|
Grumman XSBF
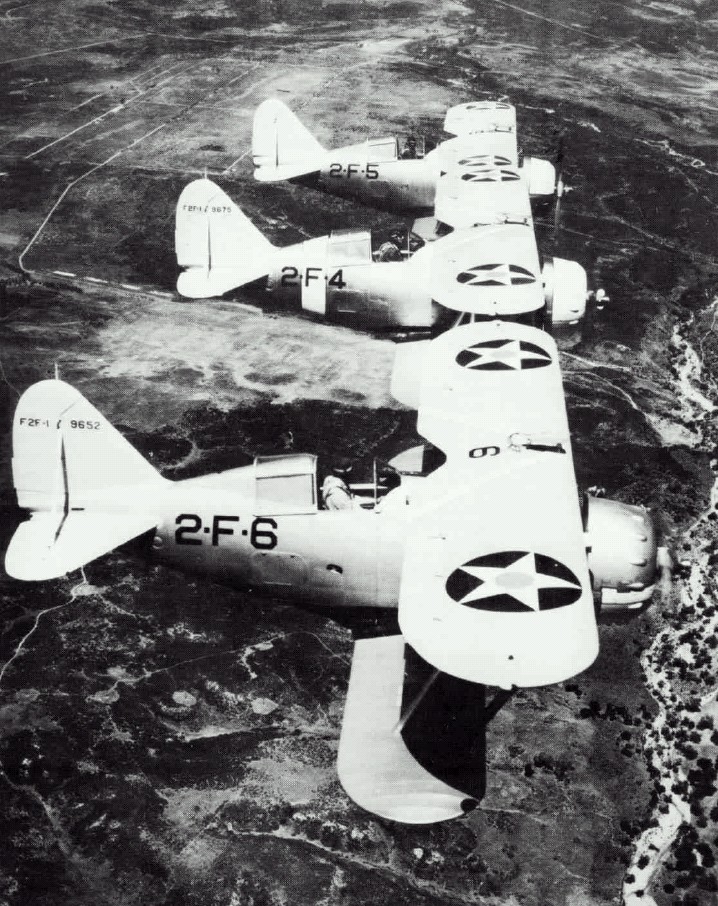
The Grumman XSBF, also known by the company designation G-14, was an American biplane scout bomber developed by Grumman Aircraft for the United States Navy during the 1930s. Derived from Grumman's successful " Fifi" fighter, the aircraft was developed at a time when the biplane was giving way to the monoplane. In competition against other aircraft it proved to possess inferior performance in its intended role, and did not enter production. The sole prototype went on to serve as a liaison aircraft, as well as being used in experiments by NACA, before being destroyed in a crash in 1939. Design and development In late 1934, the U.S. Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) issued a specification for new scout bomber and torpedo bomber designs.Dann 1996, p.20. Eight companies submitted 10 designs in response, evenly split between monoplanes and biplanes.Doll 1992, p.4. Grumman, having successfully provided the FF and F2F fighters to the Navy, along with the SF scout, submitted an ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss SBC Helldiver
The Curtiss SBC Helldiver was a two-seat scout bomber and dive bomber built by the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. It was the last military biplane procured by the United States Navy. Delivered in 1937, it became obsolete even before World War II and was kept well away from combat with Axis fighters.Wheeler 1992, p. 27. Development There was controversy in the United States Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) in the early 1930s regarding two-seat fighter planes, monoplanes and the retractable undercarriage In 1931, the Navy issued Design Specification No. 113, which detailed a requirement for a high-performance fighter with fixed undercarriage to be powered by the Wright R-1510Gunston p 199 or Pratt & Whitney's R-1535 radial engine. Seven companies submitted proposals and two companies, the Douglas Aircraft with their XFD-1 and the Chance Vought with their XF3U-1 were given contracts for one prototype each. Both of these aircraft were two-seat biplanes. The Navy then asked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1919 Browning Machine Gun
The M1919 Browning is a .30 caliber medium machine gun that was widely used during the 20th century, especially during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. The M1919 saw service as a light infantry, coaxial, mounted, aircraft, and anti-aircraft machine gun by the U.S. and many other countries. The M1919 was an air-cooled development of the standard US machine gun of World War I, the John M. Browning-designed water-cooled M1917. The emergence of general-purpose machine guns in the 1950s pushed the M1919 into secondary roles in many cases, especially after the arrival of the M60 in US Army service. The United States Navy also converted many to 7.62 mm NATO, and designated them Mk 21 Mod 0; they were commonly used on riverine craft in the 1960s and 1970s in Vietnam. Many NATO countries also converted their examples to 7.62 mm caliber, and these remained in service well into the 1990s, as well as up to the present day in some countries. Operation Loading The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable-pitch Propeller (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller (airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed (RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit. Reversible propellers are those where the pitch can be set to negative values. This creates reverse thrust for braking or going backwards without the need to change the direction of shaft revolution. Some aircraft have ground-adjustable propellers, however these are not considered variable-pitch. These are typically found only on light aircraft and microlights. Purpose When an aircraft is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings around the edge of the master rod. Extra "rows" of radial cylinders can be added i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney R-1535 Twin Wasp Junior
The Pratt & Whitney R-1535 Twin Wasp Junior was an engine used in American aircraft in the 1930s. The engine was introduced in 1932 as a 14-cylinder version of the 9-cylinder R-985. It was a two-row, air-cooled radial design. Displacement was ; bore and stroke were both . Variants * R-1535-11 - * R-1535-13 - , * R-1535-44 - * R-1535-72 - * R-1535-94 - * R-1535-96 - * R-1535-98 - * R-1535-SB4-G - Applications *Bellanca 28-70 * Boeing XF6B * Breguet 695 *Bristol Bolingbroke *Canadian Car and Foundry FDB-1 * Consolidated XB2Y * Curtiss SBC-3 Helldiver *Douglas O-46 *Fokker G.I (G.I The Wasp) *Fokker D.XXI (Finnish licence-built series 4 and 5) *Great Lakes BG *Grumman F2F * Grumman F3F-1 * Grumman XJF-1 Duck (prototype only) *Grumman XSBF * Grumman XSF-2 *Hughes H-1 Racer *Miles Master *Northrop A-17 *Northrop BT * Northrop XFT-2 *Vought SBU Corsair *Vought SB2U Vindicator *Vought V-141 *Vought XF3U * Vought XO4U-2 Engines on display * There is a R-1535-96 on display at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grumman F2F
The Grumman F2F was a single-engine, biplane fighter aircraft with retractable undercarriage, serving as the standard fighter for the United States Navy between 1936 and 1940. It was designed for both carrier- and land-based operations. Design and development Grumman's success with the two-seat FF-1, which was significantly faster than even the single-seat fighters of its time, resulted in a contract for the single-seat XF2F-1.Jordan, Corey C."Grumman's Ascendency: Chapter Two." ''Planes and Pilots Of World War Two,'' 2000. Retrieved: 22 July 2011. Armed with two .30 caliber (7.62 mm) machine guns above the cowl, the new design also incorporated watertight compartments to reduce weight and improve survivability in the event of a water landing.Cacutt 1989, pp. 155–162. The prototype first flew on 18 October 1933, equipped with the experimental XR-1534-44 Twin Wasp Junior radial engine, and reached a top speed of at – faster than the FF-1 at the same altitude. Maneuv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vought XSB3U
The Vought XSB3U was an American biplane scout bomber developed by Vought-Sikorsky for the United States Navy during the 1930s. Developed as an alternative to the SB2U Vindicator monoplane, the aircraft proved unsatisfactory to the Navy in comparison, and development was not pursued. Design and development In late 1934, the U.S. Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) issued a specification for new scout bomber and torpedo bomber designs.Dann 1996, p.20. Eight companies submitted ten designs in response, evenly split between monoplanes and biplanes.Doll 1992, p.4. Exemplifying the Bureau of Aeronautics' reluctance to fully embrace the monoplane configuration for carrier-based aircraft,Johnson 2008, p.309. the XSB3U-1 was proposed as a more conventional alternative to Vought's XSB2U-1, which was designed as a modern monoplane. The XSB3U was modified from the last production SBU Corsair, using essentially the same airframe, including a fully enclosed cockpit, and Pratt & Whitney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vought SB2U Vindicator
The Vought SB2U Vindicator is an American carrier-based dive bomber developed for the United States Navy in the 1930s, the first monoplane in this role. Vindicators still remained in service at the time of the Battle of Midway, but by 1943, all had been withdrawn to training units. It was known as the Chesapeake in Royal Navy service. Design and development In 1934, the United States Navy issued a requirement for a new Scout Bomber for carrier use, and received proposals from six manufacturers. The specification was issued in two parts, one for a monoplane, and one for a biplane. Vought submitted designs in both categories, which would become the XSB2U-1 and XSB3U-1 respectively. The biplane was considered alongside the monoplane design as a "hedge" against the U.S. Navy's reluctance to pursue the modern configuration.McKillop, Jack"Chance-Vought SB2U Vindicator" ''The Pacific War: The U.S. Navy''. Archived from the original aon 9 October 2007. The XSB2U-1 was of conventional lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas SBD Dauntless
The Douglas SBD Dauntless is a World War II American naval scout plane and dive bomber that was manufactured by Douglas Aircraft from 1940 through 1944. The SBD ("Scout Bomber Douglas") was the United States Navy's main carrier-based scout/dive bomber from mid-1940 through mid-1944. The SBD was also flown by the United States Marine Corps, both from land air bases and aircraft carriers. The SBD is best remembered as the bomber that delivered the fatal blows to the Japanese carriers at the Battle of Midway in June 1942.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 25–34, Cypress, CA, 2013. . The type earned its nickname "Slow But Deadly" (from its SBD initials) during this period. During its combat service, the SBD proved to be an excellent naval scout plane and dive bomber. It possessed long range, good handling characteristics, maneuverability, potent bomb load, great diving characteristics from the perforated dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop BT
The Northrop BT was an American two-seat, single-engine monoplane dive bomber built by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Navy. At the time, Northrop was a subsidiary of the Douglas Aircraft Company. While unsuccessful in its own right, the BT was subsequently redesigned into the Douglas SBD Dauntless, which would form the backbone of the Navy's dive bomber force. Design and development The design of the initial version began in 1935. It was powered by a Pratt and Whitney XR-1535-66 double row air-cooled radial engine and had hydraulically actuated perforated split flaps (dive brakes), and main landing gear that retracted backwards into fairing "trousers" beneath the wings.Rene J. Francillon (1990 ed), ''McDonnell Douglas Since 1920, Volume I''. Annapolis, Maryland, Naval Institute Press The perforated flaps were invented to eliminate tail buffeting during diving maneuvers. The next iteration of the BT, the XBT-1, was equipped with a R-1535. This aircraft was foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall XPTBH
The Hall XPTBH was a prototype American twin-engined seaplane, submitted to the United States Navy by the Hall Aluminum Aircraft Corporation in response to a 1934 specification for new bomber and scout aircraft. Constructed in an innovative fashion that made extensive use of aluminum, the XPTBH proved successful in flight testing, but failed to win favor with the U.S. Navy. No production contract was awarded, and the single aircraft built served in experimental duties before its destruction in a hurricane during 1938. Design and development In late 1934, the U.S. Navy's Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) issued a specification for new scout bomber and torpedo bomber designs.Dann 1996, p.20. Eight companies submitted a total of ten designs in response, evenly split between monoplanes and biplanes.Doll 1992, p.4. The Hall Aluminum Aircraft Company submitted the only seaplane design; a single prototype was ordered by the Navy for evaluation on June 30, 1934. Given the designation XPT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)