|
Guduf-Gava Language
Guduf-Gava (also known as Gudupe, Afkabiye) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Borno State, Nigeria. In a 2006 paper, Roger Blench Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and work ... classified Cineni as a dialect.Blench, 2006The Afro-Asiatic Languages: Classification and Reference List(ms) Blench (2019) lists Cikide as a dialect of Guduf. Notes Biu-Mandara languages Languages of Nigeria {{Nigeria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
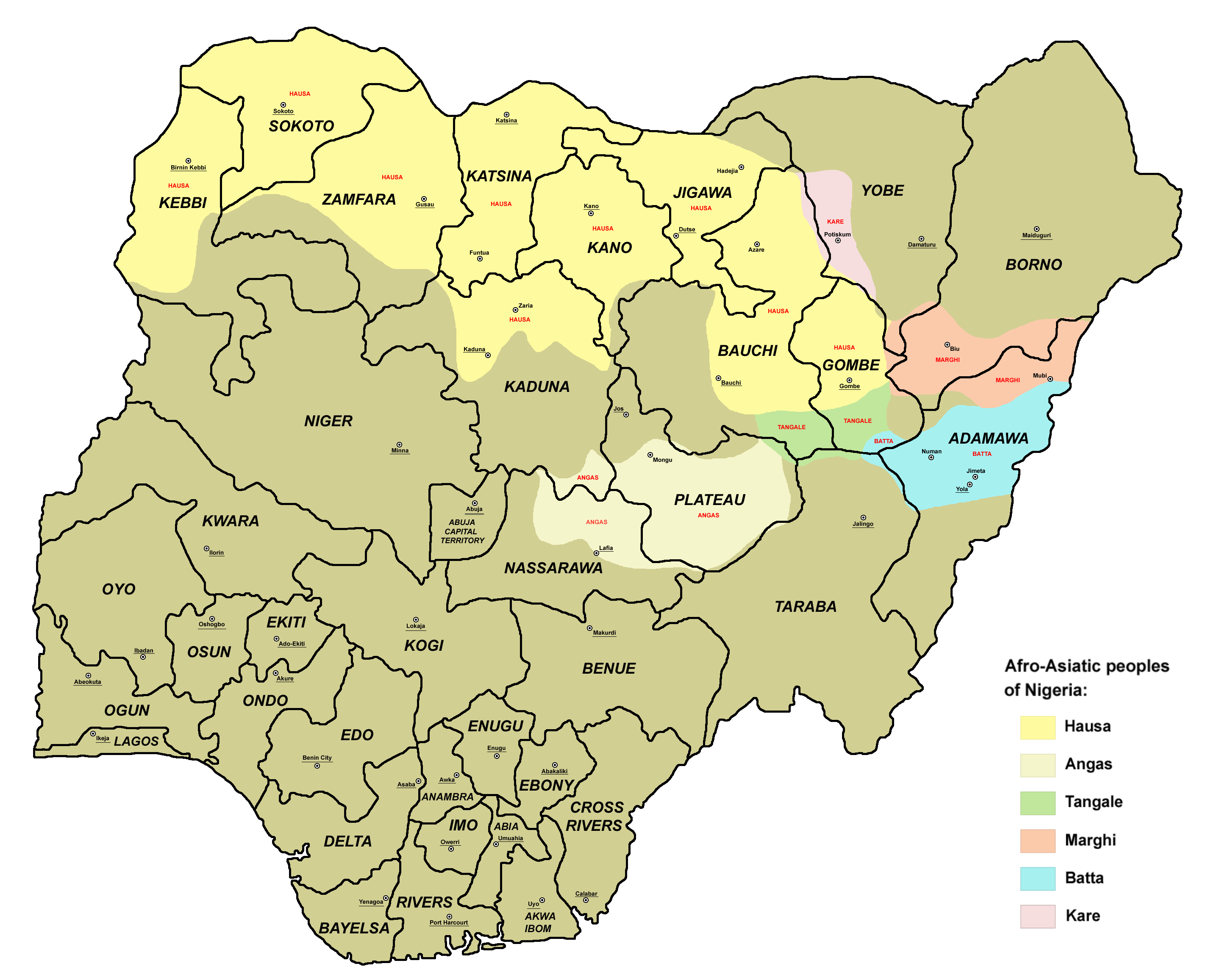
Borno State
Borno is a States of Nigeria, state in the North East (Nigeria), North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria. It is bordered by Yobe State, Yobe to the west, Gombe State, Gombe to the southwest, and Adamawa State, Adamawa to the south while its eastern border forms part of the national Cameroon-Nigeria border, border with Cameroon. Its northern border forms part of the national Niger–Nigeria border, border with Niger and its northeastern border forms all of the national Chad–Nigeria border, border with Chad. It is the only Nigerian state to border up to three countries. It takes its name from the historic Borno Emirate, emirate of Borno, with the emirate's old capital of Maiduguri serving as the capital city of Borno State. The state was formed in 1976 when the former North-Eastern State was broken up. It originally included the area that is now Yobe State, which became a distinct state in 1991. Borno is the List of Nigerian states by area, second largest in area of the States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadic Languages
The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 196 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, and northern Cameroon. By far the most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland Eastern West Africa, particularly Niger and the northern half of Nigeria. Hausa is the only Chadic language with more than 1 million speakers. Composition Paul Newman (1977) classified the languages into the four groups which have been accepted in all subsequent literature. Further subbranching, however, has not been as robust; Roger Blench (2006), for example, only accepts the A/B bifurcation of East Chadic. Subsequent work by Joseph Lovestrand argues strongly that Kujarge is a valid member of East Chadic. The placing of Luri as a primary split of West Chadic is erroneous. Bernard Caron (2004) shows that this language is South Bauchi and part of the Polci cluster. A sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biu–Mandara Languages
The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon. A reconstruction of Proto-Central Chadic has been proposed by Gravina (2014). Languages Gravina (2014) Gravina (2014) classifies Central Chadic as follows, as part of a reconstruction of the proto-language. Letters and numbers in parentheses correspond to branches in previous classifications. The greatest changes are breaking up and reassigning the languages of the old Mafa branch (A.5) and Mandage (Kotoko) branch (B.1). *Central Chadic **South ***South ****Bata (A.8) *****Bata Proper: Bacama language, Bacama, Bata language, Bata, Fali of Mubi, Fali, Gude language, Gude, Gudu language, Gudu, Holma language, Holma (†), Jimi language (Cameroon), Jimi, Ngwaba language, Ngwaba (from A.1 Tera), Nzanyi language, Nzanyi, Sharwa language, Sharwa *****Tsuvan: Tsuvan language, Tsuvan, Zizilivakan language, Zizilivakan ****Daba (A.7) *****Daba Proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandala Languages
