|
Guijarral Hills
The Guijarral Hills are a range of low hills in the inner California Coast Ranges, in Fresno County, California, Fresno County, California, about seven miles east of the town of Coalinga, California, Coalinga. Guijarral is derived from a Spanish word meaning "heap of pebbles". They are the surface expression of an anticline, anticlinal structure which continues to the south as the Kettleman Hills, and to the north as Anticline Ridge, a portion of the huge Coalinga Oil Field. The Guijarral Hills overlie the smaller and mostly exhausted Guijarral Hills Oil Field. Jayne Avenue, which connects Interstate 5 to Coalinga, is the major east–west road through the hills. References Mountain ranges of Southern California Mountain ranges of Fresno County, California California Coast Ranges Geography of the San Joaquin Valley {{FresnoCountyCA-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresno County, California
Fresno County (), officially the County of Fresno, is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 1,008,654. The county seat is Fresno, the fifth-most populous city in California. Fresno County comprises the Fresno, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of the Fresno- Madera, CA Combined Statistical Area. It is located in the Central Valley, south of Stockton and north of Bakersfield. Since 2010, statewide droughts in California have further strained both Fresno County's and the entire Central Valley's water security. History The area now known as Fresno County was the traditional homeland of Yokuts and Mono peoples, and was later settled by Spaniards during a search for suitable mission sites. In 1846, this area became part of the United States as a result of the Mexican War. Fresno County was formed in 1856 from parts of Mariposa, Merced and Tulare counties. ''Fresno'' is Spanish for "ash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, most populous U.S. state and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 3rd largest by area. It is also the most populated Administrative division, subnational entity in North America and the 34th most populous in the world. The Greater Los Angeles area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second and fifth most populous Statistical area (United States), urban regions respectively, with the former having more than 18.7million residents and the latter having over 9.6million. Sacramento, California, Sacramento is the state's capital, while Los Angeles is the List of largest California cities by population, most populous city in the state and the List of United States cities by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
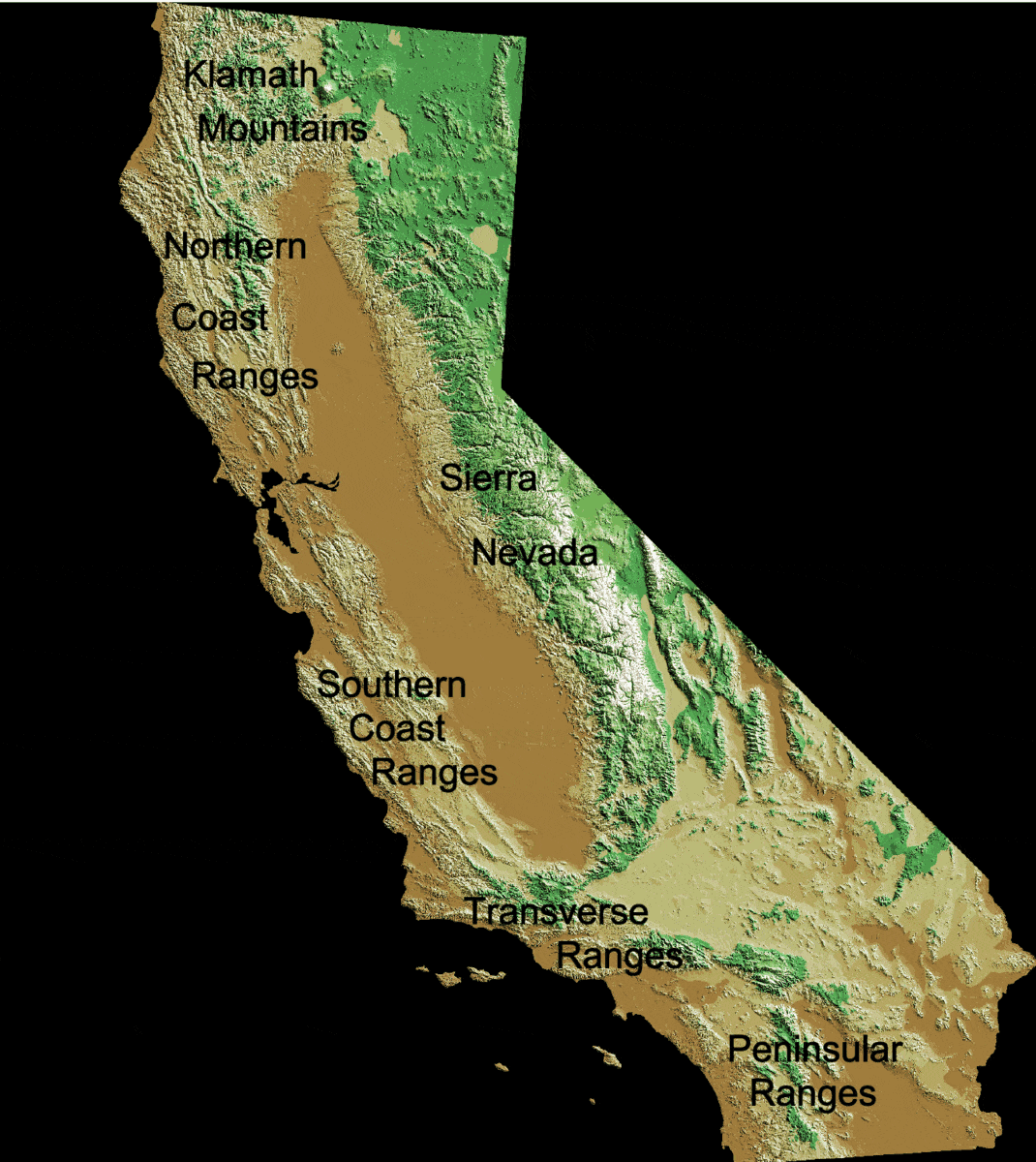
California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains. Physiographically, they are a section of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the larger Pacific Mountain System physiographic division. UNESCO has included the "California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve" in its Man and the Biosphere Programme of World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 1983. * Physiography The northern end of the California Coast Ranges overlap the southern end of the Klamath Mountains for approximately 80 miles on the west. They extend southward for more than 600 miles to where the coastline turns eastward along the Santa Barbara Channel, around the area of Point Conception. Here the southern end meets the Los Angeles Transverse Ranges, or ''Sierras de los Angeles''. The rocks themselves that com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalinga, California
Coalinga ( or ) is a city in Fresno County and the western San Joaquin Valley, in central California about 80 miles (128 km) southeast of Salinas. It was formerly known as ''Coaling Station A'', ''Coalingo'', and ''Coalinga Station''. The population was 13,380 as of the 2010 census, up from 11,668 at the 2000 census. It is the site of both Pleasant Valley State Prison and Coalinga State Hospital. History 19th century Legendary bandit Joaquin Murrieta was killed in 1853 at his headquarters, Arroyo de Cantua, north of Coalinga. California Historical Landmark #344 marks the approximate site of where he was slain, near the junction of present-day State Route 33 and Route 198. Before 20th-century diesel locomotives, steam locomotives were used, and powered in the San Joaquin Valley by burning coal mined from the northern foothills of Mount Diablo to the north. The Southern Pacific Railroad Company established the site as a coaling station in 1888, and it was called simply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kettleman Hills
The Kettleman Hills is a low mountain range of the interior California Coast Ranges, in western Kings County, California. It is a northwest–southeast trending line of hills about 30 miles long which parallels the San Andreas Fault to the west. The Kettleman Hills are named (though misspelled) after Dave Kettelman, a pioneer sheep and cattle rancher who grazed his animals there in the 1860s.Brown, Robert R. and Richmond, J.E., ''History of Kings County'', p.123, A.H. Cawston, Hanford, CA, 1940 The hills, which rise to an elevation of approximately , divide the San Joaquin Valley on the east from the much smaller Kettleman Plain to the west. They are the location of the Kettleman North Dome Oil Field. The Kettleman Hills Hazardous Waste Facility, a large () hazardous waste and municipal solid waste disposal facility operated by Waste Management, Inc., is located southwest of Kettleman City on State Route 41 The following highways are numbered 41: International * AH41, Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalinga Oil Field
The Coalinga Oil Field is a large oil field in western Fresno County, California, in the United States. It surrounds the town of Coalinga, about halfway between Los Angeles and San Francisco, to the west of Interstate 5, at the foot of the Diablo Range. Discovered in the late 19th century, it became active around 1890, and is now the eighth-largest oil field in California, with reserves totaling approximately , and over 1,600 active oil wells.California Department of Conservation, Oil and Gas Statistics, Annual Report, December 31, 2006 p. 2 The principal operators on the field, as of 2008, were |
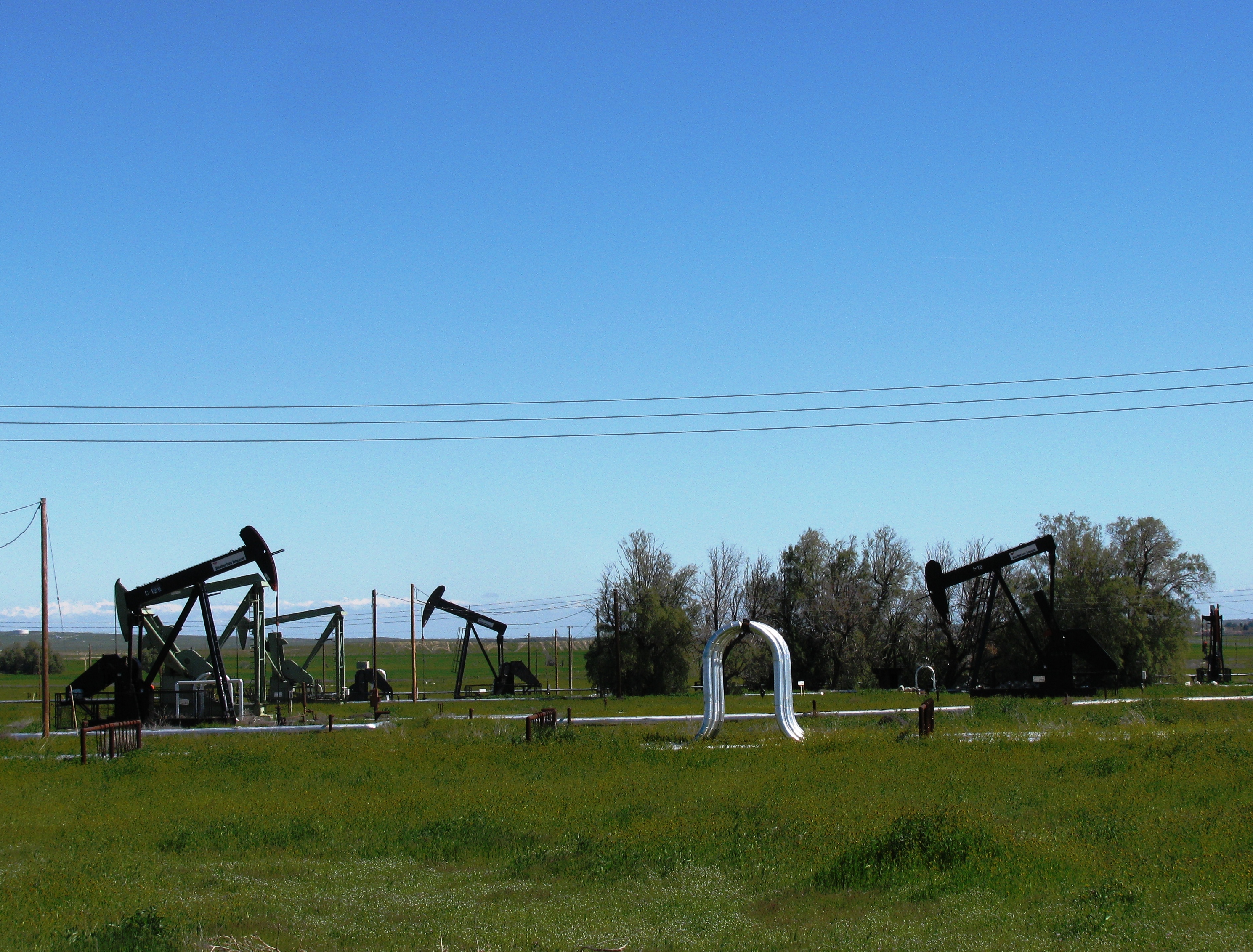
Guijarral Hills Oil Field
The Guijarral Hills Oil Field is a formerly-productive oil and gas field near Coalinga on the western side of the Central Valley in central California in the United States. Discovered in 1948, and having produced of oil during its peak year in 1950, it now has but one active oil well producing a little over a barrel of oil a day, and is very near to exhaustion, with only 343,000 recoverable barrels of oil remaining throughout its extent according to the official California State Department of Conservation estimate. p. 101-2. As of 2010, the only active operator was Longview Production Company. Setting The Guijarral Hills are a low range of hills, rising a little more than a hundred feet above the floor of the San Joaquin Valley to the east, and scarcely noticeable in the shadow of the nearby Coast Range of central California. These low hills are the surface expression of the southern portion of the Coalinga Anticline, which separates the smaller, largely agricultural Pleas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Southern California
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Fresno County, California
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |