|
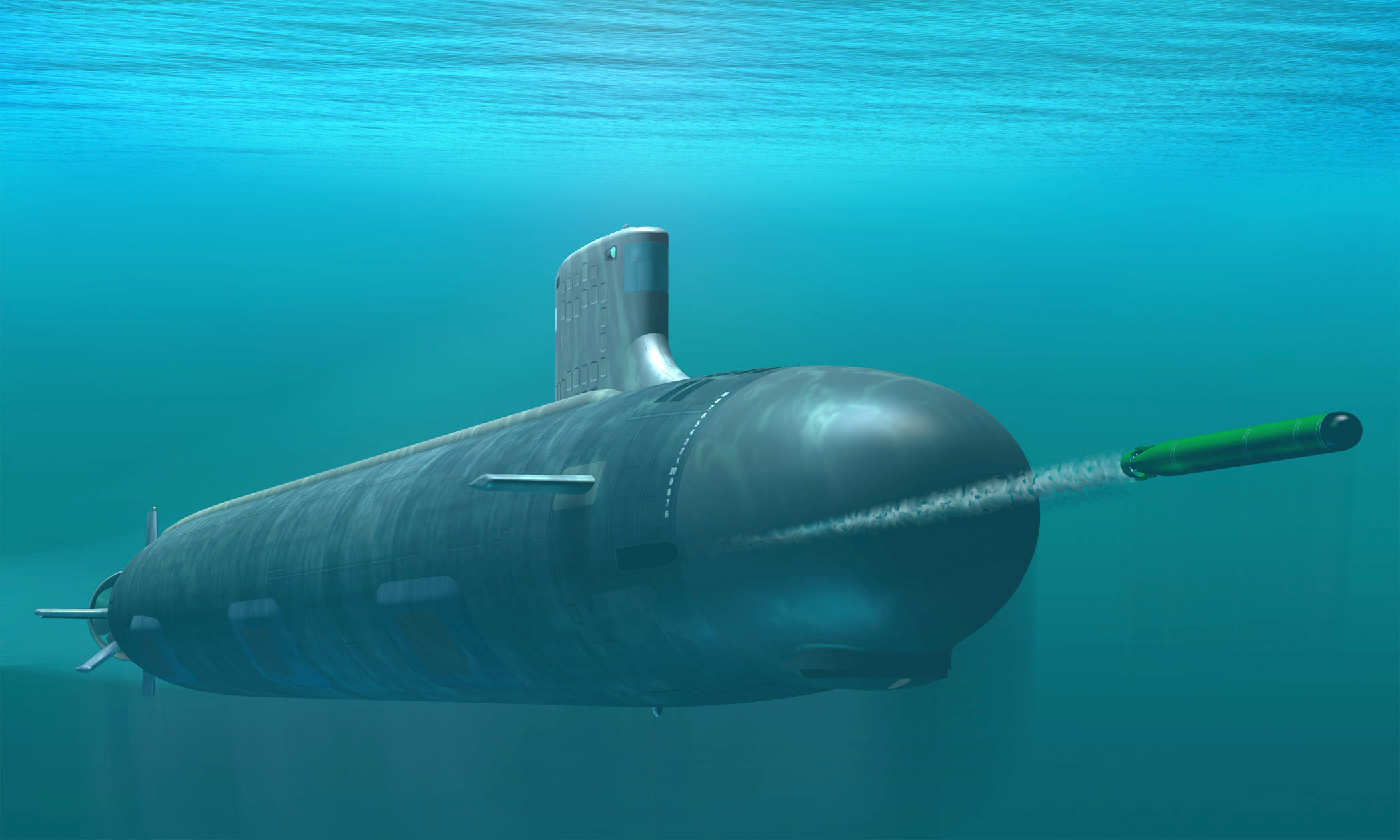
Guided-missile Submarine
A cruise missile submarine is a submarine that carries and launches cruise missiles ( SLCMs and anti-ship missiles) as its primary armament. Missiles greatly enhance a vessel's ability to attack surface combatants and strike land targets, and although torpedoes are a more stealthy option, missiles give a much longer stand-off range, as well as the ability to engage multiple targets on different headings at the same time. Many cruise missile submarines retain the capability to deploy nuclear warheads on their missiles, but they are considered distinct from ballistic missile submarines due to the substantial differences between the two weapons systems' characteristics. Originally early designs of cruise missile submarines had to surface to launch their missiles, while later designs could do so underwater via dedicated vertical launching system (VLS) tubes. Many modern attack submarines can launch cruise missiles (and dedicated anti-ship missiles) from their torpedo tubes while some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Florida (SSGN-728) Boat Enh
Several United States Navy ships have borne the name ''Florida'', in honor of the state of Florida: *''Florida'' (1824) was a sloop that served on survey duty between 1824 and 1831. Her final cruise, between 1 June 1830 and 31 May 1831, was under the command of Lieutenant T. R. Gedney. * was a side-wheel steamboat purchased in 1861 and sold after 1867. * was originally the screw frigate USS ''Wampanoag'', renamed in 1869, and sold in 1885. * was an monitor commissioned in 1903, renamed to USS ''Tallahassee'' in 1908, redesignated as IX-16 in 1921 and decommissioned and sold in 1922. * was the lead ship of her class of battleship, commissioned 1911 and scrapped in 1932. * is an cruise missile submarine, originally commissioned in 1983 as a ballistic missile submarine A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. The United States Navy's hull classification symbols for ballistic miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
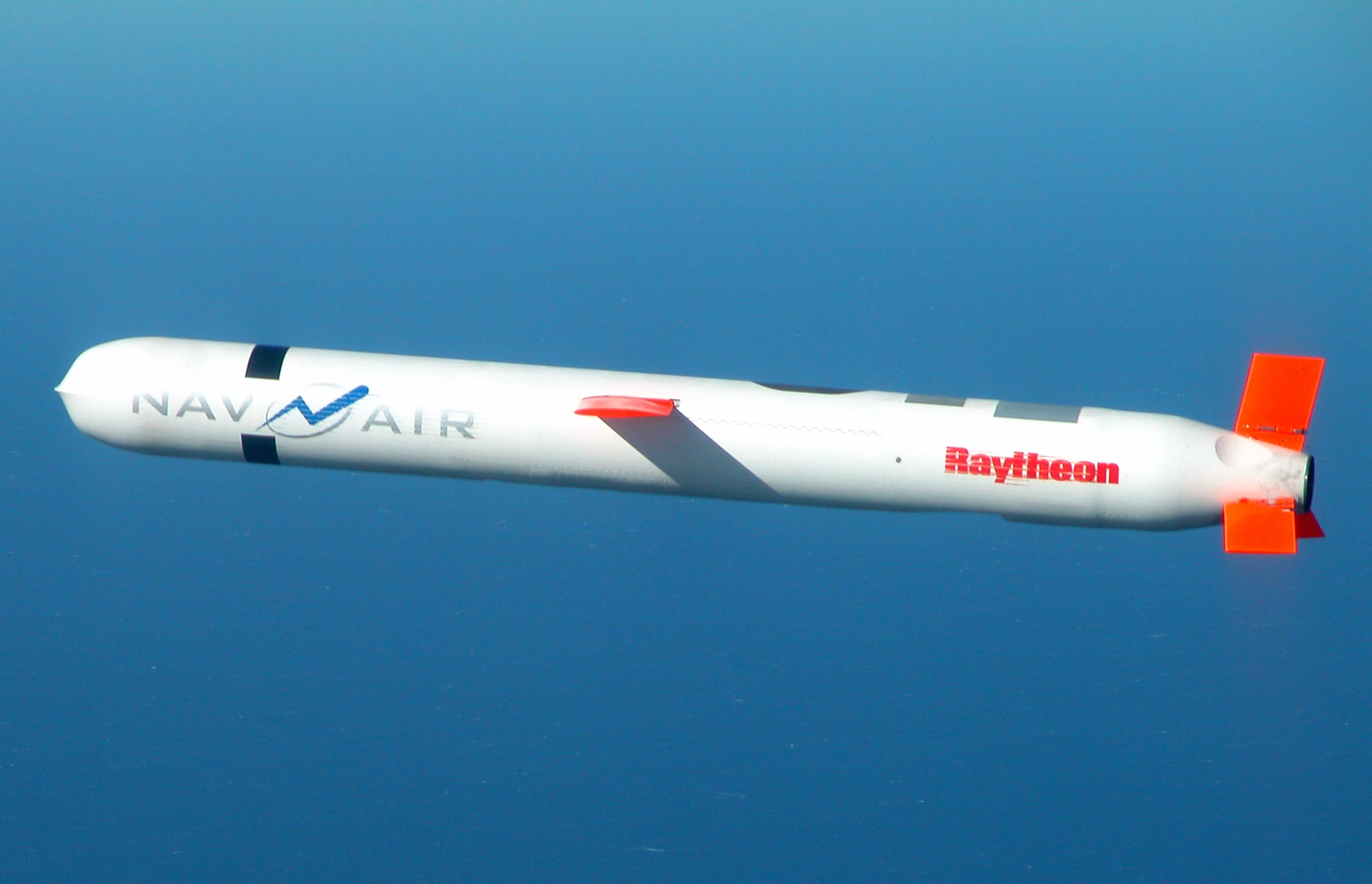
Tomahawk Cruise Missile
The Tomahawk () Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations. Under contract from the U.S. Navy, the Tomahawk was designed at the APL/ JHU in a project led by James Walker near Laurel, Maryland, and was first manufactured by General Dynamics in the 1970s. It was intended to fill the role of a medium- to long-range, low-altitude missile that could be launched from a naval surface warfare platform, and featured a modular design accommodating a wide variety of warhead, guidance, and range capabilities. At least six variants and multiple upgraded versions of the TLAM have been added since the original design was introduced, including air-, sub-, and ground-launched variants with conventional and nuclear armaments. In 1992–1994, McDonnell Douglas Corporation was the sole supplier of Tomahawk Missiles and produced Block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiskey-class Submarine
Whiskey-class submarines (known in the Soviet Union as List of ships of Russia by project number, Projects 613, 640, 644, and 665) are a class of diesel-electric attack submarines that the Soviet Union built in the early Cold War period. Design The initial design was developed in the early 1940s as a sea-going follow on to the Soviet S-class submarine, S-class submarine. As a result of war experience and the capture of German technology at the end of the war, the Soviets issued a new design requirement in 1946. The revised design was developed by the Lazurit Design Bureau based in Gorkiy. Like most conventional submarines designed 1946–1960, the design was heavily influenced by the Type XXI submarine, Type XXI U-boat. Patrol variants Between 1949 and 1958 a total of 236 of an envisaged 340 submarines of this type were commissioned into the Soviet Navy. The vessels were initially designed as coastal patrol submarines. These patrol variants are known in the west as Whiskey I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ships Of Russia By Project Number
The list of ships of Russia by project number includes all Russian ships by assigned project numbers. Ship descriptions are Russian assigned classifications when known. (The Russian term "проект" can be translated either as the cognate "project" or as "design".) * Project 1: (Series I) * Project 2: (Series I & III) * Project 3: (Series I) * Project 4: (Series II) * Project 5: ''Toplivo-1'' class water lighter * Project 6: * Project 7: * Project 7U: * Project 9: S-class diesel attack submarine * Project 19: NKVD large guard ship, cancelled * Project 20: leader * Project 21: Study for 35,500-ton -style battleship * Project 22: Heavy cruiser design cancelled 1939 * Project 23: * Project 23bis: Improvement over Project 23 with simplified belt armor of 380mm, American style TDS replacing Italian style, additional twin 100mm dual-purpose guns, 4 triple 152mm guns instead of 6 twin 152mm guns. 12 406mm gun variant was also made * Project 24: post-World War II battleship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO Reporting Name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manner in place of the original designations, which either may have been unknown to the Western world at the time or easily confused codes. For example, the Russian bomber jet Tupolev Tu-160 is simply called "Blackjack". NATO maintains lists of the names. The assignment of the names for the Russian and Chinese aircraft was once managed by the five-nation Air Standardization Coordinating Committee (ASCC), but that is no longer the case. American variations The United States Department of Defense (DOD) expands on the NATO reporting names in some cases. NATO refers to surface-to-air missile systems mounted on ships or submarines with the same names as the corresponding land-based systems, but the US DoD assigns a different series of numbers with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia-class Submarine
The ''Virginia'' class, also known as the SSN-774 class, is a class of nuclear-powered cruise missile fast-attack submarines, in service in the United States Navy. Designed by General Dynamics Electric Boat (EB) and Huntington Ingalls Industries, the ''Virginia'' class is the United States Navy's latest submarine model, which incorporates the latest in stealth, intelligence gathering, and weapons systems technology. ''Virginia''-class submarines are designed for a broad spectrum of open-ocean and littoral missions, including anti-submarine warfare and intelligence gathering operations. They are scheduled to replace older s, many of which have already been decommissioned. ''Virginia''-class submarines will be acquired through 2043, and are expected to remain in service until at least 2060, with later submarines expected to remain into the 2070s. History The class was developed under the codename Centurion, later renamed New SSN (NSSN). The "Centurion Study" was initiated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Odyssey Dawn
Operation Odyssey Dawn was the U.S. code name for the American role in the international military operation in Libya to enforce United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 during the initial period of 19–31 March 2011, which continued afterwards under NATO command as Operation Unified Protector. The initial operation implemented a no-fly zone that was proposed during the Libyan Civil War to prevent government forces loyal to Muammar Gaddafi from carrying out air attacks on anti-Gaddafi forces. On 19 March 2011, several countries prepared to take immediate military action at a summit in Paris. Operations commenced on the same day with a strike by French fighter jets, then US and UK forces conducting strikes from ships and submarines via 110 Tomahawk cruise missiles and air assets bombing Gaddafi forces near Benghazi. The goal of coalition forces was to impose a no-fly zone for Libyan government forces. The U.S. initially had strategic command of the military intervention, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the List of countries by proven oil reserves, 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yeltsin on 3 January 1993, banning the use of multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs) on intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Hence, it is often cited as the De-MIRV-ing Agreement. It was ratified by the US Senate on 26 January 1996 with a vote of 87–4. Russia ratified START II on 14 April 2000, making it conditional on preserving the ABM Treaty. When the US withdrew from the ABM Treaty on June 13, 2002, Russia withdrew from START II one day later. Thus, START II never entered into effect. Instead, SORT came into effect, which reduced the strategic warheads count per country to 1,700–2,200. Impact of MIRV ICBMs using MIRVs are considered destabilizing because they put a premium on a first strike. These missil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Underwater Vehicle
Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUV), sometimes known as underwater drones, are submersible vehicles that can operate underwater without a human occupant. These vehicles may be divided into two categories: remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROUVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). ROUVs are remotely controlled by a human operator. AUVs are automated and operate independently of direct human input. Classifications Remotely operated underwater vehicle Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicles (ROUVs) is a subclass of UUVs with the primary purpose of replacing humans for underwater tasks due to the difficult underwater conditions. ROUVs are designed to perform educational or industrial missions. They are manually controlled by an operator to perform tasks that include surveillance and patrolling. The structure of ROUVs disqualify it from being able to operate autonomously. In addition to a camera, actuators, and sensors, ROUVs often include a “gripper” or something ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Boat_Enh.jpg)