended from Northumbrian Old English. During this period, speakers referred to the language as "English" (''Inglis'', ''Ynglis'', and variants). Early examples such as Barbour’s ''The Brus'' and Wyntoun’s ''Chronicle'' are better explained as part of Northern Middle English than as isolated forerunners of later Scots, a name first used to describe the ''language'' later in the Middle Scots period. History Northumbrian Old English had been established in south-eastern Scotland as far as the River Forth in the 7th century and largely remained there until the 13th century, which is why in the late 12th century Adam of Dryburgh described his locality as "in the land of the English in the Kingdom of the Scots" and why the early 13th century author of ''de Situ Albanie'' wrote that the Firth of Forth "d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological change, form of words and, by extension, the origin and evolution of their semantic meaning across time. It is a subfield of historical linguistics, and draws upon comparative semantics, Morphology_(linguistics), morphology, semiotics, and phonetics. For languages with a long recorded history, written history, etymologists make use of texts, and texts about the language, to gather knowledge about how words were used during earlier periods, how they developed in Semantics, meaning and Phonological change, form, or when and how they Loanword, entered the language. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct information about forms that are too old for any direct information to be available. By analyzing related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Berwick
North Berwick (; gd, Bearaig a Tuath) is a seaside town A seaside resort is a town, village, or hotel that serves as a vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, such as in the German ' ... and former royal burgh in East Lothian, Scotland. It is situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, approximately east-northeast of Edinburgh. North Berwick became a fashionable holiday resort in the nineteenth century because of its two sandy bays, the East (or Milsey) Bay and the West Bay, and continues to attract holidaymakers. Golf courses at the ends of each bay are open to visitors. Name The name Berwick means "barley farmstead" (''bere'' in Old English means "barley" and ''wic'' means "farmstead"). Alternatively, like other place names in Scotland ending in 'wick', this word means 'bay' (Old Norse: vík). The word North was applied to distinguish this Berw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final phase of basic education, and level 3 (upper) secondary education or senior secondary education is the stage before tertiary education. Every country aims to provide basic education, but the systems and terminology remain unique to them. Secondary education typically takes place after six years of primary education and is followed by higher education, vocational education or employment. In most countries secondary education is compulsory education, compulsory, at least until the age of 16. Children typically enter the lower secondary phase around age 12. Compulsory education sometimes extends to age 19. Since 1989, education has been seen as a basic human right for a child; Article 28, of the Convention on the Rights of the Child states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Education
Primary education or elementary education is typically the first stage of formal education, coming after preschool/kindergarten and before secondary school. Primary education takes place in ''primary schools'', ''elementary schools'', or first schools and middle schools, depending on the location. The International Standard Classification of Education considers primary education as a single-phase where programmes are typically designed to provide fundamental reading, writing, and mathematics skills and establish a solid foundation for learning. This is ISCED Level 1: Primary education or first stage of basic education.Annex III in the ISCED 2011 English.pdf Navigate to International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) Definition The ISCED definition in 1997 po ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |