|
Grimpoteuthis Boylei
''Grimpoteuthis boylei'' is a species of octopus known from only ten individuals. Description The Grimpoteuthis Boylei is a pelagic umbrella octopus, also known as the "dumbo octopus" because it breaks resemblance to the title character of Disney's film Dumbo, 1941. It is large, reaching a total length of 470 millimeters (18.5 inches). Like all cirrates, it has a web over its arms and cirri between its suckers, as well as fins for swimming and a hard shell inside its mantle. ''G. boylei'' has a shell shaped like a saddle. Habitat ''G. boylei'' lives at abyssal depths of the Northeast Atlantic Ocean, more specifically the Porcupine Abyssal Plain and the Porcupine Seabight. It lives near two other members of its genus, '' Grimpoteuthis challengeri'' and ''Grimpoteuthis discoveryi''. The octopus is found between 4,190 and 4,848 meters deep (13,747 to 15,905.5 feet). It is likely that ''G. boylei'' is demersal The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrina
Cirrina or Cirrata is a suborder and one of the two main divisions of octopuses. Cirrate octopuses have a small, internal shell and two fins on their head, while their sister suborder Incirrina has neither. The fins of cirrate octopods are associated with a unique cartilage-like shell in a shell sac. In cross-section, the fins have distinct proximal and distal regions, both of which are covered by a thin surface sheath of muscle. The suborder is named for small, cilia-like strands (cirri) on the arms of the octopus, a pair for each sucker. These are thought to play some role in feeding, perhaps by creating currents of water that help bring food closer to the beak. Cirrate octopuses are noteworthy for lacking ink sacs. Phylogeny A molecular phylogeny based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA marker sequences by Sanchez et al., 2018, shows that the Cirrina is paraphyletic, i.e. it is not a single clade. Instead, a clade containing Opisthoteuthidae and Cirroctopodidae is sister t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrus (biology)
In biology, a cirrus , plural ''cirri'', , (from the Latin ''cirrus'' meaning a ''curl-like tuft or fringe'') is a long, thin structure in an animal similar to a tentacle but generally lacking the tentacle's strength, flexibility, thickness, and sensitivity. In the sheep liver fluke, for example, the ''cirrus'' is the worm's muscular penis and when not in use is retained within a ''cirrus sac'' or ''pouch'' near the animal's head. The same structure exists in the various ''Taenia'' species of tapeworm. In the clam worms, however, the cirrus is the tentacular process or growth on each of the feet (''parpodia''), either the ''dorsal cirrus'' or the ''ventral cirrus'', and has nothing to do with reproduction. Among the bristleworms, a cirrus is a tentacular growth near the head or notopodium containing sense organs and may be either dorsal, ventral, or lamellar. Among the ribbonworms, the ''caudal cirrus'' is a small thread-like growth at the posterior end of the worm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrate Shell
Cirrate octopuses possess a well-developed internal shell that supports their muscular swimming fins. This is in contrast to the more familiar, finless, incirrate octopuses, in which the shell remnant is either present as a pair of stylets or absent altogether. The cirrate shell is quite unlike that of any other living cephalopod group and has its own dedicated set of descriptive terms. It is usually roughly arch- or saddle-shaped and is rather soft, being similar in consistency to cartilage. Each of the eight extant cirrate genera is characterised by a distinct shell morphology: * Cirroteuthidae **'' Cirroteuthis'' — saddle-shaped, with large wings **'' Cirrothauma'' — butterfly-shaped * Opisthoteuthidae **'' Cirroctopus'' — V-shaped, lateral wings tapering to fine points **'' Cryptoteuthis'' — U-shaped, each lateral wing ending in broad lobe with pointed projection **''Grimpoteuthis'' — U-shaped, lateral wings ending bluntly **'' Luteuthis'' — W-shaped **'' Opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
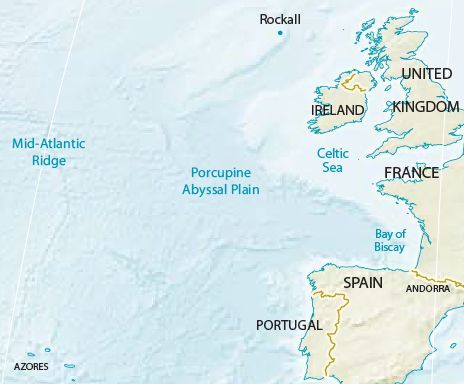
Porcupine Abyssal Plain
The Porcupine Abyssal Plain (PAP) is located in international waters, adjacent to the Irish continental margin. The PAP lies beyond the Porcupine Bank's deepest point and is southwest of it. It has a muddy seabed, with scattered abyssal hills that covers an area approximately half the size of Europe's landmass. Its depth ranges from to . Characteristics The Porcupine Abyssal Plain is a vast, relatively level stretch of seabed with a depth range of . It has a muddy floor in the abyssopelagic zone and scattered rocky abyssal hills that rise into the bathypelagic zone forming seamounts and knolls. The water at this depth is relatively stable and moving slowly towards the south and southeast. There is a downward flow of organic detritus derived from primary production in the upper layers of ocean that settles on the sea floor. Fauna A large number of marine invertebrates inhabit the abyssal plain. About 90% by number and biomass of the macrobenthos are sea cucumbers and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcupine Seabight
The Porcupine Seabight or Porcupine Basin is a deep-water oceanic basin located on the continental margin in the northeastern portion of the Atlantic Ocean. It can be found in the southwestern offshore portion of Ireland and is part of a series of interconnected basins linked to a failed rift structure associated with the opening of the Northern Atlantic Ocean. The basin extends in a North-South direction and was formed during numerous subsidence and rifting periods between the Late Carboniferous and Late Cretaceous. It is bordered by the * Goban Spur to the south * Slyne Ridge to the north * Porcupine Bank to the west * Porcupine Abyssal Plain to the southwest Due to subsidence, water depths range from 3000 m in the south near its mouth to 400 m in the north. The Porcupine Basin lies on the Caledonian metamorphic basement and preserves up to 12 km of sedimentary strata from Late Palaeozoic to Quaternary which includes significant hydrocarbon reservoirs. Sediment was likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimpoteuthis Challengeri
''Grimpoteuthis challengeri'' is a species of large octopus living in the abyssal zone. Description The octopus is 370 millimeters long in total, while its mantle reaches a length of up to 75 millimeters. It has long arms, and it has a web covering them that reaches 2/3 of the arm length. ''G. challengeri'' has between 63 and 72 suckers on its arms. Its shell is shaped like the letter "U". Like other cirrate octopods, ''G. challengeri'' has fins on either side of its mantle that it uses to swim through the ocean. This octopus's fins are long. It also has a beak, as do other octopuses. ''G. challengeri'' is a red-brown color when preserved, and its fins have a slight purple hue. The octopus's lifespan is unknown. It may lay its eggs on the seafloor, instead of brooding them. Habitat ''G. challengeri'' is known from multiple specimens collected in the Porcupine Abyssal Plain of the Northeast Atlantic Ocean, while another specimen was found in the northwest Atlantic. It lives 4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimpoteuthis Discoveryi
''Grimpoteuthis discoveryi'' is a small species of octopus known from more than 50 specimens. It was described in 2003, but specimens have been found as early as 1910. The type species was found at 49°35'N, 14°01'W. Description At maximum, ''Grimpoteuthis discoveryis mantle is 58 millimeters in length, and its body in total reaches 370 millimeters. Its arms are long. ''G. discoveryi'', like other cirrates, has a web covering its arms to some degree; this species' web reaches 2/3 of its arm length. The suckers on its arms number between 56 and 61. The suckers of female specimens are smaller than the suckers of males, and are also differently shaped. The range in mantle size are larger in females (32-58mm) than males (25-52mm). Thposterior salivary glandsand radula are both absent in this species, however, itanterior salivary glandsare present. The species' body is white, and its eyes are dark grey or black when preserved. It's possible that ''G. discoveryi'' is actually two se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer of the larger profundal zone. Being just above the ocean floor, the demersal zone is variable in depth and can be part of the photic zone where light can penetrate, and photosynthetic organisms grow, or the aphotic zone, which begins between depths of roughly and extends to the ocean depths, where no light penetrates. Fish The distinction between demersal species of fish and pelagic species is not always clear cut. The Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua'') is a typical demersal fish, but can also be found in the open water column, and the Atlantic herring (''Clupea harengus'') is predominantly a pelagic species but forms large aggregations near the seabed when it spawns on banks of gravel. Two types of fish inhabit the demersal zone: those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs Described In 2003
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs Of The Atlantic Ocean
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopuses
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various regions of the ocean, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)