The Mandara Kingdom (sometimes called Wandala or the Kingdom of Medra) was an African kingdom in the Mandara Mountains of what is today Cameroon. The Mandara people are descended from the kingdom's inhabitants. History Tradition states that Mandara was founded shortly before 1500 by a female ruler named ''Soukda'' and a non-Mandarawa hunter named ''Gaya''. The kingdom was first referred to by Fra Mauro (in 1459) and Leo Africanus (in 1526); the provenance of its name remains uncertain. Medra is mostly likely the original name of Mandara, one letter being obliterated in Leo's Arabic notes. Leo acknowledges the Kingdom of Medra (Mandara) for their good governors and rulers. The inhabitants of Medra are rich and industrious people, visited often, and great lovers of justice and equity. The region of Medra is listed on the Africae Tabula Nova in 1570. Leo Africanus visited the Kingdom of Medra, located in the south. For the kingdom's first century of history, its rulers warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cineni Language
Cineni is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Borno State, Nigeria in the single village of Cineni. In a 2006 paper, Roger Blench Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and work ... classified it as a dialect of Guduf-Gava.Blench, 2006The Afro-Asiatic Languages: Classification and Reference List(ms) Notes Biu-Mandara languages Languages of Nigeria {{Nigeria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Asiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber (Amazigh), Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch (which originated in West Asia). The five most spoken languages are; Arabic (of all varieties) which is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 411 million native speakers concentrated primarily in West Asia and North Africa, the Chadic Hausa language w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Blench
Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and works as a consultant. Career Blench is known for his wide-ranging interests and has made important contributions to African linguistics, Southeast Asian linguistics, anthropology, ethnomusicology, ethnobotany, and various other related fields. He has done significant research on the Niger–Congo, Nilo-Saharan, and Afroasiatic families, as well as the Arunachal languages. Additionally, Blench has published extensively on the relationship between linguistics and archaeology. Blench is currently engaged in a long-term project to document the languages of central Nigeria. He has also expressed concern about ranching in Nigeria. Blench collaborated with the late Professor Kay Williamson, who died in January 2005, and is now a trustee of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |