|
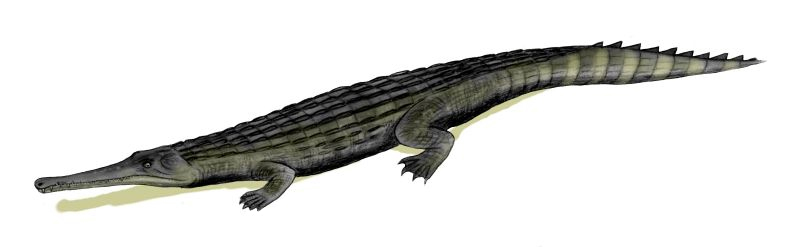
Guarinisuchus
''Guarinisuchus'' is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform from the Early Paleocene 62 million years ago of the Maria Farinha Formation, Brazil.''Guarinisuchus'' at Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals ... .org The type species is ''G. munizi''. It was a dominant predator in its environment, and probably reached a length of . '' ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiupampan
The Tiupampan ( es, Tiupampense) age is a period of geologic time (64.5–62.5 Ma) within the Paleocene epoch of the Paleogene used more specifically with South American land mammal ages (SALMA). It is the oldest SALMA age and precedes the Peligran age.Tiupampan in the Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms.
History
The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ...
Etymology The age is named after the paleontological site[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosaurids
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Farinha Formation
The Maria Farinha Formation is a geological formation of the Parnaíba Basin in Pernambuco, northeastern Brazil whose strata date back to the Danian stage of the Paleocene, or Tiupampan in the SALMA classification. The formation comprising limestones, dolomites, marly and sandy limestones has been deposited in a shallow marine platform environment. The formation has provided fossils of reptiles and fish. Description The Maria Farinha Formation crops out in the Parnaíba Basin in the northeastern state of Pernambuco of Brazil. The formation registers the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary at the base of the formation, where it overlies the Maastrichtian Gramame Formation. The thick formation is overlain by the Eocene Tambaba Formation which is overlain by the Plio-Pleistocene Barreiras Formation.Ribeiro de Santana et al., 2011, p.5 Fossil content The following fossils were reported from the formation: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 In Paleontology
Protozoa New taxa Plants Angiosperms Monocots Arthropoda Arachnids Insects Xiphosurans Fishes Bony fish Placoderms General research *Hilton & Grande redescribe the fossil mooneyes of western North America synonymizing the genus ''Eohiodon'' with ''Hiodon''. *Cicimurri, Paris, & Everhart describe a partial dentition from a Holocephali chimaeroid fish found in the Niobrara Chalk. Amphibians Jenkins, F. A., jr, Shubin, N. H., Gatesy, S. M., and Warren, A., 2008, Gerrothorax pulcherrimus from the Upper Triassic Fleming Fjord Formation of East Greenland and a reassessment of head lifting in temnospondyl feeding: Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, v. 28, n. 4, p. 935-950. Newly named amphibians Archosaurs Newly named pseudosuchians Newly named pterosaurs Dinosaurs * Oviraptorosaurian eggs with embryonic skeletons are discovered for the first time in China. * Mongolian Late Jurassic theropod fossils are found for the first time. * A new study on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Paleocene
The Danian is the oldest age or lowest stage of the Paleocene Epoch or Series, of the Paleogene Period or System, and of the Cenozoic Era or Erathem. The beginning of the Danian (and the end of the preceding Maastrichtian) is at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event . The age ended , being followed by the Selandian. Stratigraphic definitions The Danian was introduced in scientific literature by German- Swiss geologist Pierre Jean Édouard Desor in 1847 following a study of fossils found in France and Denmark.Danien He identified this stage in deposits from |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Brazil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene Brazil
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognised as a formal stratigraphic term, 'Tertiary' is still widely found in earth science literature and remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg" (but the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation PE for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps). During the Paleogene, mammals diversified from relatively small, simple forms into a large group of diverse animals in the wake of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that ended the preceding Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene Reptiles Of South America
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene Crocodylomorphs
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Marine Crocodylomorphs
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Pseudosuchian Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |