|
Griesberg
At the Griesberg near Bad Salzdetfurth in the Lower Saxon county of Hildesheim is the highest hill in the Hildesheim Forest, a small range of the Innerste Uplands. Geography Location The Griesberg is located in the southeast of the Hildesheim Forest between the town of Bad Salzdetfurth to the east and the village of Petze to the southwest in the east of the municipality of Sibbesse. Its summit region is on the territory of Almstedt, parts of the eastern and southern hillside are in the borough of Bad Salzdetfurth and other areas of the southwestern flank lie in the territory of Sibbesse. Southeast of the hill the Klusbach flows in a westerly direction into the Lamme and to the northwest is the ''Kalte Beuster'', a right-hand headstream of the Beuster. Natural regional classification The Griesberg is part of the natural regional major unit group of the Weser-Leine Uplands (No. 37), the major unit of the Innerste Uplands (379), the sub-unit of the Hildesheim Upland (3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hildesheim Forest
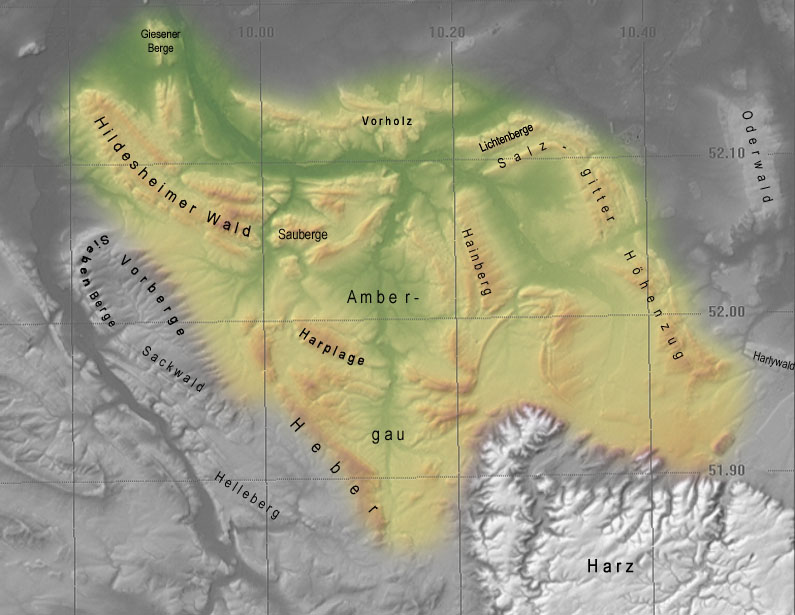
The Hildesheim Forest (german: Hildesheimer Wald) is a range of hills up to in the district of Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony. Geography The Hildesheim Forest is located in the Innerste Uplands, part of the Lower Saxon Hills, between the valleys of the Leine to the west, the Innerste to the north and the Lamme to the east. These densely forested hills, which are bordered to the east by the Sauberge and lie a few kilometres west-southwest of the Vorholz, fill an area south of Hildesheim, northwest of Bad Salzdetfurth, north of Sibbesse and southeast of Nordstemmen. Description The Hildesheim Forest, which attain a height of 359 m in the Griesberg, are crossed by numerous waterways, hiking trails and forest tracks, but only by one state road, the L 485, which links Hildesheim via Diekholzen to Sibbesse. In its northwestern part is the Beusterburg, whose circular ramparts are suggestive of a New Stone Age settlement. In the vicinity of the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills Of Lower Saxony
This List of mountains and hills in Lower Saxony shows a selection of high or well-known mountains and hills in the German state of Lower Saxony (''in order of height''). Although there is no universally agreed definition of a 'mountain', summits at 2.000 feet (610 metres) or higher may generally be referred to as mountains; those below 2.000 feet as 'hills',Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984. . hence the division of this list. By this definition, it can be seen that all the mountains in Lower Saxony occur in the Harz. Highest points in Lower Saxony's regions The following table lists the highest points in the various landscapes (hill ranges or regions) of Lower Saxony. In the "Landscape" column, major hill ranges are shown in bold. Clicking "List" in the rows of the "List" column links to other hills or mountains in that landscape – some of which are outside Lower Saxony. The table is arranged by height, but may be sorted by oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innerste Uplands
The Innerste Uplands (german: Innerstebergland) is a landscape region up to 359 m high and covering an area of over 900 km² in the northern part of the German Central Uplands. It lies within the eastern part of the Weser-Leine Uplands in Lower Saxony (Germany). The Innerste Uplands gets its name from the Innerste, a tributary of the River Leine. Geography Location The Innerste Uplands cover the catchment area of the Innerste southeast of Hildesheim and southwest to south of Salzgitter as far as Goslar and Seesen on the northwestern edge of the Harz. To the north the area is bounded by the Hildesheim Börde, to the west by the Leine Uplands and to the southeast by the North Harz Foreland. Its central and southern areas are dominated by the Ambergau, a depression dissected by the Nette, a tributary of the Innerste. In and around the Innerste Uplands there are the following clearly defined ridges, most of which are cuestas and some of which lie on the boundary wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beuster (Innerste)
Beuster is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It flows into the Innerste south of Hildesheim. Its total length, including its source river ''Warme Beuster'', is . See also *List of rivers of Lower Saxony All rivers in the German state of Lower Saxony flow directly or indirectly into the North Sea. A–Z A B D E F G H I J K L M N O P * Purrmühlenbach R S T * Tiefenbeek * Trillkebach * Trutenbeek * Twiste U * Uffe * Ulrich ... References Rivers of Lower Saxony Rivers of Germany {{LowerSaxony-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segeste
Almstedt is a village and a former municipality in the district of Hildesheim in Lower Saxony, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... Since 1 November 2016, it is part of the municipality Sibbesse. Almstedt consists of the village of Almstedt and the smaller village of Segeste. Each of the villages has a sightworthy old church and well-preserved half-timbered houses. The church in Segeste was built in 1770. Image:Almstedt 005.jpg, Protestant Church in Almstedt Image:Almstedt 001.jpg, Protestant Church in Almstedt Image:Almstedt 031.jpg, General view of Segeste Image:Almstedt 019.jpg, Main street, Segeste Image:Almstedt 016.jpg, Protestant Church, Segeste Image:Almstedt 021.jpg, Protestant Church, Segeste References Hildesheim (district) Former municip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Östrum
Östrum is a village in the southern part of the town of Bad Salzdetfurth in Lower Saxony, Germany. The L 490 state road runs through the village crossing with the L493. Its immediate neighbours are the villages of Breinum to the west and Bodenburg to the south. History As part of the administrative reform in 1974 Östrum became one of the 13 parishes in the borough of Bad Salzdetfurth. Politics As of 2022, the parish chair is Thomas Andreas (SPD). Culture and places of interest * The Protestant Chapel, which is the landmark of the village, was probably built around 800. Originally, it was dedicated to Saint Mary-Magdalena. The chapel is on a small hill which might be of an artificial origin. The year 1511 possible referring to a renovation is indicated above the entrance. The chapel has firing slits and might have been used as a fortified church during times of war in the Middle Ages. After the Reformation the chapel was allocated to the Protestants. When the chapel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landesstraße
''Landesstraßen'' (singular: ''Landesstraße'') are roads in Germany and Austria that are, as a rule, the responsibility of the respective German or Austrian federal state. The term may therefore be translated as "state road". They are roads that cross the boundary of a rural or urban district (''Landkreis'' or ''Kreisfreie Stadt''). A ''Landesstraße'' is thus less important than a ''Bundesstraße'' or federal road, but more significant than a ''Kreisstraße'' or district road. The classification of a road as a ''Landesstraße'' is a legal matter (''Widmung''). In the free states of Bavaria and Saxony – but not, however, in the Free State of Thuringia – ''Landesstraßen'' are known as ''Staatsstraßen''. Designation The abbreviation for a ''Landesstraße'' consists of a prefixed capital letter ''L'' and a serial number (e. g. L 1, L 83, L 262 or L 3190). ''Staatsstraßen'' in Saxony are similarly abbreviated using a capital ''S'' (e. g. S 190) and the ''Staatsstraßen' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser-Leine Uplands
The Lower Saxon Hills (german: Niedersächsisches Bergland) are one of the 73 natural regions in Germany defined by the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN). Geographically it covers roughly the same area as the Weser Uplands (german: Weserbergland) in its wider sense.However at least one source, Elkins (1968), uses the term to refer to the outcrops of rock to the north, west and southwest of the Harz which roughly corresponds to the eastern half of the BfN's region and extends only as far as the area between the rivers Weser and Leine. The region is part of Germany's Central Uplands with hills ranging up to in height that extend across northeast North Rhine-Westphalia, southern Lower Saxony and northern Hesse. It is classified as region number D 36 by the BfN; its full name being the ''Niedersächsisches Bergland (mit Weser- und Leine-Bergland'' (Lower Saxon Hills, including the Weser and Leine Hills). D 36 is a newly defined region that incorporates 3 geographical units f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Region
A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate. From the ecology, ecological point of view, the naturally occurring flora and fauna of the region are likely to be influenced by its geographical and geological factors, such as soil and water resources, water availability, in a significant manner. Thus most natural regions are homogeneous ecosystems. Human impact can be an important factor in the shaping and destiny of a particular natural region. Main terms The concept "natural region" is a large basic geographical unit, like the vast boreal forest region. The term may also be used generically, like in alpine tundra, or specifically to refer to a particular place. The term is particularly useful where there is no corresponding or coterminous official region. The Fens of eastern England, the Thai highlands, and the Pays de Bray in Normandy, are examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercity-Express
The Intercity Express (commonly known as ICE ()) is a system of high-speed trains predominantly running in Germany. It also serves some destinations in Austria, Denmark (ceased in 2017 but planned to resume in 2022), France, Belgium, Switzerland and the Netherlands, mostly as part of cross border services. It is the highest service category of rail and the flagship train of the German state railway, Deutsche Bahn. There are currently 315 trainsets in use. ICE trains are the highest category (Class A) trains in the fare system of the Deutsche Bahn. Their fares are not calculated on a fixed per-kilometre table as with other trains, but instead have fixed prices for station-to-station connections, levied on the grounds that the ICE trains have a higher level of comfort. Travelling at speeds up to , they are tailored for business travellers or long-distance commuters and are marketed by Deutsche Bahn as an alternative to flights. Apart from domestic use, the trains can also be see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamme
Lamme is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It flows into the Innerste near Bad Salzdetfurth. In 1945 the river was crossed by Allied Forces. See also *List of rivers of Lower Saxony All rivers in the German state of Lower Saxony flow directly or indirectly into the North Sea. A–Z A B D E F G H I J K L M N O P * Purrmühlenbach R S T * Tiefenbeek * Trillkebach * Trutenbeek * Twiste U * Uffe * Ulrich ... References Rivers of Lower Saxony Rivers of Germany {{LowerSaxony-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |