|
Greeks In Syria
The Greeks in Syria arrived in the 7th century BC and became more prominent during the Hellenistic period and when the Seleucid Empire was centered there. Today, there is a Greek community of about 4,500 in Syria, most of whom have Syrian nationality and who live mainly in Aleppo (the country's main trading and financial centre), Baniyas, Tartous, and Damascus, the capital. and refers to the conquest of the Levant, which later became known as the Islamic Province of Bilad al-Sham. On the eve of the Arab Muslim conquests the Byzantines were still in the process of rebuilding their authority in the Levant, which had been lost to them for almost twenty years. At the time of the Arab conquest, Bilad al-Sham was inhabited mainly by local Aramaic-speaking Christians, Ghassanid and Nabatean Arabs, as well as Greeks, and by non-Christian minorities of Jews, Samaritans, and Itureans. The population of the region did not become predominantly Muslim and Arab in identity until nearly a mille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorites
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian language, Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied large parts of southern Mesopotamia from the 21st century BC to the end of the 17th century BC, where they established several prominent city-states in existing locations, such as Isin, Larsa and later notably Babylon, which was raised from a small town to an independent state and a major city. The term in Akkadian and Sumerian texts refers to the Amorites, Amurru (god), their principal deity and Amurru kingdom, an Amorite kingdom. The Amorites are also mentioned in the Bible as inhabitants of Canaan both before and after the conquest of the land under Joshua. Origin In the earliest Sumerian sources concerning the Amorites, beginning about 2400 BC, the land of the Amorites ("the ''Mar.tu'' land") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East throughout much of the 8th and 7th centuries BC, becoming the largest empire in history up to that point. Because of its geopolitical dominance and ideology based in world domination, the Neo-Assyrian Empire is by many researchers regarded to have been the first world empire in history. At its height, the empire was the strongest military power in the world and ruled over all of Mesopotamia, the Levant and Egypt, as well as portions of Anatolia, Arabia and modern-day Iran and Armenia. The early Neo-Assyrian kings were chiefly concerned with restoring Assyrian control over much of northern Mesopotamia and Syria, since significant portions of the preceding Middle Assyrian Empire had been lost during a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syro-Hittite States
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwians, Luwian and Arameans, Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti (region), Hatti and Aram (region), Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian language, Luwian belonging to the Anatolian languages, Anatolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cognate with Hebrew ); the parallel Assyrian term is , , or . Etymology The English term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjeker
The Tjeker or Tjekker (Egyptian: ''ṯꜣkꜣr'' or ''ṯꜣkkꜣr'') were one of the Sea Peoples. Known mainly from the " Story of Wenamun", the Tjeker are also documented earlier, at Medinet Habu, as raiders defeated by Pharaoh Ramesses III of Egypt in years 5, 8, and 12 of his reign. They are thought to be the people who developed the port of Dor in Canaan during the 12th century BCE from a small Bronze Age town to a large city. Origin As with other Sea Peoples, the origins of the Tjeker are uncertain. Their name is an Egyptian exonym, usually romanized as ''tkr'', and expanded as ''Tjekru'' or ''Djekker''. The Egyptian may also be romanized as ''skl'', i.e. ''Sikil'' or ''Sical''. As such there is no consensus on the original form or etymology of the name, or the origin of the people. They have sometimes been identified with the Sicels of Sicily, who are also linked to ''Shekelesh'': another exonym attributed to a different group amongst the Sea Peoples. Another theory, put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaeans (Homer)
The Achaeans (; grc, Ἀχαιοί ''Akhaioí,'' "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively. The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwesh which appear in texts from the Late Bronze Age and are believed to refer to the Mycenaean civilization or some part of it. In the historical period, the term fell into disuse as a general term for Greek people, and was generally reserved for inhabitants of the region of Achaea, a region in the north-central part of the Peloponnese. The city-states of this region later formed a confederation known as the Achaean League, which was influential during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. Etymology According to Margalit Finkelberg, the name Ἀχαιοί/Ἀχαιϝοί is derived from Hittite ''Aḫḫiyawā''. However, Robert S. P. Beekes doubted the validity of this derivation and suggested a Pre-Greek proto-form ''*Akayw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denyen
The Denyen (Egyptian: ''dꜣjnjnjw'') is purported to be one of the groups constituting the Sea Peoples. Origin They are mentioned in the Amarna letters from the 14th century BC as possibly being related to the "Land of the Danuna" near Ugarit. The Egyptians described them as Sea Peoples."A dictionary of archaeology" Ian Shaw, Robert Jameson. Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. , . p. 515 Hittite Empire The Denyen have been identified with the people of , in who existed in late Hittite Empire times. They are a ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radiocarbon dating places the beginning of the New Kingdom between 1570 BC and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period. It was Egypt's most prosperous time and marked the peak of its power. The concept of a "New Kingdom" as one of three "golden ages" was coined in 1845 by German Egyptologist Baron von Bunsen, and its definition would evolve significantly throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The later part of this period, under the Nineteenth and Twentieth dynasties (1292–1069 BC), is also known as the ''Ramesside period''. It is named after the eleven pharaohs who took the name Ramesses, after Ramesses I, the founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty. Possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ... in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.Lazaridis, Iosif et al.Genetic origins of the Minoans and Mycenaeans. ''Nature'', 2017Supplementary Information "The Mycenaeans", pp. 2–3).. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greeks, Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan civilization, Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
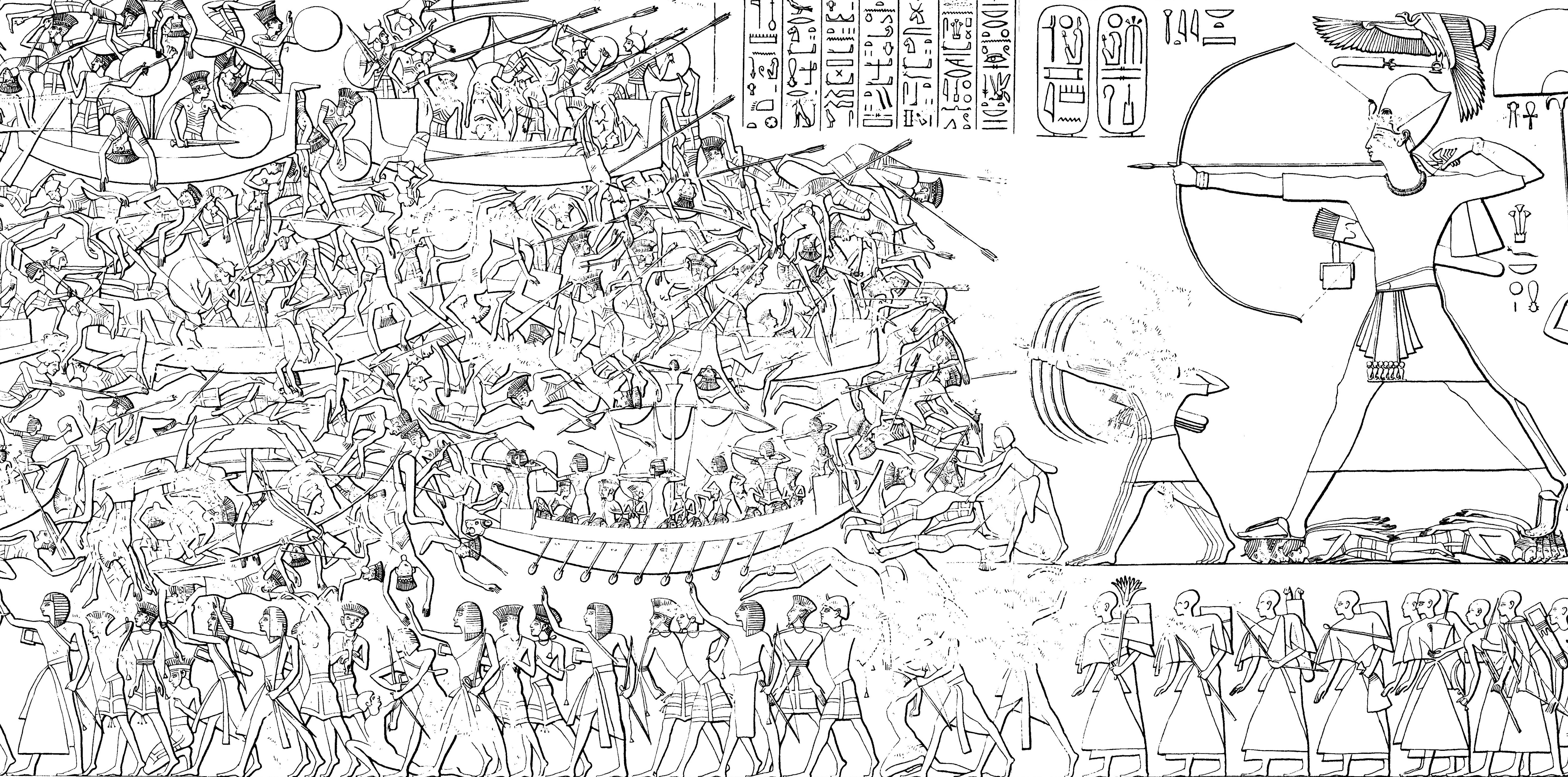
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_and_Tsakkaras_(painting).png)

.jpg)