|
Gudo Wafu Nishijima
Gudo is a former municipality in the district of Bellinzona in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. On 2 April 2017 the former municipalities of Camorino, Claro, Giubiasco, Gnosca, Gorduno, Moleno, Monte Carasso, Pianezzo, Preonzo, Sant'Antonio and Sementina merged into the new municipality of Bellinzona. History Prehistory In 1909–10, work on the banks of the Ticino river in the hamlet of Progero uncovered an extensive prehistoric burial ground. This site, known as ''A Progero'' is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. The oldest finds are pottery fragments, indicating that the area was probably inhabited in the Early Bronze Age (17th–16th century BC). The next layer of finds included grave pottery from the Late Bronze Age (13th–12th century BC). Most of the necropolis (over 300 graves) dates from the Iron Age (6th century BC). This settlement is from the Golasecca culture and lasted until about the 2nd century BC. The graves from this period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellinzona (district)
The district of Bellinzona ( it, Distretto di Bellinzona, also called ''Bellinzonese'') is a district of Canton Ticino, Switzerland. It has a population of (as of ). Geography The district has an area, . Of this area, or 13.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 68.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 8.3% is settled (buildings or roads), or 1.5% is either rivers or lakes and or 7.3% is unproductive land. Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 4.0% and transportation infrastructure made up 2.5%. Out of the forested land, 59.7% of the total land area is heavily forested and 2.2% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 7.5% is used for growing crops, while 1.7% is used for orchards or vine crops and 4.0% is used for alpine pastures. All the water in the district is flowing water. Of the unproductive areas, 5.2% is unproductive vegetation and 2.1% is too rocky for vegetation. Demographics Of the Swiss na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preonzo
Preonzo is a former municipality in the district of Bellinzona in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. On 2 April 2017, the former municipalities of Camorino, Claro, Giubiasco, Gnosca, Gorduno, Moleno, Monte Carasso, Pianezzo, Sant'Antonio and Sementina merged into the municipality of Bellinzona. History Preonzo is first mentioned in 1335 as ''Prevonzo''. In the 14th Century, Moleno and Preonzo formed a settlement. In 1335 it became a municipality in the County of Bellinzona. During the first conquest of the Ticino in 1403–22, it was ruled by the cantons of Uri and Obwalden. They granted the villages its statutes and customary rights (''Statuti'', ''ordini''), although, in contrast to Moleno, it was not incorporated in the Levantine. The parish church of SS Simone e Giuda was built in 1459. In the 17th century it was rebuilt and then renovated in 1963–66 and 1996–97. It broke away from the Church of S. Vittore in Moleno in 1545. Together with Gnosca and Moleno it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepontic Language
Lepontic is an ancient Alpine Celtic languageJohn T. Koch (ed.) ''Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia'' ABC-CLIO (2005) that was spoken in parts of Rhaetia and Cisalpine Gaul (now Northern Italy) between 550 and 100 BC. Lepontic is attested in inscriptions found in an area centered on Lugano, Switzerland, and including the Lake Como and Lake Maggiore areas of Italy. While some recent scholarship (e.g. Eska 1998) has tended to consider Lepontic simply as an early outlying form of Gaulish and closely akin to other, later attestations of Gaulish in Italy (Cisalpine Gaulish), some scholars (notably Lejeune 1971) continue to view it as a distinct Continental Celtic language. In this latter view, the earlier inscriptions found within a 50 km radius of Lugano are considered Lepontic, while the later ones, to the immediate south of this area, are considered Cisalpine Gaulish. Lepontic was assimilated first by Gaulish, with the settlement of Gallic tribes north of the River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situla (vessel)
Situla (plural ''situlae''), from the Latin word for bucket or pail, is the term in archaeology and art history for a variety of elaborate bucket-shaped vessels from the Iron Age to the Middle Ages, usually with a handle at the top. All types may be highly decorated, most characteristically with reliefs in bands or friezes running round the vessel. Decorated Iron Age situlae in bronze are a distinctive feature of Etruscan art in burials from the northern part of the Etruscan regions, from which the style spread north to some cultures in Northern Italy, Slovenia, and adjacent areas, where terms such as situla culture and situla art may be used. Situla is also the term for types of bucket-shaped Ancient Greek vases, some very finely painted. More utilitarian pottery situlae are also found, and some in silver or other materials, such as two glass ones from late antiquity in St Mark's, Venice. Ancient Egyptian and Near Eastern shapes tend to have a pointed bottom, so that they must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urns
An urn is a vase, often with a cover, with a typically narrowed neck above a rounded body and a footed pedestal. Describing a vessel as an "urn", as opposed to a vase or other terms, generally reflects its use rather than any particular shape or origin. The term is especially often used for funerary urns, vessels used in burials, either to hold the cremated ashes or as grave goods, but is used in many other contexts. Large sculpted vases are often called urns, whether placed outdoors, in gardens or as architectural ornaments on buildings, or kept inside. In catering, large vessels for serving tea or coffee are often called "tea-urns", even when they are metal cylinders of purely functional design. Urns are also a common reference in thought experiments in probability wherein marbles or balls of different colors are used to represent different results and the urn represents the "container" of the whole set of possible states. Funerary Funerary urns (also called cinerary urns a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
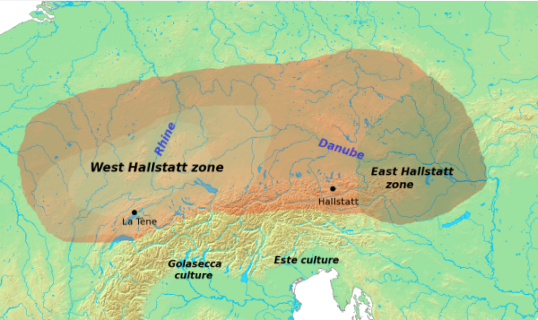
Golasecca Culture
The Golasecca culture (9th - 4th century BC) was a Late Bronze Age/Early Iron Age culture in northern Italy, whose type-site was excavated at Golasecca in the province of Varese, Lombardy, where, in the area of Monsorino at the beginning of the 19th century, Abbot Giovanni Battista Giani made the first findings of about fifty graves with pottery and metal objects. The culture's material evidence is scattered over a wide area of 20,000 km²Raffaele de Marinis, ''Liguri e Celto-Liguri'' in ''Italia. Omniun terrarum alumna'', Garzanti-Scheiwiller, 1988. south of the Alps, between the rivers Po, Serio and Sesia, and bordered on the north by the Alpine passes. Archaeological sources The name of the Golasecca culture comes from the first findings that were discovered from excavations conducted from 1822 at several locations in the Comune of Golasecca, by the antiquarian abbot Father Giovanni Battista Giani (1788–1857), who misidentified the clearly non-Roman burials as r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead". The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distance from a city, as opposed to tombs within cities, which were common in various places and periods of history. They are different from grave fields, which did not have structures or markers above the ground. While the word is most commonly used for ancient sites, the name was revived in the early 19th century and applied to planned city cemeteries, such as the Glasgow Necropolis. Necropoli in the ancient world Egypt Ancient Egypt is noted for multiple necropoleis. Ancient Egyptian funerary practices and beliefs about the afterlife led to the construction of several extensive necropoleis to secure and provision the dead in the hereafter. These necropoleis are therefore major archaeological si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (place)
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a Parish (administrative division), parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. The word and concept of a hamlet has roots in the Anglo-Norman settlement of England, where the old French ' came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic languages, West Germanic) Franconian languages. Compare with modern French ', Dutch language, Dutch ', Frisian languages, Frisian ', German ', Old English ' and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the Qila, qala (Dari language, Dari: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)