|
Gregory Of Akner
Gregory of Akner (Armenian: Գրիգոր Ակներցին) or Grigor Aknertsi, Grigor Akants, Akanc was a thirteenth-century Armenian historian and author. He is best known for his valuable work, the ''History of the Nation of the Archers'', which is an important source for the Mongol conquest of the Near East and the period of Mongol rule in Armenia. It is the only work of Armenian literature of which the original manuscript has survived to the present day. Gregory moved from Eastern Armenia to Cilicia in the years of 1265 or 1266, where he joined the Akner monastery Akner monastery (, Akner vank') is a destroyed Armenian monastery near the Eğner village of Adana province of modern Turkey. Etymology The monastery was known by different names: # Akner () (or Aknaghbyur) both in Old Armenian Language mean "''b .... His work was edited and published with an English translation by Robert P. Blake and Richard N. Frye in 1949. A new English translation by Robert Bedrosian appeared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia, the United States, France, Georgia, Iran, Germany, Ukraine, Lebanon, Brazil, and Syria. With the exceptions of Iran and the former Soviet states, the present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide. Richard G. Hovannisian, ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. Armenian is an Indo-European language. It has two mutually intelligible spoken and written forms: Eastern Armenian, today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, Iran, and the former Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasions And Conquests
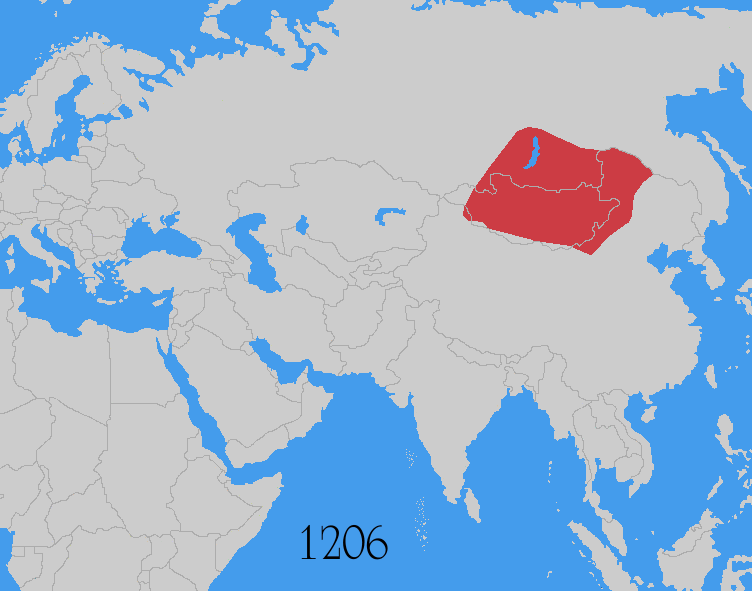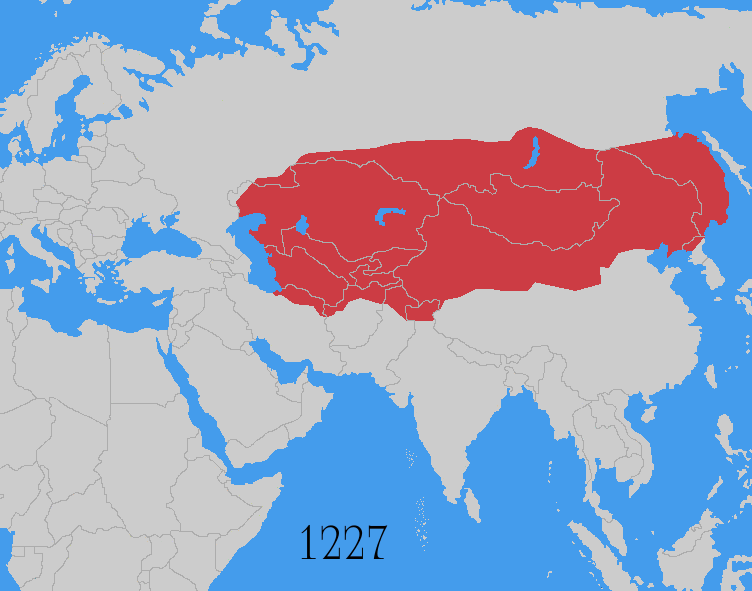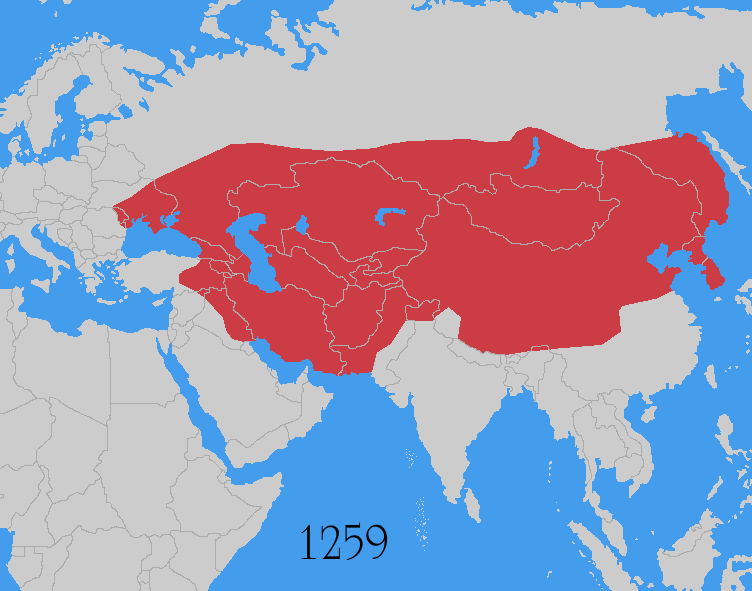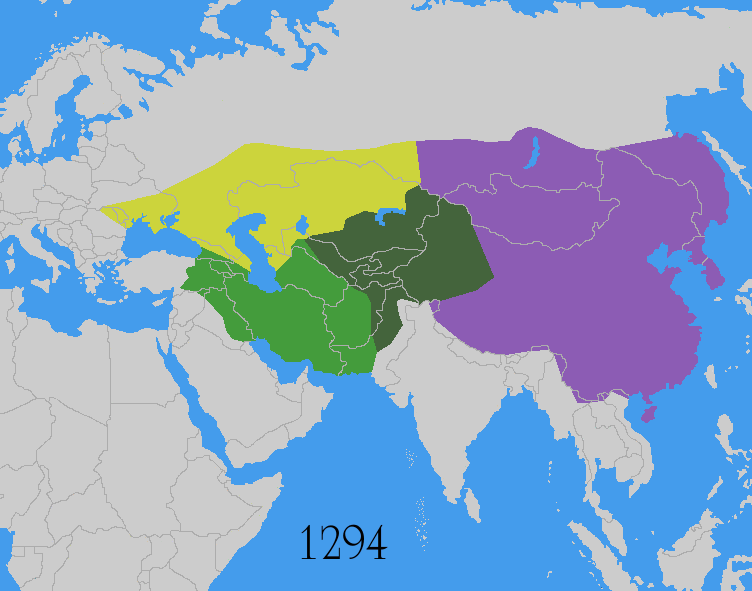
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia ( hy, Արևելյան Հայաստան ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') comprises the eastern part of the Armenian Highlands, the traditional homeland of the Armenian people. Between the 4th and the 20th centuries, Armenia was partitioned several times, and the terms ''Eastern'' and ''Western Armenia'' have been used to refer to its respective parts under foreign occupation or control, although there has not been a defined line between the two. The term has been used to refer to: * Persian Armenia (a vassal state of the Persian Empire from 387, fully annexed in 428) after the country's partition between the Byzantine and Sassanian empires and lasted until the Arab conquest of Armenia in the mid-7th century. * Iranian Armenia (1502–1813/1828), which covered the period of Eastern Armenia during the early-modern and late-modern era when it was part of the various Iranian empires, up to its annexation by the Russian Empire ( 1813 and 1828). *Russian Armenia (1828 to 1917) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilicia plain. The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye, along with parts of Hatay and Antalya. Geography Cilicia is extended along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separates it from Syria. North and east of Cilicia lie the rugged Taurus Mountains that separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, which are pierced by a narrow gorge called in antiquity the Cilician Gates. Ancient Cilicia was naturally divided into Cilicia Trachea and Cilicia Pedias by the Limonlu River. Salamis, the city on the east coast of Cyprus, was included in its administrative jurisdiction. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akner Monastery
Akner monastery (, Akner vank') is a destroyed Armenian monastery near the Eğner village of Adana province of modern Turkey. Etymology The monastery was known by different names: # Akner () (or Aknaghbyur) both in Old Armenian Language mean "''brooks''". The monastery was built up in the place full of flowing streams near ''Akner'' village that geographically correspond to ''Eğner'' village at the present time. # Akants Anapat () in Armenian language means ''the temple at the streams''. The exterior Akner monastery was built not far from Cilician Armenia's Bardzraberd stronghold at the border of two districts: Tsakhut () and Bardzraberd () for higher fortress) near the Akner (or Aknaghbyur) village at the middle course of Seyhan River () for Mountainous river) in the hilly place full of brooks. Akner monastery consisted of three churches: # St. Astvadzatzin () meaning Saint Mother of God. # St. Hakob (or St. Nshan) () meaning Saint Jack (or Saint Sign). # St. Arakelots ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Armenian Historians
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (Roman numerals, MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (Roman numerals, MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), Mamluks and Sultanate of Rum, Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |