|
Greensforge
Greensforge is a scattered hamlet on the boundary of Kinver and Swindon parishes, in South Staffordshire, England. It is noted for its Roman associations and its industrial heritage. Etymology The hamlet takes its name from a finery forge established there in the early 17th century: Mr Green's Forge. This was typical of early industrial development all along the Smestow Brook, in which bloomeries, foundries and forges used local water supplies and charcoal. History The hamlet was not the earliest settlement in the area. The name Greensforge is also used for a group of Romans forts lying on the west of the brook, partly in Ashwood. The remains of one fort, extending to 2.3 hectares, are visible as a low banked enclosure on either side of Mile Flat, just east of the canal locks and wharf. This dates from period 60-80 AD. It was identified at least as early as the 18th century and numerous finds of pottery and other objects were made before it was excavated in 1929. The other, ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smestow Brook
The Smestow Brook, sometimes called the River Smestow, is a small river that plays an important part in the drainage of Wolverhampton, South Staffordshire, and parts of Dudley in the United Kingdom, and has contributed to the industrial development of the Black Country. It is the most important tributary of the River Stour, Worcestershire and part of the River Severn catchment. Etymology and usage The name of the stream may be of Anglo-Saxon origin, although it was not written down before the 14th century in the Middle English forms ''Smetheslall'' and ''Smethestalle''. As late as the 19th century, the name was still generally rendered ''Smestall'' in surveys of the county. It means ″place of the smiths″. The whole of this part of the West Midlands was famed for iron production from the Middle Ages onwards. The nearby Kinver Forest and Wyre Forest supplied charcoal for smelting and working iron before the Industrial Revolution. Both the lower Smestow and the Stour were line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swindon, Staffordshire
Swindon is a village and civil parish located in the West Midlands. The nearest major town is Dudley, approximately five miles eastwards. It stands today that Swindon is in fact actually in Wombourne and used to be where less wealthy people would live. Historically, Swindon was part of Seisdon rural district, but in 1974 was incorporated into the new local authority of South Staffordshire. It has a few local shops including a convenience store, two churches and a pub (The Old Bush Inn). Until recently there was another pub, The Greyhound, but this has since been converted into homes. Having at one time seen a gradually reduced bus service through the village, in recent years a more frequent service has run. The village is served by National Express West Midlands service 16 between Wolverhampton and Stourbridge. This service runs every 30 minutes Monday to Saturday daytime and hourly on Sundays and Bank Holidays including late night journeys. Schools *St John's CofE Primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashwood, Staffordshire
Ashwood is a small area of Staffordshire, England. It is situated in the South Staffordshire district, approximately two miles west of the West Midlands conurbation and the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley. Population details for the 2011 census can be found under Kinver. There are a small number of predominantly older scattered houses in it, as well as marina off the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal. There is no nucleated village. More built-up nearby areas include Kingswinford, Stourbridge, Kinver and Wolverhampton. The nearest public amenities are approximately one mile away in Wall Heath village. Wooded Pool near Ashwood, Staffordshire History Ashwood was formerly an area of medieval woodland and later heathland, bounded by the Smestow Brook, the River Stour, and cultivated lands in Kingswinford. It was one of the medieval hays (enclosures) of Kinver Forest. It was managed by a bailiff, who had a small farm at Prestwood by the service of keeping the hay. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinver
Kinver is a large village in the District of South Staffordshire in Staffordshire, England. It is in the far south-west of the county, at the end of the narrow finger of land surrounded by the counties of Shropshire, Worcestershire and the West Midlands. The nearest towns are Stourbridge, West Midlands, Kidderminster in Worcestershire and Bridgnorth, Shropshire. The Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal passes through, running close to the course of the meandering River Stour. According to the 2011 census Kinver ward had a population of 7,225. The village today The village has three schools: Foley Infant Academy, Brindley Heath Academy and Kinver High School, now part of the Invictus Multi Academy Trust. During normal times, the Infant school rings the home time bell 20 minutes before the junior or high schools. This is to allow the parents collecting children from both sites to cover the three-quarters of a mile journey. During lockdown and as the return to school is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assart
Assarting is the act of clearing forested lands for use in agriculture or other purposes. In English land law, it was illegal to assart any part of a royal forest without permission. This was the greatest trespass that could be committed in a forest, being more than a waste: while waste of the forest involves felling trees and shrubs, which can regrow, assarting involves completely uprooting all trees—the total extirpation of the forested area. The term ''assart'' was also used for a parcel of land assarted. Assart rents were those paid to the British Crown for the forest lands assarted. The etymology is from the French word ''essarter'' meaning to remove or grub out woodland. In northern England this is referred to as ''ridding''. Process In the Middle Ages, the land cleared was usually common land but after assarting, the space became privately used. The process took several forms. Usually it was done by one farmer who hacked out a clearing from the woodland, leaving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlets In Staffordshire
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a Parish (administrative division), parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. The word and concept of a hamlet has roots in the Anglo-Norman settlement of England, where the old French ' came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic languages, West Germanic) Franconian languages. Compare with modern French ', Dutch language, Dutch ', Frisian languages, Frisian ', German ', Old English ' and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the Qila, qala (Dari language, Dari: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Brindley
James Brindley (1716 – 27 September 1772) was an English engineer. He was born in Tunstead, Derbyshire, and lived much of his life in Leek, Staffordshire, becoming one of the most notable engineers of the 18th century. Early life Born into a well-to-do family of yeoman farmers and craftsmen in the Peak District, which in those days was extremely isolated, Brindley received little formal education, but was educated at home by his mother. At age 17, encouraged by his mother, he was apprenticed to a millwright in Sutton, Macclesfield, and soon showed exceptional skill and ability. Having completed his apprenticeship he set up business for himself as a wheelwright in Leek, Staffordshire. In 1750 he expanded his business by renting a millwright's shop in Burslem from the Wedgwoods who became his lifelong friends. He soon established a reputation for ingenuity and skill at repairing many different kinds of machinery. In 1752 he designed and built an engine for draining a coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staffordshire And Worcestershire Canal
The Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal is a navigable narrow canal in Staffordshire and Worcestershire in the English Midlands. It is long, linking the River Severn at Stourport in Worcestershire with the Trent and Mersey Canal at Haywood Junction by Great Haywood. History Creation James Brindley was the chief engineer of the canal, which was part of his "Grand Cross" plan for waterways connecting the major ports at Hull (via the Trent), Liverpool (via the Mersey), Bristol (via the Severn) and London (via the Thames). The Act of Parliament authorising the canal was passed on 14 May 1766. This created "The Company of Proprietors of the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal Navigation", which was empowered to raise an initial £70,000 (equivalent to £ in ),, with a further £30,000 (equivalent to £ in ), if needed, to fund the canal's construction. The canal was completed in 1771 for a cost that exceeded the authorised capital, and opened to trade in 1772. It was a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Mill
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and middlings. The term can refer to either the grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that has been separated from its chaff in preparation for grinding. History Early history The Greek geographer Strabo reports in his ''Geography'' a water-powered grain-mill to have existed near the palace of king Mithradates VI Eupator at Cabira, Asia Minor, before 71 BC. The early mills had horizontal paddle wheels, an arrangement which later became known as the " Norse wheel", as many were found in Scandinavia. The paddle wheel was attached to a shaft which was, in turn, attached to the centre of the millstone called the "runner stone". The turning force produced by the water on the paddles was transferred directly to the runner stone, causing it to grind against a stationary "bed", a stone of a similar size and shape. This simple arrangement required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
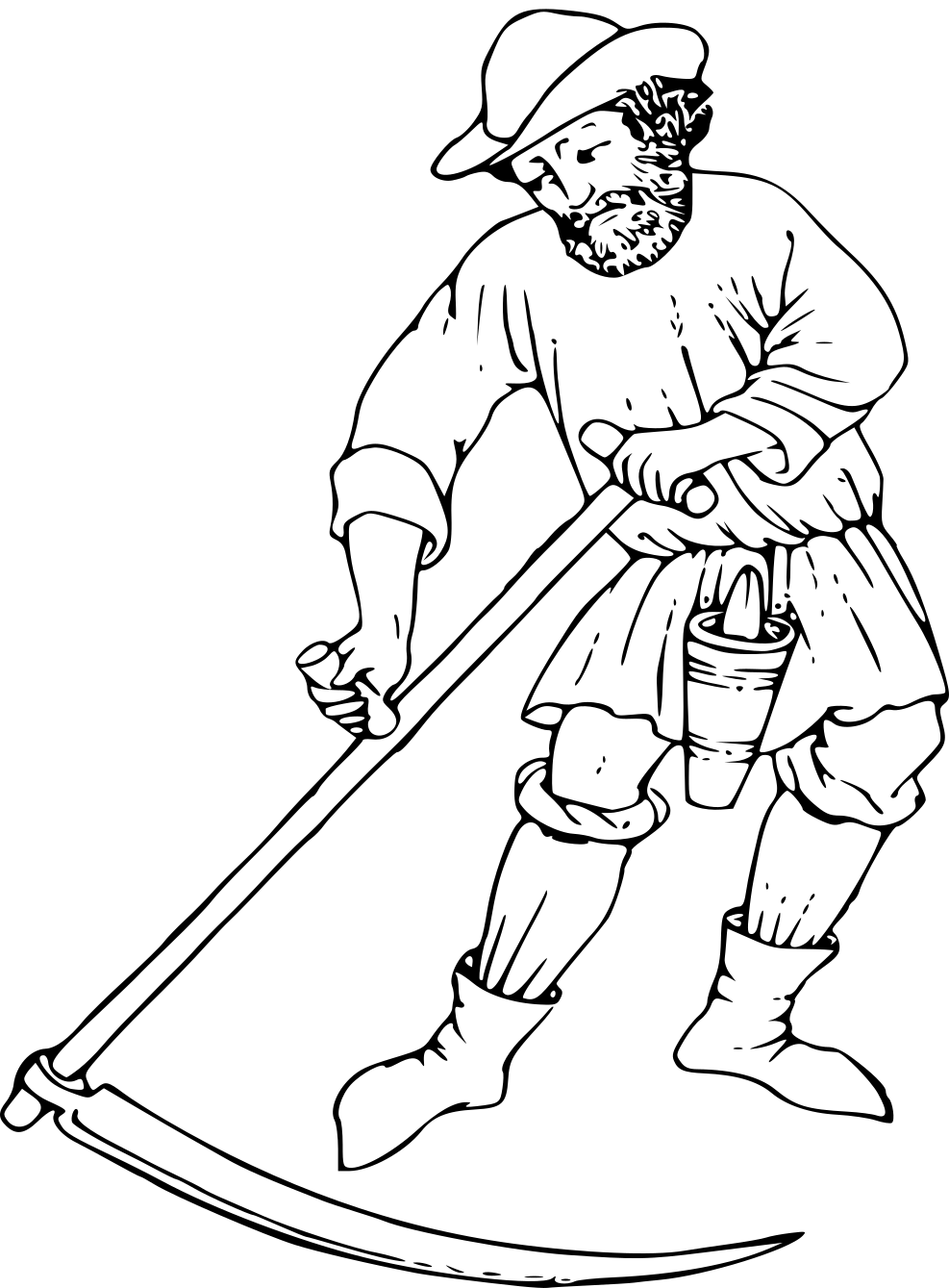
Scythe
A scythe ( ) is an agricultural hand tool for mowing grass or harvesting crops. It is historically used to cut down or reap edible grains, before the process of threshing. The scythe has been largely replaced by horse-drawn and then tractor machinery, but is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting of the scythe, and sometimes subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelt ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) the word was related to the Latin ''scindere'' (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ''snath'', ''snathe'' or ''sned'', traditionally made of wood but now sometimes me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade Mill
A blade mill was a variety of water mill used for sharpening newly fabricated blades, including scythes, swords, sickles, and knife, knives. In the Sheffield area, they were known as cutlers wheels, scythesmiths wheels, etc. Examples are preserved in Abbeydale Industrial Hamlet. They also existed in the 17th century and 18th century in Birmingham and in connection with the scythe industry in Belbroughton and Chaddesley Corbett in north Worcestershire. There were also small numbers in other areas of England. A water wheel was used to turn a grind stone, which wore down from being up to two metres in diameter to a 'cork' of a fraction of this size. The dust generated by the process was bad for the grinder's health, and many of them died young from silicosis, 'grinder's disease'. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dud Dudley
Dudd (Dud) Dudley (1600–1684) was an English metallurgist, who fought on the Royalist side in the English Civil War as a soldier, military engineer, and supplier of munitions. He was one of the first Englishmen to smelt iron ore using coke. Background and early life Dudley was the illegitimate son of Edward Sutton, 5th Baron Dudley of Dudley Castle. Dudd was the fourth of Lord Dudley's eleven children by his 'concubine' Elizabeth, the daughter of William Tomlinson (she died 3 July 1629). Strictly, he was called Dudd Dudley otherwise Tomlinson. His eldest brother was Robert Dudley of Netherton Hall. Dudd married Eleanor Heaton, (1606–1675), on 12 October 1626, at St. Helen's Church, Worcester. Lord Dudley (though he had a legitimate son, and a granddaughter by him, as well as four legitimate daughters and numerous grandchildren) seemed to have attended to the up-bringing of his natural children by Elizabeth Tomlinson; he educated and provided for them. On the other hand, he f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |