|
Grimoires In Popular Culture
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons.Davies (2009:1) In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers, although in many cultures, other sacred texts that are not grimoires (such as the Bible) have been believed to have supernatural properties intrinsically. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all ''books on magic'' could be thought of as grimoires, not all ''magical books'' should be thought of as grimoires. While the term ''grimoire'' is originally European—and many Europeans throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talis02
Talis or TALIS may refer to: People * Talis J. Colberg, attorney general of Alaska, appointed 2006 * Talis Kitsing, Estonian kickboxer and politician * Talis Kimberley, English folk singer-songwriter Places * Talis, Pakistan, a village in Ghanche District, Pakistan * Talış (other), any of several places in Azerbaijan and Iran Other uses * Talis (moth), ''Talis'' (moth), a genus of moths of the family Crambidae * Talis Group, a software company in Birmingham, England * Tallit, a Jewish prayer shawl * Metaclazepam, an anxiolytic drug (trade name Talis) * Teaching and Learning International Survey, an OECD survey See also * Tallis (other) * Thales (other) * Thalys, a train service between Paris, Brussels, Cologne and Amsterdam {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunning Folk
Cunning folk, also known as folk healers or wise folk, were practitioners of folk medicine, helpful folk magic and divination in Europe from the Middle Ages until the 20th century. Their practices were known as the cunning craft. Their services also included thwarting witchcraft. Although some cunning folk were denounced as witches themselves, they made up a minority of those accused, and the common people generally made a distinction between the two. The name 'cunning folk' originally referred to folk-healers and magic-workers in Britain, but the name is now applied as an umbrella term for similar people in other parts of Europe. Names given to folk-healers and magic-workers in Europe include: * the French ''devins-guérisseurs'' ("soothsayer-healers") and ''leveurs de sorts'' ("curse-lifters") * the Italian '' fattucchiere'' ("fixers"), '' guaritori'' ("healers") or ''benandanti'' ("good walkers") * the Dutch ''toverdokters'' ("magic-doctors") or ''duivelbanners'' ("devil-bann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Iraqi Arabs, Kurds, Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Armenians in Iraq, Armenians, Yazidis, Mandaeans, Iranians in Iraq, Persians and Shabaks, Shabakis with similarly diverse Geography of Iraq, geography and Wildlife of Iraq, wildlife. The vast majority of the country's 44 million residents are Muslims – the notable other faiths are Christianity in Iraq, Christianity, Yazidism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Zoroastrianism. The official langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papyrus Magique - Charme D'amour - BNUS Inv 1167
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a document written on sheets of such material, joined side by side and rolled up into a scroll, an early form of a book. Papyrus is first known to have been used in Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. It was also used throughout the Mediterranean region. Apart from a writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets. History Papyrus was first manufactured in Egypt as far back as the fourth millennium BCE.H. Idris Bell and T.C. Skeat, 1935"Papyrus and its uses"(British Museum pamphlet). The earliest archaeological evidence of papyrus was excavated in 2012 and 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
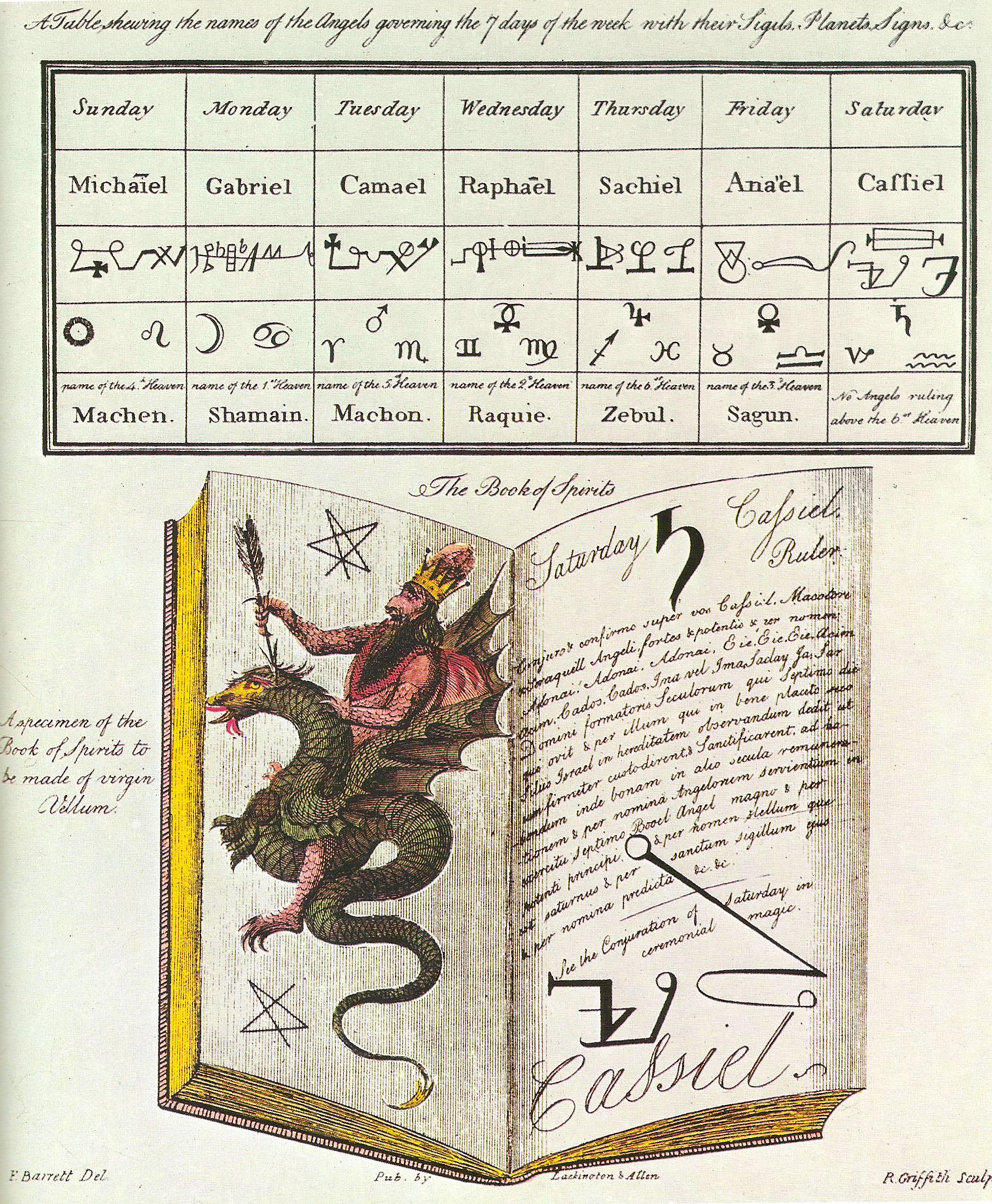
The Magus (handbook)
''The Magus, or Celestial Intelligencer'' is a handbook of the occult and ceremonial magic compiled by occultist Francis Barrett published in 1801. Contents and Sources Much of the material was actually collected by Barrett from older occult handbooks, as he hints in the preface: We have collected out of the works of the most famous magicians, such as Zoroaster, Hermes, Apollonius, Simon of the Temple, Trithemius, Agrippa, Porta (the Neapolitan), Dee, Paracelsus, Roger Bacon, and a great many others... In fact, most of the material comes from Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' and Pietro d'Abano's ''Heptameron''. Previous demonologists such as Binsfeld (1589) had drawn up lists that comprised a hierarchy of devils, and attributed them with the power to instigate people to commit the seven deadly sins. Lucifer was associated with Pride, Satan with Anger and so forth. In ''The Magus'' Barrett altered the "roster of devils" and Satan now became a prince of deluders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Barrett (occultist)
Francis Barrett (born probably in London around 1770–1780, died ''after'' 1802) was an English occultist. Background Barrett, an Englishman, claimed himself to be a student of chemistry, metaphysics and natural occult philosophy. He was known to be an extreme eccentric who gave lessons in the magical arts in his apartment and fastidiously translated Kabbalistic and other ancient texts into English, such as von Welling's work, ''Philosophy of The Universe'' circa 1735, from German (1801). According to his biographer Francis X. King, Barrett's parents were humble folk married in the parish of St. Martin's in the Fields on 29 September 1772. ''The Magus'' Barrett was enthusiastic about reviving interest in the occult arts, and published a magical textbook called ''The Magus''. It was a compilation, almost entirely consisting of selections from Cornelius Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'', the ''Fourth Book of Occult Philosophy'' attributed to Agrippa, and Robert Tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occultism
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism and their varied spells. It can also refer to supernatural ideas like extra-sensory perception and parapsychology. The term ''occult sciences'' was used in 16th-century Europe to refer to astrology, alchemy, and natural magic. The term ''occultism'' emerged in 19th-century France, amongst figures such as Antoine Court de Gébelin. It came to be associated with various French esoteric groups connected to Éliphas Lévi and Papus, and in 1875 was introduced into the English language by the esotericist Helena Blavatsky. Throughout the 20th century, the term was used idiosyncratically by a range of different authors, but by the 21st century was commonly employed – including by academic scholars of esotericism – to refer to a range of es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure Of Speech
A figure of speech or rhetorical figure is a word or phrase that intentionally deviates from ordinary language use in order to produce a rhetorical effect. Figures of speech are traditionally classified into '' schemes,'' which vary the ordinary sequence of words, and '' tropes,'' where words carry a meaning other than what they ordinarily signify. An example of a scheme is a polysyndeton: the repetition of a conjunction before every element in a list, whereas the conjunction typically would appear only before the last element, as in "Lions and tigers and bears, oh my!"—emphasizing the danger and number of animals more than the prosaic wording with only the second "and". An example of a trope is the metaphor, describing one thing as something that it clearly is not in order to lead the mind to compare them, in "All the world's a stage." Four rhetorical operations Classical rhetoricians classified figures of speech into four categories or :Jansen, Jeroen (2008) Imitatio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old French Language
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligible yet diverse, spoken in the northern half of France. These dialects came to be collectively known as the , contrasting with the in the south of France. The mid-14th century witnessed the emergence of Middle French, the language of the French Renaissance in the Île de France region; this dialect was a predecessor to Modern French. Other dialects of Old French evolved themselves into modern forms (Poitevin-Saintongeais, Gallo, Norman, Picard, Walloon, etc.), each with its own linguistic features and history. The region where Old French was spoken natively roughly extended to the northern half of the Kingdom of France and its vassals (including parts of the Angevin Empire, which during the 12th century remained under Anglo-Norman rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, Media, Parthia and Persis), Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands (Turkey's Eastern Anatolia Region, Armenia, northwestern Iran, southern Georgia, and western Azerbaijan), the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date it ends varies. The term covers the Bronze Age and the Iron Age in the region, until either the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, that by the Macedonian Empire in the 4th century BC, or the Muslim conquest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |