|
Greene's Tu Quoque
''Greene's Tu Quoque,'' also known as ''The City Gallant,'' is a Jacobean era stage play, a comedy written by John Cooke. The play was a major popular success upon its premier and became something of a legend in the theatre lore of the seventeenth century. Performance Cooke's play was performed by Queen Anne's Men at the Red Bull Theatre in 1611. The play satirises ''Coryat's Crudities,'' the travelogue by Thomas Coryat published in that year. The company's leading clown, Thomas Greene, played the role of Bubble in the play, and his rendering of Bubble's catch phrase "Tu quoque" (Latin for "you also" or, colloquially, "the same to you"), repeated through the play, captured the audience's fancy. The play was performed twice at Court, on 27 December 1611 and 2 February 1612 (Candlemas night), before King James I and Queen Anne; Greene, representing his troupe, received a payment of £20 for the two performances on 18 June 1612 (which shows how long the players sometimes waited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literature In English
English literature is literature written in the English language from United Kingdom, its crown dependencies, the Republic of Ireland, the United States, and the countries of the former British Empire. ''The Encyclopaedia Britannica'' defines English literature more narrowly as, "the body of written works produced in the English language by inhabitants of the British Isles (including Ireland) from the 7th century to the present day. The major literatures written in English outside the British Isles are treated separately under American literature, Australian literature, Canadian literature, and New Zealand literature." However, despite this, it includes literature from the Republic of Ireland, "Anglo-American modernism", and discusses post-colonial literature. ; See also full articles on American literature and other literatures in the English language. The English language has developed over the course of more than 1,400 years. The earliest forms of English, a set of Anglo-Fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Size
The size of a book is generally measured by the height against the width of a leaf, or sometimes the height and width of its cover. A series of terms is commonly used by libraries and publishers for the general sizes of modern books, ranging from ''folio'' (the largest), to ''quarto'' (smaller) and ''octavo'' (still smaller). Historically, these terms referred to the format of the book, a technical term used by printers and bibliographers to indicate the size of a leaf in terms of the size of the original sheet. For example, a quarto (from Latin ''quartō'', ablative form of ''quartus'', fourth) historically was a book printed on sheets of paper folded in half twice, with the first fold at right angles to the second, to produce 4 leaves (or 8 pages), each leaf one fourth the size of the original sheet printed – note that a ''leaf'' refers to the single piece of paper, whereas a ''page'' is one side of a leaf. Because the actual format of many modern books cannot be determined fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Jonson
Benjamin "Ben" Jonson (c. 11 June 1572 – c. 16 August 1637) was an English playwright and poet. Jonson's artistry exerted a lasting influence upon English poetry and stage comedy. He popularised the comedy of humours; he is best known for the satirical plays ''Every Man in His Humour'' (1598), '' Volpone, or The Fox'' (c. 1606), '' The Alchemist'' (1610) and '' Bartholomew Fair'' (1614) and for his lyric and epigrammatic poetry. "He is generally regarded as the second most important English dramatist, after William Shakespeare, during the reign of James I." Jonson was a classically educated, well-read and cultured man of the English Renaissance with an appetite for controversy (personal and political, artistic and intellectual) whose cultural influence was of unparalleled breadth upon the playwrights and the poets of the Jacobean era (1603–1625) and of the Caroline era (1625–1642)."Ben Jonson", ''Grolier Encyclopedia of Knowledge'', volume 10, p. 388. His ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metafiction
Metafiction is a form of fiction which emphasises its own narrative structure in a way that continually reminds the audience that they are reading or viewing a fictional work. Metafiction is self-conscious about language, literary form, and story-telling, and works of metafiction directly or indirectly draw attention to their status as artifacts. Metafiction is frequently used as a form of parody or a tool to undermine literary conventions and explore the relationship between literature and reality, life, and art. Although metafiction is most commonly associated with postmodern literature that developed in the mid-20th century, its use can be traced back to much earlier works of fiction, such as ''The Canterbury Tales'' (Geoffrey Chaucer, 1387), ''Don Quixote'' (Miguel de Cervantes, 1605), ''The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman'' (Laurence Sterne, 1759), and '' Vanity Fair'' (William Makepeace Thackeray, 1847). Metafiction became particularly prominent in the 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercery
Mercery (from French , meaning "habderdashery" (goods) or "haberdashery" (a shop trading in textiles and notions) initially referred to silk, linen and fustian textiles among various other piece goods imported to England in the 12th century. Eventually, the term evolved to refer to a merchant or trader of textile goods, especially imported textile goods, particularly in England. A merchant would be known as a ''mercer'', and the profession as ''mercery''. The occupation of mercery has a rich and complex history dating back over 1,000 years in what is now the United Kingdom. London was the major trade centre in England for silk during the Middle Ages, and the trade enjoyed a special position in the economy amongst the wealthy. A typical mercery business was family-run, consisting of a mercer, wife, their family, servants, and apprentices. The husband would be tasked with the marketing and sale of the business' wares to the public in places such as a small storefront, at market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
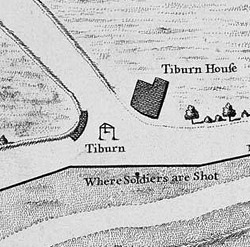
Tyburn
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street), the junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For this reason, for many centuries, the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment, it having been the principal place for execution of London criminals and convicted traitors, including many religious martyrs. It was also known as 'God's Tribunal', in the 18th century. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream',Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. but Tyburn Brook should not be confused wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Roaring Girl
''The Roaring Girl'' is a Jacobean stage play, a comedy written by Thomas Middleton and Thomas Dekker 1607–1610. The play was first published in quarto in 1611, printed by Nicholas Okes for the bookseller Thomas Archer. The title page of the first edition states that the play was performed at the Fortune Theatre by Prince Henry's Men, the troupe known in the previous reign as the Admiral's Men. The title page also attributes the authorship of the play to "T. Middleton and T. Dekkar", and contains an "Epistle to the Comic Play-Readers" signed by "Thomas Middleton". The Epistle is noteworthy for its indication that Middleton, atypically for dramatists of his era, composed his plays for readers as well as theatre audiences. ''The Roaring Girl'' is a fictionalized dramatization of the life of Mary Frith, known as "Moll Cutpurse", a woman who had gained a reputation as a ''virago'' in the early 17th century. (The term "roaring girl" was adapted from the slang term "roaring boy" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastward Hoe
''Eastward Hoe'' or ''Eastward Ho!'' is an early Jacobean-era stage play written by George Chapman, Ben Jonson and John Marston. The play was first performed at the Blackfriars Theatre by a company of boy actors known as the Children of the Queen's Revels in early August 1605, and it was printed in September the same year. ''Eastward Ho!'' is a citizen or city comedy about Touchstone, a London goldsmith, and his two apprentices, Quicksilver and Golding. The play is highly satirical about social customs in early modern London, and its anti-Scottish satire resulted in a notorious scandal in which King James was offended and the play's authors were imprisoned. ''Eastward Ho!'' also references, even parodies, popular plays performed by adult companies such as ''The Spanish Tragedy'', ''Tamburlaine'' and ''Hamlet''. The play's title alludes to ''Westward Ho!'' by Thomas Dekker and John Webster who also wrote '' Northward Ho!'' in response that year. Characters * Touchstone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Men (playing Company)
The King's Men is the acting company to which William Shakespeare (1564–1616) belonged for most of his career. Formerly known as the Lord Chamberlain's Men during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, they became the King's Men in 1603 when King James I ascended the throne and became the company's patron. The royal patent of 19 May 1603 which authorised the King's Men company named the following players, in this order: Lawrence Fletcher, William Shakespeare, Richard Burbage, Augustine Phillips, John Heminges, Henry Condell, William Sly, Robert Armin, Richard Cowley, "and the rest of their associates...." The nine cited by name became Grooms of the Chamber. On 15 March 1604, each of the nine men named in the patent was supplied with four and a half yards of red cloth for the coronation procession. Chronologically typed To 1610 In their first winter season, between December 1603 and February 1604 the company performed eight times at Court and eleven times in their second, from N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cooke
Alexander Cooke (died February 1614) was an actor in the King's Men and the Lord Chamberlain's Men, the acting companies of William Shakespeare, John Heminges and Richard Burbage. Cooke was most likely introduced to the theatre by John Heminges, to whom he was apprenticed under the Grocer's Guild on 26 January 1597. While guild records state that his indenture was to last seven years, Cooke was not freed until 22 March 1609. Cooke bound Walter Haynes under the same guild on 28 March 1610. Cooke's full name first appears in the plot for Ben Jonson's "Sejanus His Fall" (1603) in which he is listed as a "principle tragedian". This might indicate that he was a young actor in a prominent female role, perhaps Agrippina. He became a shareholder in the King's Men in 1604 when the number of shareholders was expanded to twelve. He was also cast in ''Volpone'' ( 1605), in which he may have been Lady Would-be; Jonson's ''The Alchemist'' ( 1610); ''Catiline'' (1611) and Beaumont and Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Payne Collier
John Payne Collier (11 January 1789, London – 17 September 1883, Maidenhead) was an English Shakespearean critic and forger. Reporter and solicitor His father, John Dyer Collier (1762–1825), was a successful journalist, and his connection with the press obtained for his son a position on the ''Morning Chronicle'' as leader writer, dramatic critic and reporter, which continued until 1847; he was also for some time a reporter for ''The Times''. He was summoned before the House of Commons in 1819 for giving an incorrect report of a speech by Joseph Hume. He entered the Middle Temple in 1811, but was not called to the bar until 1829. The delay was partly due to his indiscretion in publishing the ''Criticisms on the Bar'' (1819) by "Amicus Curiae." Controversial Shakespearean scholar Collier's leisure was given to the study of Shakespeare and the early English drama. After some minor publications, he produced in 1825–1827 a new edition of Dodsley's ''Old Plays'' and in 1833 a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |