|
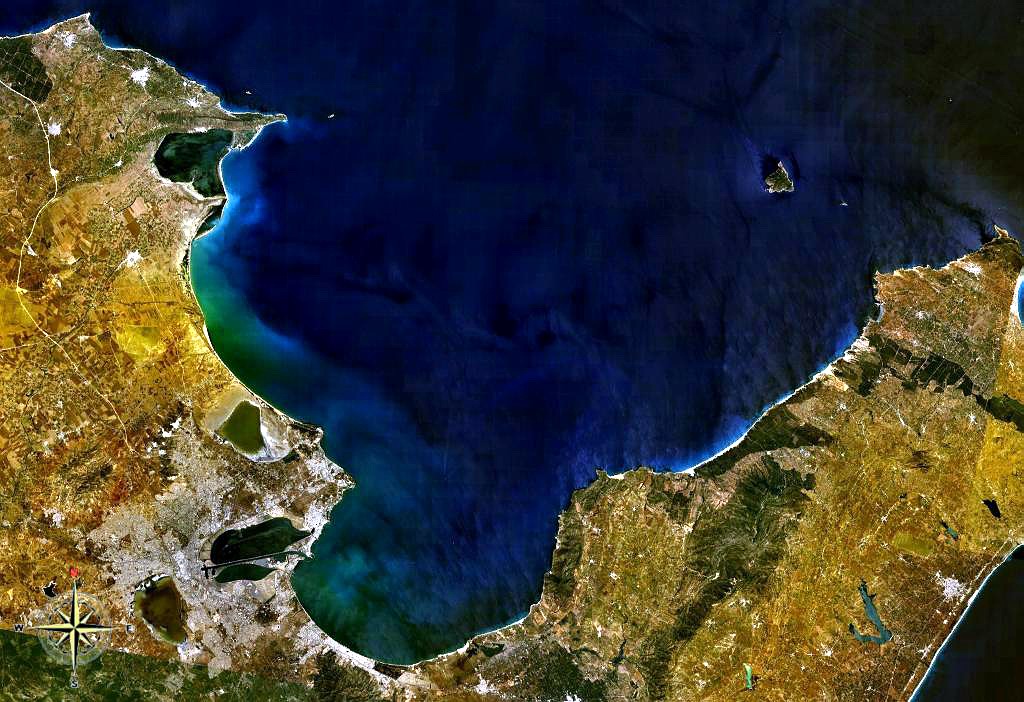
Gulf Of Chania
The Gulf of Chania is an embayment of the Sea of Crete in the northwestern region of the island of Crete in present-day Greece. One headland forming the Gulf of Chania is the promontory known as the Akrotiri Peninsula. Ancient history In prehistory the powerful city of Kydonia commanded the Gulf of Chania and was a center of early Cretan art and culture in western Crete. By 74 BC the city-state of Kydonia fended off an attack by Rome in a naval battle in the Gulf of Chania.Chania during antiquity See also *Britomartis Britomartis (; grc-gre, Βριτόμαρτις) was a Greek goddess of mountains and hunting, who was primarily worshipped on the island of Crete. She was sometimes believed to be an oread, or a mountain nymph, but she was often conflated or sy ... Line notes References Chania during antiquity* C. Michael Hogan* Robert Lambert Playfair (1892) ''Handbook to the Mediterranean: Its Cities, Coasts and Islands'', J. Murray publisher Gulfs of Greece Gulfs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Chania Satellite Picture
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ..., Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden. See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embayment
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, east of the islands of Kythera and Antikythera, south of the Cyclades, and west of the Dodecanese islands of Rhodes, Karpathos and Kassos. The bounding sea to the west is the Ionian Sea. To the northwest is the Myrtoan Sea, a subdivision of the Mediterranean Sea that lies between the Cyclades and Peloponnese. To the east-southeast is the rest of the Mediterranean Sea, sometimes credited as the Levantine Sea. Across the island of Crete, to the opposite shore of it begins the Libyan Sea. Ferry routes to and from Piraeus and Heraklion, as well as the southern islands of the Aegean and the Dodecanese, run in this area. Just off the coastline of Northeastern Crete, the sea reaches a maximum depth of near 3,293 m (10,000 ft). Other source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akrotiri (Crete)
Akrotiri ( el, Ακρωτήρι, literally "promontory") is a peninsula and former municipality in the Chania regional unit, Crete, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Chania, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of . Its ancient name was ''Kiamon'' while the Byzantines called it ''Charaka''. The largest town in the peninsula is Kounoupidiana. The beach at Stavros became famous because of the film Zorba the Greek. Geography and environment Akrotiri is a rocky promontory on the northern side of the island of Crete, in the Sea of Crete. It is roughly circular in shape, connected to the rest of the island by a wide causeway between Chania and the town of Souda. To the south, Souda Bay is found between the peninsula and the island. Most of the peninsula is a plateau somewhat elevated from the sea. There is a string of hills along the northern coast. A variety of flora occur on the rocky promontory of Akrotiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kydonia
Kydonia or Cydonia (; grc, Κυδωνία; lat, Cydonia) was an ancient city-state on the northwest coast of the island of Crete. It is at the site of the modern-day Greek city of Chania. In legend Cydonia was founded by King Cydon (), a son of Hermes or Apollo and of Akakallis, the daughter of King Minos. According to Pausanias he was son of king Tegeates. Diodorus Siculus mentions that the city was founded by King Minos. The editors of the ''Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World'' suggest that the city also bore the name Apollonia ( grc, Ἀπολλωνία). Prehistoric period The name of the city is first mentioned in Linear B tablets from Knossos (ku-do-ni-ja). At Kastelli hill, which is the citadel of Chania's harbor, archaeological excavations have discovered ceramic sherds, which date back to Neolithic era. Scarce finds such as walls and ground floors confirm that the systematic habitation of the hill began during Early Minoan (EM) II period. A Minoan Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Christ
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "''anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi''", which translates to 'in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ'. The form "BC" is specific to English and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin form is but is rarely seen. This calendar era is based on the traditionally reckoned year of the conception or birth of Jesus, ''AD'' counting years from the start of this epoch and ''BC'' denoting years before the start of the era. There is no year zero in this scheme; thus ''the year AD 1 immediately follows the year 1 BC''. This dating system was devised in 525 by Dionysius Exiguus, but was not widely used until the 9th century. Traditionally, English follows Latin usage by placing the "AD" abbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britomartis
Britomartis (; grc-gre, Βριτόμαρτις) was a Greek goddess of mountains and hunting, who was primarily worshipped on the island of Crete. She was sometimes believed to be an oread, or a mountain nymph, but she was often conflated or syncretized with Artemis and Aphaea, the "invisible" patroness of Aegina. She is also known as Dictynna (Δίκτυννα; derived by Hellenistic writers as from δίκτυα 'diktya'' "hunting nets"). Many writers have related her to the presumed mother goddess of much earlier Minoan religion; however, there is no evidence from archaeology for this. In the 16th century, the naming of a character identified with English military prowess as "Britomart" in Edmund Spenser's knightly epic ''The Faerie Queene'' (probably just because "Brit" seemed to fit well with "Britain", with "mart" from Mars, the god of war) led to a number of appearances by "Britomart" figures in British art and literature. Etymology According to Solinus, the name ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Playfair
Sir (Robert) Lambert Playfair (21 March 1828 – 18 February 1899) was a British soldier, diplomat, naturalist and author. Early life Lambert Playfair was a grandson of James Playfair, principal of the University of St Andrews, and son of George Playfair (1782–1846), chief inspector-general of hospitals in Bengal, and his wife Jessie Ross. Lambert was born in St Andrews when his parents were at home on leave, and left there to be educated when they returned to India. His elder brother, Lyon, became Lyon Playfair, 1st Baron Playfair. Another brother was Dr William Smoult Playfair, who became involved in a notorious court case, Kitson v. Playfair. Career and later life Playfair was a military cadet at Addiscombe College, then joined the Madras Army in 1846 at the age of 18. He became an artillery officer and with the rank of Captain was appointed to the Madras Staff Corps in 1858. He was promoted to Major in 1866, and left the army with the honorary rank of Lieutenant-Colonel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulfs Of Greece
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe .... See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |